Dedicated transformers are specifically assigned to serve a single load or a defined group of loads, ensuring stable power quality and optimal performance. Unlike shared transformers, they minimize electrical disturbances caused by other equipment on the same power supply. This targeted approach is critical in applications requiring sensitive, high-reliability, or continuous operation, such as hospitals, data centers, and industrial plants.
Why Are Transformers Critical in Commercial Buildings and High-Rise Facilities?

In commercial buildings and high-rise facilities, electrical continuity is non-negotiable—downtime can disrupt operations, cause safety risks, and incur substantial financial losses. Transformers here must handle diverse load profiles (HVAC, elevators, lighting, IT systems), often in space-constrained environments with strict fire, safety, and noise requirements. Without proper transformer selection and configuration, facilities risk overheating, inefficient power distribution, and premature equipment failure.
Transformers in commercial and high-rise applications are designed to convert medium-voltage utility supply to low-voltage distribution efficiently, while meeting space, safety, and noise constraints. Commonly used types include dry-type (cast resin, VPI) for indoor installations due to fire safety, and oil-immersed units in basement or dedicated outdoor spaces. Key considerations include load diversity, harmonic mitigation, energy efficiency (per DOE/IEC/CSA), ventilation, and integration with building automation systems.
When done right, transformer systems ensure reliable, safe, and efficient building operation for decades.
Oil-immersed transformers are always prohibited in commercial buildings.False
While dry-type transformers are preferred for indoor use due to fire safety, oil-immersed transformers can be used in dedicated, fire-rated rooms or outdoor enclosures in compliance with codes.
Key Challenges for Transformers in Commercial and High-Rise Settings
| Challenge | Design & Selection Response |
|---|---|
| Limited space | Use compact dry-type units, low-profile enclosures |
| Fire safety compliance | Dry-type transformers, fire barriers, flame-retardant insulation |
| Noise control | Low-noise core design, acoustic shielding |
| Load diversity | High efficiency at partial loads, K-rated for harmonic loads |
| Ventilation limits | Forced-air cooling, ducted exhaust systems |
| Maintenance access | Front access panels, modular design |
| Aesthetics & integration | Architectural enclosures for lobby or public areas |
Typical Transformer Configurations in High-Rise Facilities
| Location | Type | Cooling Method | Reason for Choice |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basement electrical room | Oil-immersed | ONAN/ONAF | Large capacity, away from occupied floors |
| Mechanical floors | Dry-type cast resin | AN/AF | Safe, reduced fire load, low maintenance |
| Rooftop substations | Oil-immersed in weatherproof | ONAF | Outdoor exposure, easy heat dissipation |
| Tenant floors | Small dry-type | AN | Localized distribution, compact, low noise |
Dry-type transformers are the safest option for indoor commercial spaces.True
Dry-type units eliminate liquid dielectric risks, reduce fire hazards, and require minimal containment.
Case Example: 60-Story Mixed-Use Tower
Requirements:
- Mixed load: retail (ground floors), offices, residential
- 33 kV utility feed
- Tight service core with limited ventilation
Solution:
- 2 × 3 MVA dry-type transformers (VPI) on mechanical floors
- Harmonic filters for elevator and HVAC drives
- Centralized BMS integration for thermal monitoring
- Forced-air cooling with ducted exhaust to building ventilation
Result:
- Reduced electrical losses by 7%
- Maintained transformer temps below 80°C under peak load
- No fire code violations; passed acoustic limits for occupied floors
Maintenance & Reliability in High-Rises
| Task | Frequency | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal inspection | Quarterly | IR scanning via viewing ports |
| Air filter replacement (AF) | Semi-annual | Maintain airflow and dust control |
| Core & coil cleaning | Annual | Vacuum/low-pressure air, avoid moisture |
| Oil sampling (if applicable) | Annual | Dissolved gas analysis (DGA) |
| Electrical connection torque | Annual | Prevents overheating from loose joints |
| Acoustic/vibration check | Quarterly | Identifies mechanical looseness or core noise issues |
Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
| Design Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High-efficiency core steel | Reduces no-load losses |
| Low-loss winding design | Reduces load losses |
| Harmonic mitigation | Improves power factor, reduces heating |
| Eco-friendly materials | Complies with LEED/BREEAM sustainability credits |
| Adaptive cooling | Optimizes fan use to save energy |
Why Are Specialized Transformers Essential for Underground and Subterranean Installations?
Operating transformers in underground and subterranean environments presents a unique set of challenges: space is extremely limited, ventilation is constrained, ambient temperatures can be elevated, and fire safety requirements are stringent. Without proper transformer design and installation, these conditions can lead to overheating, rapid insulation degradation, moisture ingress, and safety hazards for both equipment and personnel.
Transformers in underground installations are engineered to provide reliable power conversion in confined spaces with limited airflow, often using dry-type sealed units or hermetically sealed oil-immersed designs. Key considerations include forced ventilation systems, fire-rated enclosures, moisture protection, and compliance with local codes for underground power equipment. In many cases, they are paired with remote monitoring to reduce the need for frequent on-site access.
This specialized environment demands not just a transformer, but a fully integrated electrical and environmental control solution.
Standard outdoor distribution transformers can be directly installed underground without modification.False
Underground environments require transformers with enhanced moisture protection, ventilation management, and safety compliance—standard outdoor units are not designed for these conditions.
Key Constraints in Underground Transformer Applications
| Constraint | Design & Engineering Response |
|---|---|
| Limited space | Compact footprint designs, front-access panels |
| Poor ventilation | Forced-air ducted systems or liquid cooling |
| High humidity/moisture | Sealed windings, anti-condensation heaters |
| Fire safety | Non-flammable dielectric fluids or dry-type insulation |
| Restricted maintenance access | Remote monitoring, long-interval maintenance schedules |
| High ambient temperature | Enhanced thermal class insulation, adaptive cooling |
Common Transformer Types for Underground Installations
| Transformer Type | Cooling Method | Application Scenario | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry-Type Cast Resin | AN/AF | Subway systems, underground malls, basements | Fire safe, low maintenance, moisture-resistant |
| Hermetically Sealed Oil-Immersed | ONAN/ONAF | Utility vaults, tunnels, mining power rooms | High capacity, long life, reduced oxidation risk |
| Liquid-Filled with Ester Fluid | KNAN/KNAF | Urban vaults, high-safety spaces | High fire point, environmentally friendly |
Dry-type transformers are the only option for underground power rooms.False
While dry-type units are common for fire safety, sealed oil-immersed designs with fire-safe fluids are also used successfully underground.
Ventilation and Cooling Design
Typical Underground Transformer Cooling Strategy
| Cooling Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ducted Airflow System | Moves heat to surface ventilation shafts |
| Liquid Cooling Loops | Transfers heat to external heat exchangers |
| Anti-Condensation Heaters | Prevents moisture on coils during idle periods |
| Thermal Sensors & Fans | Automated temperature regulation |
A metro substation, for example, might use two dry-type 2 MVA units in a fire-rated vault, with ducted exhaust fans pushing heat into an above-ground air handling unit.
Case Study: Metro Underground Power Room
Project Requirements:
- 6 MVA total capacity
- Located 30 meters below street level
- 40°C ambient, 85% humidity
- 24/7 operation with no direct human supervision
Solution Implemented:
- Two 3 MVA cast resin dry-type transformers
- Ducted forced ventilation connected to station HVAC
- Remote thermal and partial discharge monitoring
- Anti-condensation heaters and epoxy-sealed windings
Outcome:
- 99.98% uptime over 5 years
- No unplanned outages
- Reduced ventilation energy cost by 15% with adaptive fan control
Maintenance Strategy for Underground Transformers
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal scanning | Quarterly | Remote IR sensors reduce human access needs |
| Ventilation filter cleaning | Semi-annual | Ensures airflow efficiency |
| Heater system check | Semi-annual | Avoids moisture buildup during idle cycles |
| Winding insulation testing | Annual | Detects early degradation from humidity |
| Dielectric fluid testing (if applicable) | Annual | Ensures fluid fire safety and dielectric performance |
Why Are Specialized Transformers Critical for Industrial Plants and Manufacturing Facilities?
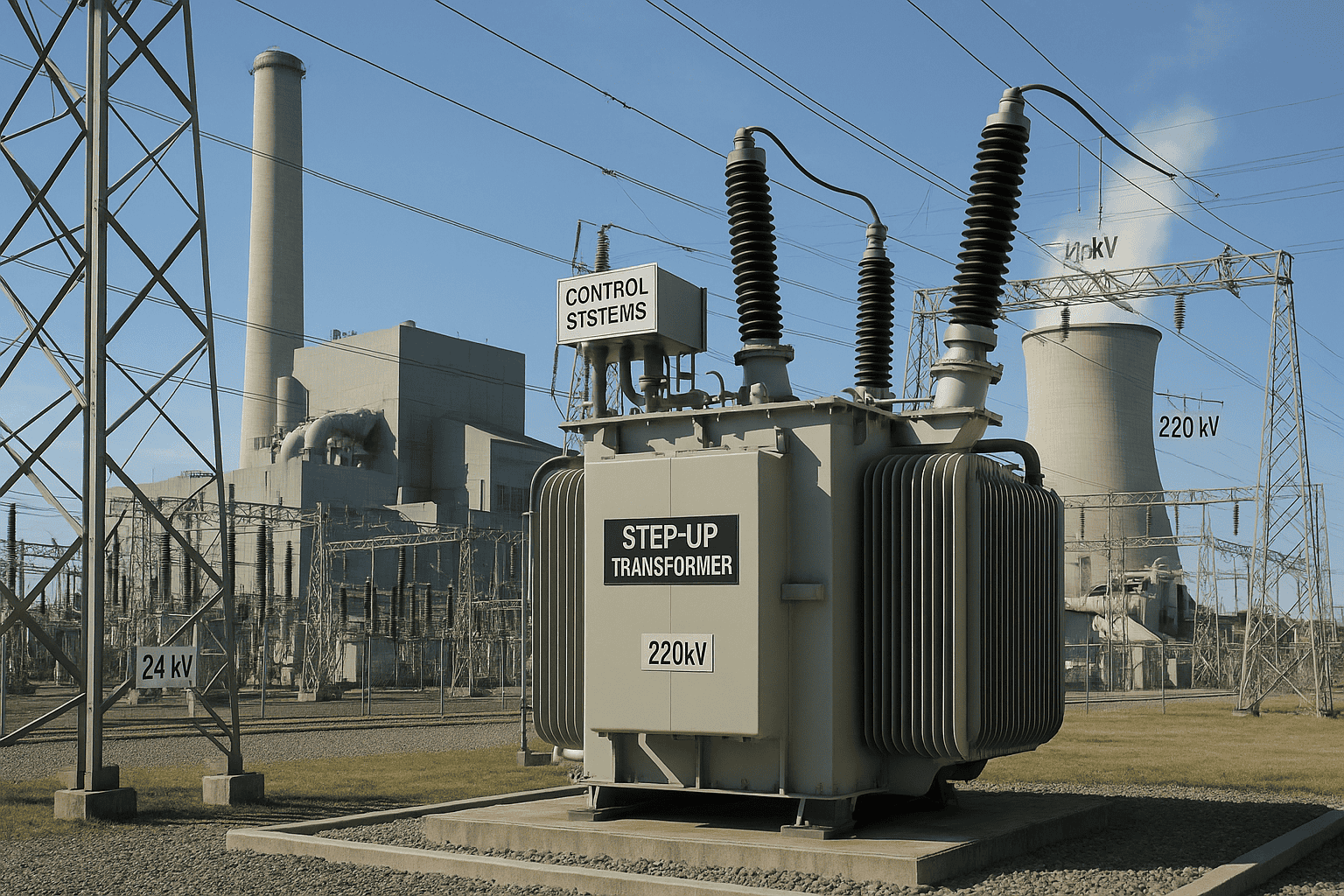
Industrial plants and manufacturing facilities place extreme demands on their transformers—continuous high loads, frequent switching of heavy motors, exposure to dust, vibration, temperature fluctuations, and sometimes corrosive environments. Inadequate transformer selection or design in these environments can cause voltage instability, equipment failures, unplanned downtime, and even catastrophic safety incidents.
Transformers in industrial plants are engineered for high mechanical strength, superior thermal performance, and resilience against electrical and environmental stresses. These units often feature reinforced windings, specialized cooling systems, and protective enclosures to withstand heavy motor starting currents, harmonics from variable frequency drives (VFDs), and harsh ambient conditions. They are also designed to comply with stringent IEEE, ANSI, or IEC performance and safety standards.
In industrial power distribution, transformer reliability directly translates into production uptime, which means selecting the right transformer is both an engineering and business-critical decision.
Any commercial-grade transformer can be used in an industrial plant without modifications.False
Industrial applications require transformers with enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical designs to handle high inrush currents, harmonics, and harsh operating environments.
Key Challenges in Industrial Transformer Applications
| Challenge | Engineering Solution |
|---|---|
| High inrush currents from motors | Windings with high mechanical strength, low-impedance designs |
| Harmonics from drives and inverters | K-factor rated transformers to reduce heating from harmonics |
| Dust, oil mist, and particles | IP-rated enclosures, sealed or cast resin insulation |
| Vibration and mechanical stress | Rigid core clamping, shock-absorbing mounts |
| Continuous high load operation | Enhanced cooling systems (OFAF, ONAF) and high-temperature insulation |
| Corrosive or humid environments | Special coatings, stainless steel fittings, anti-condensation heaters |
Common Transformer Types for Industrial Plants
| Transformer Type | Cooling Method | Ideal Use Cases | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil-Immersed Power Transformer | ONAN/ONAF/OFAF | Large motor loads, heavy manufacturing, steel mills | High capacity, long service life, good thermal performance |
| Dry-Type Cast Resin Transformer | AN/AF | Food processing, chemical plants, indoor workshops | Fire-safe, moisture-resistant, low maintenance |
| K-Rated Transformer | AN/AF or Liquid | Facilities with many VFDs, welding equipment | Designed for harmonic-rich loads, prevents overheating |
| Autotransformer | AN/AF or Liquid | Motor starting, voltage matching between processes | High efficiency, reduced size and cost for certain uses |
K-rated transformers are only needed in IT server rooms.False
K-rated transformers are used in any environment with significant non-linear loads, including manufacturing plants with VFDs, welders, and robotics.
Thermal and Mechanical Design Considerations
Industrial Transformer Cooling Requirements
| Cooling Method | Description | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| ONAN | Oil Natural Air Natural – passive cooling | Low to medium load plants with steady operation |
| ONAF | Oil Natural Air Forced – fans assist cooling | Steel mills, large conveyor systems |
| OFAF | Oil Forced Air Forced – pumps circulate oil, fans blow air | Continuous casting, aluminum smelters |
| AF (dry-type) | Air Forced – fans push air through dry coils | Printing presses, automated assembly lines |
Industrial processes with 24/7 high load cycles often demand redundant cooling fans or pumps, with automatic switchover in case of a failure.
Case Study: Steel Rolling Mill Power System
Project Specs:
- 10 MVA total transformer capacity
- 3 × 3.33 MVA oil-immersed ONAF transformers
- High harmonic environment due to 6-pulse drives
- Ambient 45°C with heavy dust contamination
Solution:
- K-factor 13 rated windings to handle harmonic heating
- IP55 rated radiator enclosures with dust filters
- Online dissolved gas analysis (DGA) sensors for real-time monitoring
- Oil temperature and load tap changer remote monitoring
Results:
- Zero unplanned outages in 4 years
- 12% reduction in energy losses through proper sizing
- Improved rolling mill uptime and reduced maintenance labor
Maintenance Strategy in Industrial Environments
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oil analysis and DGA | Quarterly | Detects early faults |
| Cooling system inspection | Monthly | Fans, pumps, filters |
| Harmonic load monitoring | Continuous | Prevents overload on windings |
| Insulation resistance testing | Annual | Detects moisture ingress |
| Core and coil vibration check | Annual | Avoids mechanical loosening |
Why Are Specialized Transformers Essential for Renewable Energy Installations?
Renewable energy projects—whether solar farms, wind parks, or hybrid microgrids—place unique and fluctuating demands on their transformers. Unlike conventional grid transformers that operate under relatively predictable loads, renewable energy transformers must manage variable generation, bidirectional power flow, harmonics from inverters, and challenging environmental exposure. A poorly designed transformer in such a setting can lead to energy loss, grid instability, and even premature failure, which can drastically undermine project profitability.
Transformers for renewable energy installations are purpose-built to handle fluctuating load profiles, high harmonic content from power electronics, and frequent voltage/frequency variations. They typically feature specialized insulation systems, low-loss cores, reinforced windings, and corrosion-resistant housings. Designs often include sealed or conservator-type oil systems, optimized cooling for outdoor exposure, and compliance with IEEE, IEC, and local grid interconnection standards.
In renewable energy projects, the transformer is not just a passive component—it is the critical link between variable generation sources and the stability of the transmission or distribution network.
Standard distribution transformers can be directly used in solar farms without modification.False
Renewable energy transformers require designs that address harmonics, variable loads, and environmental challenges, which standard distribution transformers are not optimized for.
Key Technical Challenges in Renewable Transformer Design
| Challenge | Engineering Solution |
|---|---|
| Variable and intermittent loads | Low-loss, high-efficiency cores designed for partial load conditions |
| Harmonics from inverters | K-rated or specially wound designs to minimize harmonic heating |
| Bidirectional power flow | Winding and core design to handle reverse energy flow without losses |
| Outdoor environmental exposure | IP55+ enclosures, corrosion-resistant materials, UV-resistant paint |
| Remote location maintenance difficulty | Online monitoring, dissolved gas analysis (DGA), thermal sensors |
| Extreme climates | Anti-condensation heaters, special cooling (ONAF, OFAF), tropicalization |
Common Transformer Types in Renewable Installations
| Transformer Type | Cooling Method | Primary Application | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pad-Mounted Oil-Immersed Transformer | ONAN/ONAF | Solar PV farms | Compact, secure, weatherproof, good for utility tie-in |
| Cast Resin Dry-Type Transformer | AN/AF | Offshore wind substations, rooftops | Fire-safe, moisture-resistant, minimal maintenance |
| Collector Step-Up Transformer | OFAF | Wind farms (66kV to transmission grid) | Handles large power blocks, robust cooling, high insulation strength |
| Inverter Duty Transformer | AN/AF or Liquid | Solar inverters, battery storage | Handles high harmonics, designed for power electronics |
All renewable energy transformers are dry-type.False
While dry-type transformers are used in some renewable installations, oil-immersed designs remain common for higher voltage and capacity requirements.
Transformer Cooling in Renewable Applications
| Cooling Code | Description | Typical Renewable Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| ONAN | Oil Natural Air Natural – passive cooling | Small to mid-sized pad-mounted units in PV arrays |
| ONAF | Oil Natural Air Forced – fans for higher capacity | Wind farm collection transformers |
| OFAF | Oil Forced Air Forced – pumps and fans for maximum cooling | High-voltage export transformers in offshore substations |
| AF | Air Forced – fans in dry-type units | Rooftop PV and battery energy storage systems |
Example: 100 MW Solar PV Plant Transformer Setup
System Specs:
- 40 × 2.5 MVA pad-mounted oil-immersed transformers
- Primary: 34.5 kV, Secondary: 0.6 kV for inverter connection
- Cooling: ONAN with fan-assisted ONAF for high-temperature operation
- Ambient: Desert environment, 50°C max, high dust load
Design Adaptations:
- Hermetically sealed tanks to prevent oil oxidation and moisture ingress
- Radiators with removable dust filters for easy cleaning
- Anti-corrosion epoxy paint system tested for UV exposure
- Integrated fiber optic temperature sensors in windings
Results:
- 98.5% average transformer efficiency over first 3 years
- No oil contamination events
- Remote monitoring reduced site visits by 35%
Preventive Maintenance in Remote Renewable Sites
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection & thermography | Semi-annual | Detect hot spots, oil leaks, loose connections |
| Oil or insulation testing | Annual | Includes DGA for oil-immersed, partial discharge test for dry-type |
| Cooling system inspection | Quarterly | Especially important for ONAF and OFAF systems |
| Bushing cleaning and torque check | Annual | Prevent flashover in dusty/windy conditions |
| Online monitoring system check | Continuous | Alerts for load or temperature abnormalities |
Why Do Schools, Data Centers, and Public Infrastructure Require Specialized Transformers?
In facilities like schools, data centers, and public infrastructure hubs, transformer reliability and safety directly impact human safety, operational continuity, and even national security. A failure in these settings can mean more than a temporary outage—it can disrupt education, halt critical digital operations, and paralyze public services like transportation or emergency response. Additionally, these environments often have space constraints, stringent fire safety codes, noise limits, and high energy efficiency requirements that standard industrial transformers may not meet.
Transformers for these facilities are engineered for high reliability, minimal fire risk, quiet operation, and high efficiency, while meeting strict building codes and operational demands. They often employ dry-type insulation in occupied spaces for fire safety, or sealed oil-immersed units in outdoor or isolated areas. Features include low-noise cores, harmonic mitigation for sensitive electronics, redundant cooling systems, and monitoring for predictive maintenance.
In such mission-critical environments, the transformer is not just a piece of equipment—it is part of a broader resilience strategy to ensure continuous, safe, and efficient operations.
Any industrial transformer can be installed in a school building without modification.False
Transformers in schools must meet strict fire safety, noise, and energy efficiency codes, which many industrial units are not designed for.
Transformer Selection Challenges for These Facilities
| Challenge | Engineering Response |
|---|---|
| High fire safety requirements | Cast resin or vacuum pressure impregnated (VPI) dry-type transformers |
| Low noise limits | Core and winding design optimization, sound insulation enclosures |
| Space constraints | Compact or pad-mounted configurations |
| Harmonic-rich loads (IT, HVAC, lighting) | K-rated or harmonic mitigating transformer designs |
| Continuous, critical load | Redundant units, online monitoring, predictive maintenance |
| Sensitive indoor environment | Ventilated dry-type with low partial discharge |
Typical Transformer Types by Application
| Application | Transformer Type | Cooling Method | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schools | Dry-type VPI or cast resin | AN/AF | Fire-safe, quiet, low maintenance |
| Data Centers | K-rated dry-type or liquid-cooled pad-mount | AN/AF or ONAN | Harmonic tolerance, redundancy-ready, high efficiency |
| Public Infrastructure | Oil-immersed or dry-type, depending on site | ONAN/ONAF or AF | Durability, environmental sealing, compliance with IEC/IEEE safety codes |
Oil-immersed transformers cannot be used in public infrastructure.False
Oil-immersed transformers can be used in public infrastructure if located in suitable outdoor or isolated areas with appropriate containment and fire protection.
Special Design Considerations
| Design Aspect | Schools | Data Centers | Public Infrastructure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fire Safety | NFPA 70 & IEC 60076-11 compliance | FM Approved / UL Listed designs | NFPA & local safety regulations |
| Noise Control | ≤ 50 dB(A) near classrooms | ≤ 60 dB(A) in equipment rooms | ≤ 65 dB(A) in public areas |
| Load Profile | Variable (day/night cycles) | Constant, high load 24/7 | Variable with peak periods |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Moderate for lighting/HVAC | High for server loads | Moderate for transport electronics |
| Cooling Method | Natural or forced air | Forced air or liquid cooling | Depends on environmental exposure |
Example: 50 MVA Data Center Transformer System
System Specs:
- 4 × 12.5 MVA cast resin dry-type transformers
- Primary: 132 kV, Secondary: 11 kV to UPS systems
- Cooling: AF with redundancy (N+1 configuration)
- Harmonic Tolerance: K-20 rating
- Ambient: Controlled indoor environment, 25°C ± 2°C
Design Adaptations:
- Copper windings with high mechanical strength for short-circuit withstand
- Epoxy resin insulation for zero fire propagation
- Integrated harmonic filters to protect UPS and server racks
- Remote thermal and load monitoring linked to BMS (Building Management System)
Results:
- 99.2% operational uptime over 5 years
- No thermal or electrical failures recorded
- Predictive maintenance reduced emergency interventions by 80%
Maintenance Priorities for Critical Facility Transformers
| Task | Frequency | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection & thermography | Quarterly | Identify overheating and insulation degradation early |
| Harmonic load analysis | Annual | Adjust load balancing or filtering if required |
| Cooling system check | Monthly | Critical in forced-air and liquid-cooled systems |
| Noise and vibration assessment | Annual | Early detection of core or winding looseness |
| Insulation resistance testing | Annual | Ensure dielectric integrity |
Why Do Marine, Offshore, and Mining Operations Require Specialized Transformers?

In the marine, offshore, and mining industries, transformers operate under extreme mechanical, thermal, and environmental stress. Salt-laden air in coastal and offshore sites accelerates corrosion, mining environments generate abrasive dust and vibration, and offshore oil platforms face explosive gas hazards. A transformer failure here can halt production, endanger lives, and cause millions in losses due to downtime or accidents. These sectors demand transformers with specialized enclosures, robust insulation, enhanced cooling systems, and compliance with marine classification societies or mining safety codes.
Transformers for these industries are purpose-built for harsh environments—featuring corrosion-resistant housings, vibration-resistant cores, explosion-proof or flameproof designs, and cooling systems capable of handling high ambient temperatures or restricted airflow. They must meet classification standards such as ABS, DNV, IECEx, and MSHA, and often incorporate condition monitoring for predictive maintenance.
These environments leave no room for equipment compromise. Transformers here are not just power delivery components—they are survival-critical assets in the operational ecosystem.
Standard indoor dry-type transformers can be installed directly on an offshore platform without modification.False
Offshore transformers must meet marine classification standards, have corrosion protection, and be resistant to salt spray, vibration, and explosive atmospheres.
Key Challenges in Harsh Environment Transformer Design
| Challenge | Engineering Response |
|---|---|
| Corrosion from saltwater or chemical exposure | Marine-grade stainless steel or coated enclosures, anti-condensation heaters |
| Explosive atmospheres (gas/dust) | Explosion-proof enclosures, flameproof bushings, IECEx/ATEX certification |
| High vibration and shock loads | Vibration-damped core mounting, reinforced winding supports |
| Dust and particulate contamination | IP55–IP66 enclosure ratings, filtered and sealed ventilation |
| Limited maintenance access | Online monitoring for temperature, oil quality, and load |
| Extreme temperature swings | Forced oil or air cooling, thermostatically controlled heating elements |
Common Transformer Types in These Applications
| Application | Transformer Type | Cooling Method | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine vessels | Cast resin or hermetically sealed oil | AN/AF or ONAN | Salt spray resistance, low vibration, compact for confined spaces |
| Offshore platforms | Explosion-proof oil-immersed or dry-type | ONAN/ONAF | IECEx/ATEX compliance, corrosion-proof, extended maintenance intervals |
| Mining operations | Flameproof oil-immersed or dry-type | ONAN/OFAF | MSHA certification, dustproof housing, shock resistance |
Explosion-proof transformers are mandatory for all mining sites.False
Explosion-proof transformers are only required in mining areas with hazardous gases or dust. Non-hazardous mining locations may use standard industrial designs with dust protection.
Special Design Considerations
| Design Aspect | Marine | Offshore Oil & Gas | Mining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Protection | Epoxy-coated windings, marine paint | 316L stainless enclosures, heavy-duty coating | Epoxy resin coating, dust filters |
| Explosion Protection | Not always required | Mandatory for hazardous zones | Required in gassy mines |
| Cooling Method | Air or forced air | Oil cooling with heat exchangers | Oil cooling with fin radiators |
| Space Optimization | Critical | Critical | Moderate |
| Certifications | ABS, DNV, Lloyd’s Register | IECEx, ATEX, ABS, DNV | MSHA, IECEx, ATEX |
Example: Offshore Platform Transformer Case Study
System Specs:
- 2 × 5 MVA oil-immersed explosion-proof transformers
- Primary: 6.6 kV, Secondary: 440 V distribution to drilling equipment
- Cooling: ONAN with stainless steel radiators
- Ambient: 45°C, 95% humidity, salt-laden air
- Certification: IECEx Zone 1 hazardous area rating
Design Adaptations:
- Hermetically sealed tank with nitrogen blanket to prevent moisture ingress
- Marine-grade epoxy coating on windings
- Integrated oil monitoring sensors for dielectric strength and moisture content
- Anti-condensation heaters for standby periods
Results:
- Continuous operation for 8 years without unplanned downtime
- 30% lower maintenance cost compared to non-marine-protected units
- Zero corrosion-related failures recorded
Maintenance Priorities
| Task | Frequency | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Salt spray washdown (marine/offshore) | Monthly | Use demineralized water and approved cleaning agents |
| Oil quality analysis | Semi-annual | Check dielectric strength, acidity, and moisture levels |
| Vibration inspection (mining) | Quarterly | Detect core or winding loosening early |
| Explosion-proof seal inspection | Annual | Ensure compliance with hazardous area standards |
| Enclosure coating integrity check | Annual | Recoat if corrosion or damage is detected |
Conclusion
Dedicated transformers play an essential role in delivering clean, stable, and reliable power to critical loads. By isolating sensitive systems from other electrical disturbances, they help extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and ensure uninterrupted operation. For facilities with mission-critical processes or stringent safety requirements, a dedicated transformer is not just an option—it’s a necessity.
FAQ
Q1: What is a dedicated transformer?
A1: A dedicated transformer is assigned to supply power to a specific load, system, or facility, rather than being shared among multiple circuits. This setup ensures stable voltage, improved reliability, and reduced electrical interference.
Q2: Why are dedicated transformers important for sensitive equipment?
A2: Sensitive electronics—like medical imaging devices, data servers, or precision manufacturing tools—require clean, stable power. Dedicated transformers isolate them from voltage fluctuations, surges, and electrical noise that can occur in shared systems.
Q3: How do dedicated transformers enhance power quality?
A3: By supplying only one load or system, dedicated transformers minimize harmonic distortion, voltage drops, and transient disturbances, ensuring optimal performance and lifespan of connected equipment.
Q4: In what industries are dedicated transformers most used?
A4: They are common in:
Healthcare (MRI, CT scanners)
IT/Data Centers (servers, networking gear)
Manufacturing (CNC machines, robotics)
Broadcasting (audio/video production equipment)
Laboratories (research and testing instruments)
Q5: Can dedicated transformers reduce downtime?
A5: Yes. By isolating a critical load from the rest of the electrical network, faults in other systems won’t cause outages in the dedicated supply. This improves uptime and prevents costly interruptions.
References
Electrical4U – Isolation and Dedicated Transformers
https://www.electrical4u.com/isolation-transformer/
Schneider Electric – Transformer Solutions for Sensitive Loads
https://www.se.com/ww/en/work/products/transformers/
IEEE Standards – Transformer Applications
https://standards.ieee.org/standard/C57_12_00-2015.html
Eaton – Dedicated Transformer Advantages
https://www.eaton.com/us/en-us/products/transformers.html
Doble Engineering – Reducing Electrical Noise in Power Systems
https://www.doble.com/resources/electrical-noise-and-isolation/
NEMA – Transformer Efficiency and Applications
https://www.nema.org/standards/view/efficiency-transformers
ScienceDirect – Harmonic Mitigation with Dedicated Transformers
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142061519305025


