Luneng Taishan® oil-immersed transformers are available in various capacities and configurations for both small and large-scale applications. They comply with international standards like IEC, ANSI, and GB, ensuring high performance. Customizable to meet specific voltage, power, and environmental requirements, they are widely used in industrial, commercial, and utility sectors. Offering cost-effective and durable solutions, these transformers can help optimize your energy distribution network.
Transformer Capacity Range:
We specialize in medium to large capacity transformers tailored for industrial and utility-scale applications. Oil-immersed Transformers: Minimum capacity of 630 kVA. We have extensive expertise in manufacturing high-capacity transformers above 5000 kVA, offering customized solutions for complex and demanding power systems. Please note: While we are capable of producing low-capacity transformers (below 630 kVA), such as distribution transformers, we do not supply them as standalone products. These are only available as part of a complete solution in combination with medium- or large-capacity transformers.



Trusted by world-class brands & organizations of all sizes



















Luneng Taishan® oil-immersed transformers are available in various capacities and configurations for both small and large-scale applications. They comply with international standards like IEC, ANSI, and GB, ensuring high performance. Customizable to meet specific voltage, power, and environmental requirements, they are widely used in industrial, commercial, and utility sectors. Offering cost-effective and durable solutions, these transformers can help optimize your energy distribution network.
| Type | Rated Capacity (kVA) | Class 1, Type 22 | Class 2, Type 20 | Class 3, Type 18 | Short-circuit Impedance(%) | Weight(t) | Overall Dimension(mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | Transport weight (nitrogen) | Total | L | W | H | |||
| S-6300/110 | 6300 | 4.1 | 32 | 4.8 | 32 | 5.9 | 33 | 10.5 | 20 | 33 | 5600 | 5200 | 6400 |
| S-8000/110 | 8000 | 4.9 | 38 | 5.8 | 38 | 7.1 | 40 | 22 | 38 | 5800 | 5300 | 6300 | |
| S-10000/110 | 10000 | 5.8 | 45 | 6.8 | 45 | 8.4 | 48 | 23 | 43 | 6000 | 5400 | 6200 | |
| S-12500/110 | 12500 | 6.8 | 53 | 8.1 | 53 | 9.9 | 56 | 24 | 48 | 6200 | 5500 | 6100 | |
| S-16000/110 | 16000 | 8.3 | 65.7 | 9.8 | 65.7 | 12 | 69 | 26 | 53 | 6400 | 5600 | 6000 | |
| S-20000/110 | 20000 | 9.7 | 79 | 11.4 | 79 | 14.1 | 84 | 34 | 58 | 6600 | 5700 | 5900 | |
| S-25000/110 | 25000 | 11.4 | 94 | 13.5 | 94 | 16.6 | 99 | 41 | 63 | 6800 | 5800 | 5800 | |
| S-31500/110 | 31500 | 13.5 | 111 | 16 | 111 | 19.7 | 117 | 44 | 68 | 7000 | 5900 | 5700 | |
| S-40000/110 | 40000 | 16.2 | 133 | 19.1 | 133 | 23.5 | 141 | 48 | 73 | 7200 | 6000 | 5600 | |
| S-50000/110 | 50000 | 19.4 | 158 | 22.9 | 158 | 28.2 | 166 | 54 | 78 | 7400 | 6100 | 5500 | |
| S-63000/110 | 63000 | 22.9 | 187 | 27 | 187 | 33.3 | 189 | 60 | 83 | 7600 | 6200 | 5800 | |
| S-75000/110 | 75000 | 26.6 | 212 | 30.7 | 212 | 37.8 | 224 | 12 ~ 14 | 75 | 90 | 7750 | 6300 | 6000 |
| S-90000/110 | 90000 | 29.9 | 245 | 35.4 | 245 | 43.5 | 258 | 70 (nitrogen) | 100 | 7850 | 6400 | 6200 | |
| S-120000/110 | 120000 | 37.3 | 303 | 44.1 | 303 | 54.2 | 320 | 75 (nitrogen) | 110 | 8000 | 6500 | 6250 | |
| S-150000/110 | 150000 | 44.1 | 359 | 52.1 | 359 | 64.1 | 379 | 80 (nitrogen) | 125 | 8100 | 6600 | 6300 | |
| S-180000/110 | 180000 | 49.5 | 411 | 58.5 | 411 | 72 | 434 | 92(nitrogen) | 132 | 9000 | 6700 | 6400 | |
| Note: 1、The above data for selection reference, our company reserves the right to amend; 2、lt can provide the corresponding parameter product according to the customer request. | |||||||||||||
| Type | Rated Capacity (kVA) | Class 1, Type 22 | Class 2, Type 20 | Class 3, Type 18 | Short-circuit Impedance(%) | Weight(t) | Overall Dimension(mm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | Step-up | Step-down | Transport weight (nitrogen) | Total | L | W | H | ||
| SS-6300/110 | 6300 | 4.9 | 40 | 5.8 | 40 | 7.1 | 42 | High-Medium 17.5 ~ 18.5 High-Low 10.5 Medium-Low 6.5 | High-Medium 10.5 High-Low 17.5 ~ 18.5 Medium-Low 6.5 | 24 | 34 | 5500 | 5400 | 4900 |
| SS-8000/110 | 8000 | 5.8 | 48 | 6.9 | 48 | 8.5 | 50 | 29 | 36 | 5700 | 5500 | 4900 | ||
| SS-10000/110 | 10000 | 6.9 | 56 | 8.2 | 56 | 10.1 | 59 | 36 | 46 | 5900 | 5600 | 5000 | ||
| SS-12500/110 | 12500 | 8.1 | 67 | 9.6 | 67 | 11.8 | 70 | 40 | 50 | 6100 | 5700 | 5100 | ||
| SS-16000/110 | 16000 | 9.8 | 81 | 11.6 | 81 | 14.3 | 86 | 42 | 54 | 6300 | 5800 | 5200 | ||
| SS-20000/110 | 20000 | 11.6 | 95 | 13.7 | 95 | 16.9 | 101 | 46 | 57 | 6500 | 5900 | 5300 | ||
| SS-25000/110 | 25000 | 13.5 | 113 | 16 | 113 | 19.7 | 120 | 49 | 61 | 6700 | 6000 | 5400 | ||
| SS-31500/110 | 31500 | 16.2 | 134 | 19.1 | 134 | 23.5 | 142 | 50 | 68 | 6900 | 6100 | 5500 | ||
| SS-40000/110 | 40000 | 19.1 | 161 | 22.6 | 161 | 27.8 | 170 | 56 | 76 | 7100 | 6200 | 5600 | ||
| SS-50000/110 | 50000 | 22.9 | 192 | 27 | 192 | 33.3 | 202 | 58 | 81 | 7300 | 6300 | 5700 | ||
| SS-63000/110 | 63000 | 27.1 | 230 | 32 | 230 | 39.4 | 243 | 68 | 91 | 7500 | 6400 | 5800 | ||
| Note: 1、The above data for selection reference, our company reserves the right to amend; 2、lt can provide the corresponding parameter product according to the customer request. | ||||||||||||||
| Type | Rated Capacity (kVA) | Class 1, Type 22 | Class 2, Type 20 | Class 3, Type 18 | Short-circuit Impedance(%) | Weight(t) | Overall Dimension(mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | Transport weight (nitrogen) | Total | L | W | H | |||
| SSZ-6300/110 | 6300 | 5.3 | 40 | 6.2 | 40 | 7.7 | 42 | High-Medium 10.5 High-Low 17.5 ~ 18.5 Medium-Low 6.5 | 24 | 38 | 6000 | 5500 | 4900 |
| SSZ-8000/110 | 8000 | 6.3 | 48 | 7.5 | 48 | 9.2 | 50 | 28 | 41 | 6200 | 5600 | 4900 | |
| SSZ-10000/110 | 10000 | 7.5 | 56 | 8.8 | 56 | 10.9 | 59 | 29 | 50 | 6400 | 5700 | 5000 | |
| SSZ-12500/110 | 12500 | 8.9 | 67 | 10.5 | 67 | 12.9 | 70 | 30 | 54 | 6600 | 5800 | 5100 | |
| SSZ-16000/110 | 16000 | 10.6 | 81 | 12.5 | 81 | 15.4 | 86 | 36 | 58 | 6800 | 5900 | 5200 | |
| SSZ-20000/110 | 20000 | 12.5 | 95 | 14.8 | 95 | 18.2 | 101 | 38 | 61 | 7000 | 6000 | 5300 | |
| SSZ-25000/110 | 25000 | 14.9 | 113 | 17.6 | 113 | 21.6 | 120 | 42 | 65 | 7200 | 6100 | 5400 | |
| SSZ-31500/110 | 31500 | 17.7 | 134 | 20.9 | 134 | 25.7 | 142 | 50 | 72 | 7400 | 6200 | 5500 | |
| SSZ-40000/110 | 40000 | 21.2 | 161 | 25 | 161 | 30.8 | 170 | 56 | 80 | 7600 | 6300 | 5600 | |
| SSZ-50000/110 | 50000 | 25 | 192 | 29.6 | 192 | 36.4 | 202 | 62 | 85 | 7800 | 6400 | 5700 | |
| SSZ-63000/110 | 63000 | 29.8 | 230 | 35.2 | 230 | 43.3 | 243 | 72 | 95 | 8000 | 6500 | 5800 | |
| Note: 1、The above data for selection reference, our company reserves the right to amend; 2、lt can provide the corresponding parameter product according to the customer request. | |||||||||||||
| Type | Rated Capacity (kVA) | Class 1, Type 22 | Class 2, Type 20 | Class 3, Type 18 | Short-circuit Impedance(%) | Weight(t) | Overall Dimension(mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | Transport weight (nitrogen) | Total | L | W | H | |||
| S-6300/110 | 6300 | 4.4 | 33 | 5.2 | 33 | 6.4 | 35 | 10.5 | 20 | 33 | 5600 | 5200 | 6400 |
| S-8000/110 | 8000 | 5.3 | 40 | 6.2 | 40 | 7.7 | 42 | 22 | 38 | 5800 | 5300 | 6300 | |
| S-10000/110 | 10000 | 6.2 | 47 | 7.3 | 47 | 9 | 49 | 23 | 43 | 6000 | 5400 | 6200 | |
| S-12500/110 | 12500 | 7.2 | 56 | 8.5 | 56 | 10.5 | 59 | 24 | 48 | 6200 | 5500 | 6100 | |
| S-16000/110 | 16000 | 8.6 | 68 | 10.1 | 68 | 12.5 | 72 | 26 | 53 | 6400 | 5600 | 6000 | |
| S-20000/110 | 20000 | 10.2 | 85 | 12 | 85 | 14.8 | 89 | 34 | 58 | 6600 | 5700 | 5900 | |
| S-25000/110 | 25000 | 12.1 | 99 | 14.2 | 99 | 17.5 | 105 | 41 | 63 | 6800 | 5800 | 5800 | |
| S-31500/110 | 31500 | 14.3 | 120 | 16.8 | 120 | 20.7 | 126 | 44 | 68 | 7000 | 5900 | 5700 | |
| S-40000/110 | 40000 | 16.9 | 140 | 20 | 140 | 24.6 | 147 | 48 | 73 | 7200 | 6000 | 5600 | |
| S-50000/110 | 50000 | 20.3 | 174 | 24 | 174 | 29.5 | 183 | 54 | 78 | 7400 | 6100 | 5500 | |
| S-63000/110 | 63000 | 24 | 209 | 28.3 | 209 | 34.9 | 220 | 60 | 83 | 7600 | 6200 | 5400 | |
| Note: 1、The above data for selection reference, our company reserves the right to amend; 2、lt can provide the corresponding parameter product according to the customer request. | |||||||||||||
| Type | Rated Capacity (kVA) | Class 1, Type 22 | Class 2, Type 20 | Class 3, Type 18 | Short-circuit Impedance(%) | Weight(t) | Overall Dimension(mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | No-Load Loss (kW) | Load Loss (kW) | Transport weight (nitrogen) | Total | L | W | H | |||
| SZ-6300/110 | 6300 | 4.4 | 32 | 5.2 | 32 | 6.4 | 33 | 10.5 | 20 | 36 | 5800 | 5400 | 4700 |
| SZ-8000/110 | 8000 | 5.3 | 38 | 6.2 | 38 | 7.7 | 40 | 24 | 38 | 6000 | 5500 | 4900 | |
| SZ-10000/110 | 10000 | 6.2 | 45 | 7.3 | 45 | 9 | 48 | 28 | 41 | 6200 | 5600 | 4900 | |
| SZ-12500/110 | 12500 | 7.4 | 53 | 8.7 | 53 | 10.7 | 56 | 29 | 50 | 6400 | 5700 | 5000 | |
| SZ-16000/110 | 16000 | 8.9 | 66 | 10.5 | 66 | 12.9 | 69 | 30 | 54 | 6600 | 5800 | 5100 | |
| SZ-20000/110 | 20000 | 10.6 | 79 | 12.5 | 79 | 15.4 | 84 | 36 | 58 | 6800 | 5900 | 5200 | |
| SZ-25000/110 | 25000 | 12.5 | 94 | 14.8 | 94 | 18.2 | 99 | 38 | 61 | 7000 | 6000 | 5300 | |
| SZ-31500/110 | 31500 | 14.9 | 111 | 17.6 | 111 | 21.6 | 117 | 42 | 65 | 7200 | 6100 | 5400 | |
| SZ-40000/110 | 40000 | 17.8 | 140 | 21 | 140 | 25.8 | 148 | 50 | 72 | 7400 | 6200 | 5500 | |
| SZ-50000/110 | 50000 | 21 | 175 | 24.8 | 175 | 30.6 | 187 | 56 | 80 | 7600 | 6300 | 5600 | |
| SZ-63000/110 | 63000 | 25 | 209 | 29.5 | 209 | 36.3 | 220 | 62 | 85 | 7800 | 6400 | 5700 | |
| Note; 1 The above data for selection reference, our company reserves the right to amend; 2、lt can provide the corresponding parameter product according to the customer request. | |||||||||||||
Contact us to upgrade or install your energy system.
Luneng Taishan® oil-immersed transformer is based on the digestion and absorption of advanced technology at domestic and abroad, for the transformation of urban and rural power grids to develop their own, its product performance is better than GB/T6451, in full compliance with national standards like GB1094 and international standards like IEC.
Luneng Taishan® oil-immersed transformers are designed with advanced computer simulation software, optimizing energy efficiency. The products surpass national energy-saving standards, ensuring that users experience reduced operational costs, especially in power substations, over a ten-year period.
Our independent research and development of oil-immersed power transformers, through continuous reference at domestic and abroad advanced technology, after a continuous summary, absorption, with a distinctive characteristics of the low-side, low noise, low loss, high reliability characteristics.
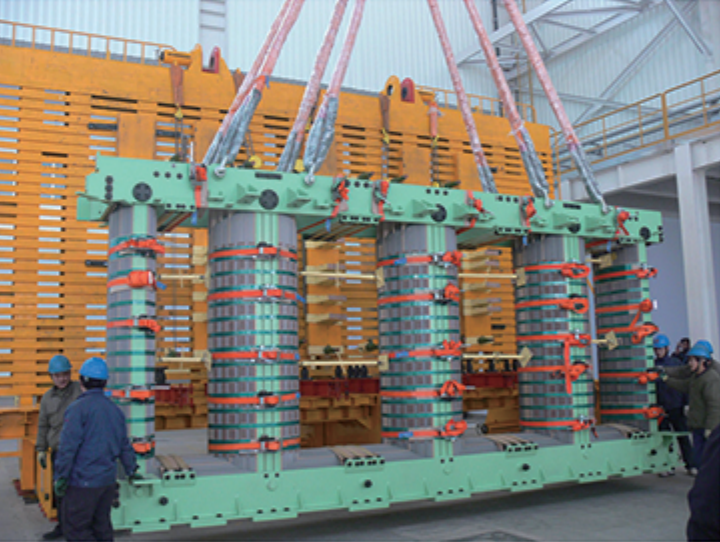
The core is made of high quality cold rolled grain oriented high permeability silicon steel sheet, silicon steel sheet by the Swiss introduction of the shear line cutting, shear burr is not greater than 0.02mm. Advanced core stacking turntable, the domestic first-class non-stacking yoke process, reducing the silicon steel sheet excess handling process, fully guarantee the performance of cold-rolled silicon steel sheet, effectively reducing the transformer no-load loss. Reasonable design clip, pull the board, the beam, pad feet, making it a solid whole, to ensure that the core film in the best state of force. Not only reduces the no-load loss, but also greatly improves the transformer no-load performance. Core structure according to the design needs can be single-phase double column, single-phase three-column, single-phase four-post, three-phase three-column, three-phase five-column structure, at the same time according to the needs of the process, the core film stack can be used in general structure or frame structure.

Active Part Insulation

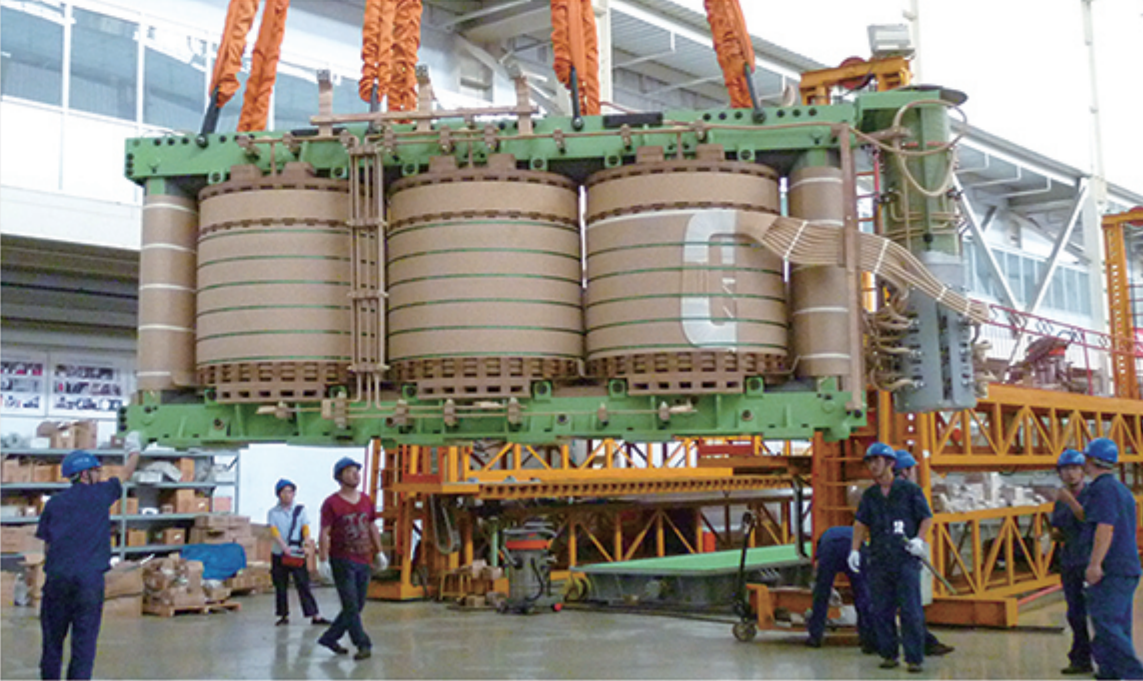
Transformer winding
Winding are wound on high-strength, ductile T4 cardboard tube. The high-voltage winding is made of high-density cable paper composite wire, which greatly reduces the eddy current loss of the wire. In the low-voltage winding using self-adhesive transposition wire wound, the inside of the auxiliary support to increase the wire support points, all winding have locking bars on the outside, and the winding are designed with “0” margin. All of the mats have been densely treated to greatly enhance the mechanical strength and short circuit resistance of the winding. In addition, the winding are equipped with oil-oriented structure, improve the oil flow path, reducing the warmest winding temperature rise, and slow down the aging of the insulation, extending the life of the transformer. Reasonable choice of winding form, high voltage winding with inner screen continuous winding, reduces the welding process in the welding point, so that the transformer operating failure rate greatly reduced. Reasonable distribution of the winding between the ampoule distributions, reducing the imbalance caused by the ampoule of the lateral magnetic flux leakage, improves short-circuit resistance of winding.
The active part assembly and coil winding are completed in the fully enclosed purification plant. At the same time the use of kerosene gas drying process, drying process with kerosene vapor washed back to the transformer active part impurities, the product cleanliness effect is better, drying efficiency is also greatly improved.
Transformer active part using advanced integrated phase set technology, all the winding alone dry, separate the height and then bake, after all the coil assembly and then dry again, three times drying, three times to adjust the height, ensure uniform height of the winding, reducing short-circuit mechanical force.
The lower part of the active part pallet and the upper pressure plate all use a high mechanical strength and good electrical performance electrical laminate. Transformer stays, pads, etc. have two times pressure and rounding process, reducing the partial discharge. According to the result of dynamic stability calculation, the number and position of the pressure plate are arranged reasonably, so as to press the active part as much as possible to improve the overall stability of the

Active Part Insulation
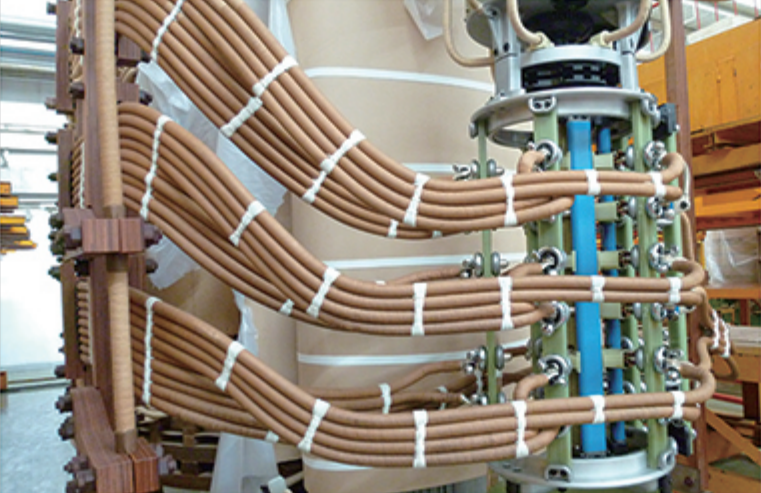
Lead
active part. The upper and lower active part is made of steel positioning, to ensure that the active part can withstand a variety of transport conditions under the impact of the test and the operation of the axial electric power without displacement. The active part is used up and down the use of steel positioning to ensure that the active part can withstand a variety of transport conditions under the impact of the test and the operation of the axial electric power without displacement, so that the scene is not hanging. Just do a simple transfer acceptance test, the product can be put into operation.
Reasonable layout of the transformer lead, take shape beautiful, to ensure adequate electrical strength and mechanical strength, widely used cold welding, all welding all metal shield, the effective control of the transformer partial discharge.
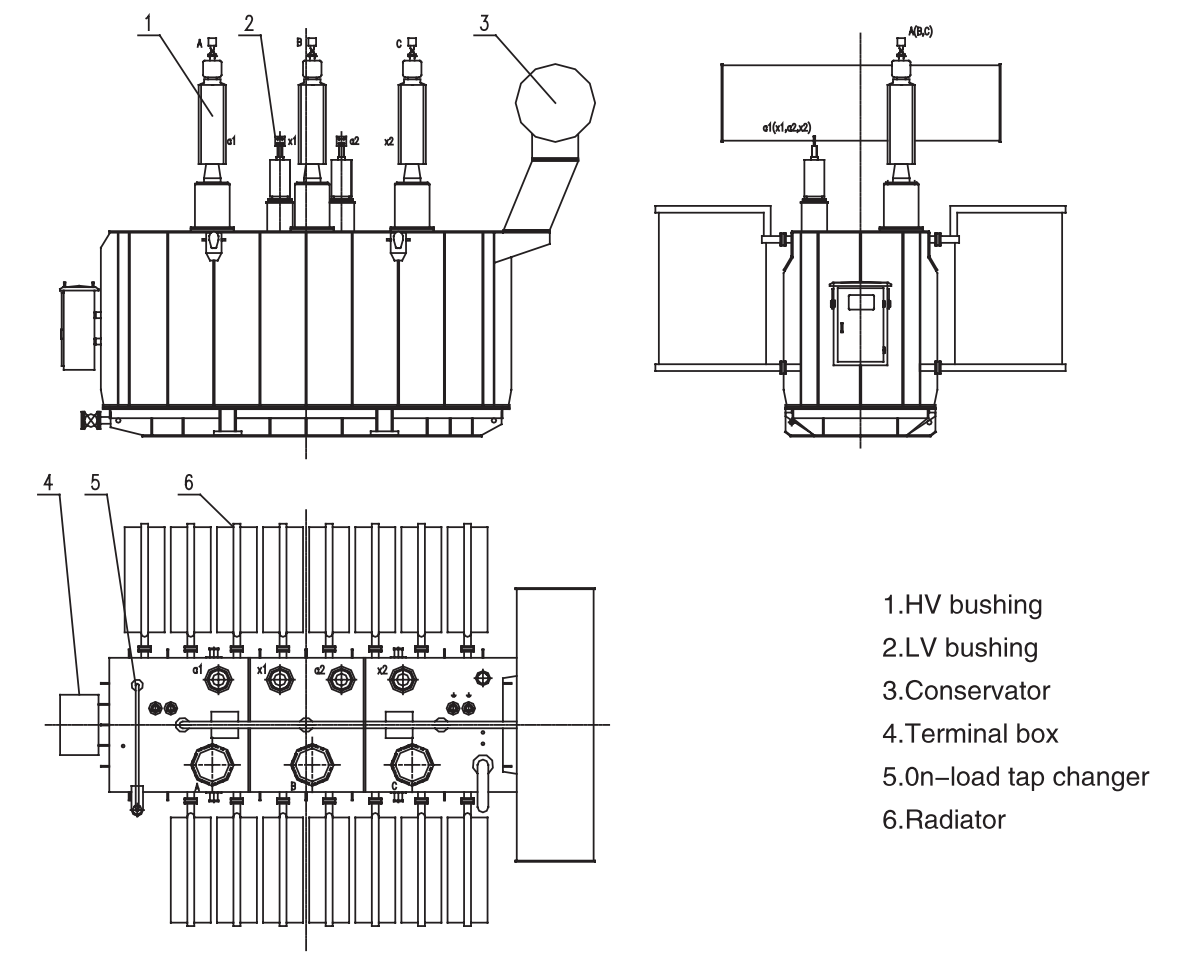
The plate oil tank has undergone a shot blasting process to completely remove sharp corners, welding slag, and other burrs produced during processing, thereby improving the adhesion of the paint and ensuring a beautiful and durable appearance. All flange sealing surfaces have been precisely machined and have a slot and limit structure. Oil-resistant and aging-resistant high-quality gaskets are used. Coolers or radiators and their components are tested under simulated harsh operating conditions to effectively ensure the complete elimination of leakage points. Welding is performed by senior welders who have won excellent results in domestic machinery industry labor competitions. The company also has advanced equipment such as automatic submerged arc welding, CO2 gas shielded welding, and CNC cutting machines, which guarantee the quality of welds and prevent oil leakage. The connection between the upper and lower sections of the oil tank can also be welded along the edges according to customer requirements.
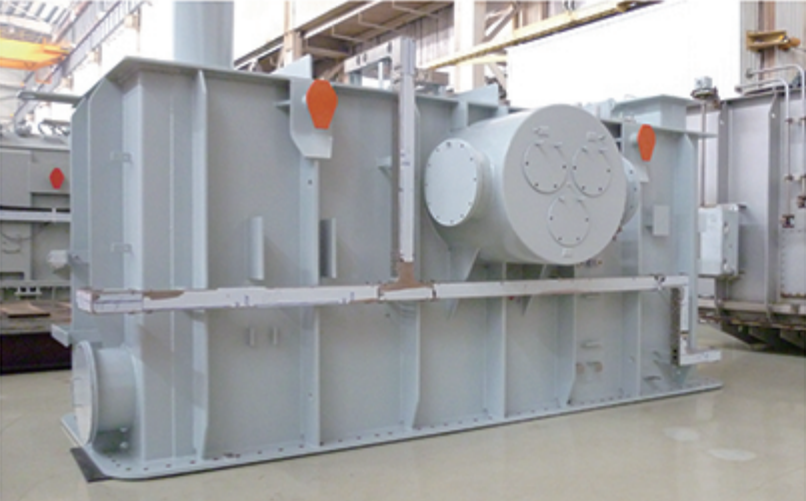

Plate oil tank
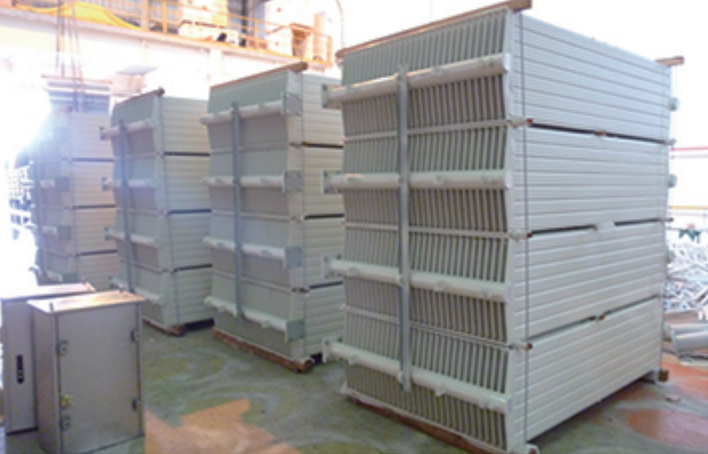

Radiator
According to the standard and the requirements of the rational allocation of external components, and strictly control the quality of supporting manufacturers components to ensure that the quality of the package will not affect the safe operation of the transformer. All secondary cables are all made of oil-resistant flame-retardant armored shielded cable, and all through the metal drag trough to the body terminal box, the user wiring only from the terminal box into the main control room. Air cooling control cabinet with dual power supply, with overheating, lack of equal motor protection, automatic can be switch manual, the shell using high-quality stainless steel plate.
Conservator for the capsule type (can be imported), built with oil, air tightness of the capsule, configured the pointer level gauge, both intuitive and avoid the fake oil level, while fully ensuring the capsule and air contact, to achieve a fully sealed, maintenance-free, reliable operation characteristics.
Cooling device using high-quality wide-chip cooler or radiator, disc valve using high-quality aluminum alloy or plate disc valve to ensure that the transformer life without leakage. We equipped it with advanced pressure relays, gas relays, temperature relays and other detection devices to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the transformer.
In response to fierce market competition and to meet customer demands, our company adheres to a market-oriented approach and a customer-centric philosophy. We have earned widespread recognition from our clients through efficient, comprehensive services and superior product quality.
We offer comprehensive after-sales services, including free guidance for installation and commissioning. After the product is operational, if the customer requires support, our service team will respond promptly:
Additionally, we have established a robust regular follow-up system. We conduct periodic written or on-site visits to monitor the performance of in-service products, ensuring our customers have continuous peace of mind.
Remote Technical Assistance
Our service team provides 24/7 online technical support, including video calls, troubleshooting guides, and documentation, ensuring immediate assistance regardless of time zones.
Detailed remote diagnostics can be conducted using customer-provided data or live visual inspections.
On-Site Support
For complex issues, we dispatch experienced technicians to the customer site promptly, adhering to the agreed international response timelines.
On-site services include installation guidance, commissioning, maintenance, and repairs.
Dedicated Service Representatives
Each international client is assigned a dedicated service representative to coordinate all aspects of after-sales support, including issue resolution and regular follow-ups.
Local Service Partnerships
We collaborate with certified local service partners in key markets to ensure faster response times and efficient support. These partners are fully trained in our products and processes to uphold our quality standards.
Regular Follow-Up Visits
Post-installation, we perform scheduled follow-up visits, either in person or virtually, to monitor product performance and address customer feedback. This proactive approach ensures optimal operation and customer satisfaction.
Why This Matters
Our comprehensive international service system combines swift response, advanced technical support, and localized expertise to provide our global clients with reliable and professional after-sales services. We are committed to building lasting partnerships through consistent support and excellence.
Oil-immersed transformers, widely used in electrical power distribution, are available in a range of voltage and power ratings to suit different applications. The specific voltage and power ratings vary depending on the transformer’s design, manufacturer, and the intended application (e.g., utility grids, industrial, or commercial use). Below are the typical voltage and power ratings available:
Primary Voltage (High Voltage Side):
Secondary Voltage (Low Voltage Side):
Small Power Ratings (for low-voltage transformers):
Medium Power Ratings:
Large Power Ratings:
Transformers can be designed for specific applications with tailored voltage and power ratings. If you have a particular power requirement or voltage need (e.g., for specialized industrial systems), custom transformers can be engineered to meet those needs.
The voltage and power ratings of oil-immersed transformers are diverse, with voltages ranging from 0.4 kV to 800 kV or more, and power ratings from as low as 25 kVA to well over 500 MVA, depending on the application. If you have a specific range or application in mind, I can help narrow down the most suitable ratings.
The efficiency and loss profile of an oil-immersed transformer are critical performance characteristics that directly impact its operational cost, energy consumption, and longevity. These losses primarily manifest as no-load losses (core losses) and load losses (copper losses), both of which can affect the transformer’s overall efficiency.
No-load losses occur when the transformer is energized but not supplying any load (i.e., when it is idle). These losses are primarily due to the magnetizing current in the core material (typically made from silicon steel), which causes eddy currents and hysteresis.
Nature: Constant, independent of the load on the transformer.
Sources:
Typical Values:
Example: A 10 MVA transformer might have no-load losses around 20 to 50 kW.
Load losses are dependent on the current flowing through the transformer’s windings, i.e., they occur when the transformer is supplying load. These losses arise due to the resistance of the windings (copper loss) and the induced eddy currents in the winding material.
The total losses in a transformer are the sum of no-load losses and load losses. The efficiency of a transformer is defined as the ratio of output power to input power, which can be expressed as:
Efficiency=Output PowerInput Power×100\text{Efficiency} = \frac{\text{Output Power}}{\text{Input Power}} \times 100
Or equivalently:
Efficiency=Rated Power−Total LossesRated Power×100\text{Efficiency} = \frac{\text{Rated Power} - \text{Total Losses}}{\text{Rated Power}} \times 100
The efficiency generally improves with the size of the transformer due to more optimized design, better materials, and better cooling techniques.
No Load: At no-load (transformer energized but no load connected), only the core losses (no-load losses) are significant, and the transformer will consume energy primarily to overcome magnetizing forces in the core.
Partial Load: As the load increases, the load losses (copper losses) increase quadratically with the load current, while no-load losses remain constant. The total loss profile becomes a combination of both.
Full Load: At full-load conditions, load losses are at their peak, but the transformer operates most efficiently at its rated capacity. The efficiency is typically close to 98% or better at full load.
Larger transformers are designed to minimize losses, particularly no-load losses. The design often uses high-quality steel for the core and larger winding cross-sections, which reduce resistive losses. As transformers grow in size, their relative losses (as a percentage of rated power) typically decrease.
| Transformer Rating | No-Load Losses (% of Rated Power) | Load Losses (% of Rated Power) | Total Losses at Full Load (%) | Efficiency at Full Load (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up to 1 MVA | 0.1% to 0.3% | 1% to 1.5% | 1.1% to 1.8% | 98% to 99% |
| 1–10 MVA | 0.05% to 0.2% | 0.8% to 1.2% | 1% to 1.4% | 99% to 99.5% |
| 10–100 MVA | 0.03% to 0.1% | 0.6% to 1% | 0.6% to 1.1% | 99% to 99.9% |
| Above 100 MVA | 0.03% to 0.05% | 0.5% to 0.8% | 0.6% to 0.9% | 99.5% to 99.9% |
Oil-immersed transformers typically use oil-based cooling systems, which are essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and preventing overheating. The oil not only serves as a coolant but also as an insulator, ensuring that the transformer operates safely and efficiently. The cooling system plays a crucial role in the performance of the transformer, especially in different climates and under varying load conditions.
ONAN (Oil Natural Air Natural) Cooling:
OFAF (Oil Forced Air Forced) Cooling:
OFAF with Radiators and Fans:
ODAF (Oil Directed Air Forced) Cooling:
Oil-Immersed with Water Cooling (Hybrid Cooling):
Hot Climates:
Cold Climates:
Temperate Climates:
The cooling system in an oil-immersed transformer is crucial for its performance, especially in varying environmental conditions. The choice of cooling system (ONAN, OFAF, ODAF, or hybrid systems) affects the transformer's efficiency, operational lifespan, and ability to handle both light and heavy loads.
Each transformer cooling system needs to be tailored to the specific environmental conditions and operational requirements of the site to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
The insulation class and breakdown voltage (dielectric strength) of an oil-immersed transformer are essential aspects of its design, as they determine the transformer's ability to withstand electrical stresses without failure. These properties help ensure the transformer can operate safely and reliably under high voltage conditions.
The insulation class refers to the maximum temperature that the transformer insulation (including the oil and solid components like paper or resin) can safely withstand during operation. Insulation class affects the transformer’s maximum operating temperature, heat dissipation efficiency, and its overall lifespan.
Typical Insulation Classes for Oil-Immersed Transformers:
Common Insulation Materials:
The breakdown voltage (also referred to as the dielectric strength) is the maximum voltage that the insulation material (oil and solid insulation) can withstand before it breaks down, resulting in a failure of the insulating properties and a potential short circuit. This is an essential specification to ensure the transformer’s reliability during normal and fault conditions.
Dielectric Strength of Transformer Oil:
Transformer Oil Breakdown Voltage:
Solid Insulation Breakdown Voltage:
Several factors can influence the dielectric strength of the oil and solid insulation:
Temperature: As temperature increases, the dielectric strength of both oil and solid insulation decreases. It’s critical to maintain the oil temperature within the rated limits to ensure optimal performance.
Moisture and Contaminants: Water, air, or solid contaminants can degrade the dielectric strength of both oil and solid insulation. Proper maintenance and filtration of transformer oil are essential for maintaining high dielectric strength over time.
Oil Quality: The quality and purity of the transformer oil directly affect its dielectric strength. Transformer oil undergoes aging and can absorb moisture, which decreases its dielectric strength. Regular oil testing and maintenance (such as degassing or filtration) can help retain its insulating properties.
To assess and ensure the transformer’s insulation system can withstand high voltages without failure, the breakdown voltage is regularly tested according to industry standards, such as:
| Insulation Class | Maximum Temperature | Typical Dielectric Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Class A | 105°C | 50-70 kV/cm (for new oil) |
| Class E | 120°C | 50-60 kV/cm |
| Class B | 130°C | 50-60 kV/cm |
| Class F | 155°C | 50-60 kV/cm |
| Class H | 180°C | 50-60 kV/cm |
The insulation class determines the thermal limits of the transformer, impacting its operation under varying load and ambient temperature conditions. Transformer oils generally have a dielectric strength ranging from 30 kV/cm to 70 kV/cm, with the oil quality and maintenance being crucial factors in ensuring that the transformer operates safely over time. Proper insulation and breakdown voltage management are key to ensuring that the transformer can handle the rated voltage without risk of failure.
The operational lifespan of Taishan® transformers is no less than 30 years.
The expected lifespan of an oil-immersed transformer under typical operating conditions can vary based on several factors, including the design, quality of materials, operational environment, maintenance practices, and the load profile of the transformer. However, transformers are designed to be long-lasting, and with proper care and maintenance, they can operate reliably for decades.
On average, the expected lifespan of an oil-immersed transformer is typically in the range of 30 to 40 years. However, many transformers can last even longer — up to 50 years or more — depending on the factors listed below.
Quality of Materials and Design:
Operating Conditions:
Maintenance Practices:
External Factors:
Oil Condition and Insulation Degradation:
| Factor | Effect on Lifespan | Expected Lifespan |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | High temperatures accelerate aging of oil and insulation | ~30 to 40 years (typical) |
| Oil Quality & Maintenance | Regular oil testing, degassing, and filtration extend lifespan | 40 to 50+ years with good maintenance |
| Load Profile | Frequent overloading or high utilization can reduce lifespan | ~30 to 40 years under typical load conditions |
| Ambient Conditions | High humidity, contaminants, or corrosive environments shorten lifespan | ~30 to 40 years if kept in controlled environment |
| Faults or Overloads | Can significantly reduce lifespan if faults are frequent | ~20 to 30 years if overloaded or exposed to frequent faults |
| Maintenance (Monitoring) | Regular diagnostics (DGA, temperature, partial discharge) improve longevity | ~40 to 50 years with proactive monitoring |
Proper preventive maintenance can extend the lifespan of an oil-immersed transformer beyond its typical 30–40 years. Some key maintenance actions include:
Regular Oil Testing: This includes checking for moisture content, acidity, dielectric strength, and gas levels in the oil. Using DGA (Dissolved Gas Analysis) helps detect early signs of degradation, such as overheating or electrical faults, allowing for proactive action.
Cooling System Checks: Ensuring that the transformer’s cooling system (ONAN, OFAF, etc.) is clean and functioning well to prevent overheating.
Insulation Monitoring: Using partial discharge (PD) testing and other diagnostic techniques to monitor the condition of solid insulation, including paper and pressboard.
Temperature Control: Regularly checking the operating temperatures and ensuring the transformer is not running at sustained high temperatures. This includes ensuring the cooling system (oil circulation and air cooling) is functioning as intended.
Dehydration and Filtration: Periodic oil filtering and dehydration help remove moisture and contaminants that could degrade oil quality and insulation.
Under optimal conditions (moderate load, proper cooling, and regular maintenance), oil-immersed transformers can exceed 40 years of service life, potentially lasting 50 years or more with proper care.
Under harsh conditions (frequent overloading, high ambient temperatures, poor maintenance), the lifespan might be shorter, potentially in the 20–30 year range.
The expected lifespan of an oil-immersed transformer under typical operating conditions is generally 30 to 40 years, with the potential to extend beyond 50 years if the transformer is well-maintained, operates under moderate load, and is subjected to optimal environmental conditions. Regular maintenance, such as oil testing, insulation monitoring, and cooling system checks, is essential to maximize the operational life of the transformer.
The type of oil used in oil-immersed transformers plays a critical role in their insulation and cooling systems. The oil must have specific properties, such as high dielectric strength, low viscosity, and good thermal stability, to ensure the transformer operates safely and efficiently over time. Additionally, with increasing environmental awareness and regulations, the toxicity and biodegradability of transformer oils have become important factors in their selection.
Mineral Oil (Petroleum-Based Oil):
Vegetable Oil-Based (Natural Ester Oil):
Synthetic Ester Oil:
Silicone-Based Oil:
| Oil Type | Toxicity | Biodegradability | Other Environmental Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral Oil | Low to moderate | Not highly biodegradable | Persistent in the environment; requires careful disposal |
| Vegetable Oil (Natural Ester) | Very low (non-toxic) | Highly biodegradable | Safer for the environment; sustainable and renewable |
| Synthetic Ester Oil | Low (non-toxic) | Highly biodegradable | More expensive but environmentally friendly |
| Silicone Oil | Low (non-toxic) | Slow to biodegrade | More stable at high temperatures but not as environmentally friendly as esters |
For companies and utilities that prioritize environmental responsibility and sustainable operations, vegetable ester-based oils or synthetic esters are becoming the preferred choice. However, mineral oil remains widespread due to its lower cost and established use in the industry, though it requires careful environmental management practices.
Yes, oil-immersed transformers are typically designed and manufactured to meet a range of international and national standards that ensure their performance, safety, reliability, and environmental impact. These standards and certifications are crucial for guaranteeing that the transformer complies with the technical, safety, and environmental regulations required for different applications. Some of the most important standards include those set by organizations like IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers), and various national regulatory bodies.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is a global standards organization that defines various technical requirements and guidelines for electrical and electronic equipment, including transformers. Many oil-immersed transformers are designed to meet IEC standards to ensure they are safe, reliable, and interoperable across regions.
IEC 60076 Series: This is the primary standard for power transformers and is globally recognized. It includes multiple parts that cover the design, construction, testing, and performance requirements of transformers. Key parts of this series include:
IEC 60296: Specifications for mineral insulating oils used in transformers, including their chemical properties, testing methods, and requirements for safe use.
IEC 60815: Defines high-voltage insulation coordination for transformers, ensuring they can withstand overvoltages during operation.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) provides additional technical standards that complement IEC standards. These standards are widely used in North America and other regions.
IEEE C57.12 Series: This series outlines the standards for power transformers, covering various aspects of their design, testing, and operation. Key parts include:
IEEE 592: Standard for insulating oil used in transformers, which includes testing and monitoring of oil quality, ensuring the dielectric strength and performance of the transformer.
In addition to international standards, oil-immersed transformers are also designed to meet the national standards specific to the country in which they are manufactured or deployed. Some of the most common national standards include:
ANSI Standards (American National Standards Institute): These standards, often adopted by IEEE, govern transformer design and testing procedures in the United States.
BS Standards (British Standards): The British Standards Institution (BSI) issues standards that may apply to transformers, especially those used in the UK and the Commonwealth.
IS Standards (Indian Standards): In India, transformers are designed to meet the standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), such as:
JIS Standards (Japanese Industrial Standards): Japan has its own set of transformer standards governed by the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. For example:
AS Standards (Australian Standards): In Australia, transformers must comply with AS 60076 standards, which align closely with IEC and IEEE standards.
In addition to performance and technical standards, oil-immersed transformers are often designed to meet environmental and safety certifications, especially regarding the use of non-toxic, biodegradable oils and their environmental impact.
RoHS Compliance: The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) certification ensures that transformers are free from hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and other toxic elements. This is particularly important for transformers that are intended for use in countries with strict environmental regulations, such as the EU.
ISO 9001: Transformers may be certified with ISO 9001, the global standard for quality management systems, ensuring that the manufacturer maintains high standards of design, production, and testing.
ISO 14001: ISO 14001 certification pertains to environmental management. Manufacturers that meet this standard are committed to minimizing their environmental impact, including reducing emissions, waste, and the use of hazardous substances in manufacturing.
UL Certification: In North America, transformers may also carry Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification to meet safety standards for electrical products.
For transformers operating in specific environments or with certain types of oils (such as vegetable esters or synthetic oils), additional standards may apply:
| Standard/Certification | Area of Focus | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60076 Series | Design, construction, testing, and performance of power transformers | International (Global) |
| IEEE C57.12 Series | General requirements for transformers, including testing and loading conditions | North America, Global |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems for manufacturing | International (Global) |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management for reducing environmental impact | International (Global) |
| RoHS | Restriction of hazardous substances in electrical products | EU, Global |
| UL Certification | Safety standards for electrical products | North America |
| IEC 60296 | Transformer oil specifications and testing | International (Global) |
| NFPA 70 | Fire safety standards for electrical equipment | North America |
| IEC 60815 | High-voltage insulation coordination for transformers | International (Global) |
Yes, oil-immersed transformers are designed to meet multiple industry standards and certifications from global organizations like IEC, IEEE, and national bodies like ANSI, BSI, and BIS. These standards ensure the transformer meets critical requirements for performance, safety, and environmental impact. Additionally, manufacturers may also seek certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and RoHS to ensure high-quality production and environmental responsibility. These industry standards are critical in ensuring that the transformers operate safely, reliably, and efficiently in a wide range of applications.
Oil-immersed transformers are designed with various protection mechanisms to safeguard against overloading, overheating, and short-circuits. These protections are essential for ensuring safe and reliable operation, preventing damage to the transformer, and minimizing risks to personnel and surrounding equipment. Below are the key protection measures implemented in oil-immersed transformers:
Overloading occurs when the transformer is subjected to a load beyond its rated capacity. While transformers can withstand short periods of overload (depending on design), sustained overloading can cause excessive heating and damage to the internal components, including insulation.
Thermal Protection (Temperature Sensing):
On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC) Protection: In some designs, an on-load tap changer can adjust the voltage level to manage load fluctuations. This helps balance the transformer and avoid excessive loading. However, protection mechanisms, such as fuses or circuit breakers, still play a vital role in case of overload.
Overload Trip Relays: Transformers are often equipped with overload trip relays that are calibrated based on the transformer's capacity. If the transformer operates above its rated load for too long, the relay trips and disconnects the transformer from the power source, preventing further damage.
Overheating can result from overloading, poor ventilation, inadequate cooling, or environmental factors. Excessive heat can degrade the transformer's insulation, shortening its lifespan or causing a catastrophic failure.
Oil-Filled Cooling Systems:
Temperature Indicators and Alarms:
Overtemperature Relay: An overtemperature relay is a critical protection element. It continuously monitors the temperature of the transformer windings or oil. If the temperature exceeds a threshold (e.g., 95°C to 105°C for oil), the relay will trigger an alarm or disconnect the transformer from the grid to prevent damage.
Thermal Overload Protection: In case of sustained overload conditions, transformers may have thermal overload protection that limits operation based on temperature rise rather than current. These protections consider the time-temperature relationship and can provide more accurate overload protection by allowing short-term overloads without tripping immediately.
Short circuits, caused by faults like insulation failure, conductor faults, or lightning strikes, can result in rapid increases in current and cause severe damage to transformers if not properly protected.
Fuses:
Circuit Breakers:
Current Transformers (CTs) and Protective Relays:
Ground Fault Protection: Transformers often include ground fault protection that detects any abnormal ground currents. When a ground fault occurs, the protection system isolates the fault by opening the circuit.
Buchholz Relay: In oil-immersed transformers, a Buchholz relay is a key safety feature that detects gas accumulation due to internal faults, such as short circuits or overheating. The relay can trigger an alarm or activate a shutdown sequence to prevent further damage.
Pressure Relief Valve: A pressure relief valve (sometimes combined with the Buchholz relay) is installed to prevent dangerous build-up of gas pressure within the transformer due to internal arcing or faults. If the pressure exceeds a threshold, the valve opens, allowing gas to escape safely.
Surge Arresters: Surge arresters or lightning arresters are installed on the transformer to protect against transient voltage spikes, such as those caused by lightning or switching surges. These devices clamp high-voltage surges to a safe level and prevent damage to the transformer.
Voltage Regulation: Automatic voltage regulators (AVRs) may be included to adjust voltage levels within the transformer, helping to mitigate risks from voltage surges and under-voltage conditions, both of which can affect transformer performance.
| Protection Type | Mechanism | Triggered By | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overload Protection | Temperature sensing (RTDs), overload relays, on-load tap changers | Excessive load or overheating | Alarm, load reduction, or disconnection |
| Overheating Protection | Temperature sensors, oil and winding temperature monitoring | Overheating due to load, poor cooling | Alarm, shutdown, or forced cooling |
| Short-Circuit Protection | Fuses, circuit breakers, current transformers, differential relays | Fault current, short circuits | Isolation, shutdown, or trip |
| Gas Accumulation Protection | Buchholz relay, pressure relief valve | Gas accumulation from internal fault | Alarm, shutdown, or disconnection |
| Surge Protection | Surge arresters | Voltage spikes (e.g., lightning) | Clamps excessive voltage to safe levels |
Oil-immersed transformers are equipped with a variety of protection systems to guard against overloading, overheating, and short-circuits. These protections include thermal monitoring, overload relays, temperature sensors, fuses, circuit breakers, Buchholz relays, and surge arresters. Together, these mechanisms ensure the transformer operates within safe parameters, prevent catastrophic failures, and protect both the transformer and the connected electrical network. Proper operation and maintenance of these protection systems are critical to ensuring the long-term reliability and safety of oil-immersed transformers.
Yes, oil-immersed transformers can be customized to meet special requirements, including the integration of remote monitoring capabilities and other advanced features. Customization allows the transformer to better fit the specific needs of particular applications, environments, or regulatory requirements. Here are several common customization options available for transformers, with a focus on remote monitoring and other specialized features:
Remote monitoring allows operators to track the transformer's health, performance, and operational parameters in real-time, even when the transformer is located in remote or hard-to-access locations. This type of customization can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of transformer operations.
Temperature Monitoring:
Load Monitoring:
Oil Quality Monitoring:
Vibration Monitoring:
Buchholz Relay and Gas Detection:
Circuit Breaker Monitoring:
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): A common system for monitoring and controlling industrial equipment remotely. Transformers can be integrated into a SCADA system, which collects real-time data from sensors (temperature, load, oil quality, etc.) and presents it on a centralized dashboard for easy access by operators.
IoT (Internet of Things) Connectivity: With IoT integration, transformers can send data to the cloud via wireless communication technologies like 4G/5G, Wi-Fi, or LoRaWAN. The data can then be accessed remotely on smartphones, tablets, or computers for analysis and decision-making.
Modbus or DNP3 Protocol: Many transformers can be customized with Modbus or DNP3 (Distributed Network Protocol), which are industry-standard communication protocols for remote monitoring and control. These protocols allow easy integration into supervisory systems and ensure reliable data transmission.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Some manufacturers offer cloud-based monitoring solutions, where the transformer’s operational data is stored and analyzed in real-time in the cloud. This allows for easy access to historical data, trend analysis, and predictive maintenance insights.
In addition to remote monitoring, transformers can also be customized for a wide variety of special requirements based on specific application needs. Some common customizations include:
Extreme Temperature Operation: If the transformer is located in an area with extremely high or low temperatures, it can be customized with enhanced cooling systems (e.g., OFAF, OFWF) or specialized insulation materials that can handle the temperature extremes.
Seismic Protection: In seismic regions, transformers can be equipped with additional shock protection and seismic mounts to prevent damage during earthquakes.
Explosion-Proof Design: For use in hazardous areas, transformers can be customized to be explosion-proof by incorporating special sealing and materials that meet standards such as ATEX or IECEx.
Corrosion Resistance: For coastal or industrial environments with high levels of pollutants or salt in the air, transformers can be customized with corrosion-resistant coatings for the external components, such as the tank and bushings.
Compact Design: In applications where space is limited (such as urban areas or offshore platforms), transformers can be customized to have a compact footprint without compromising on efficiency or performance.
Voltage Adjustment: On-load tap changers (OLTC) can be integrated for voltage regulation to suit specific voltage needs, ensuring stable voltage output under varying load conditions.
Multi-Tap and Multi-Voltage Configurations: Transformers can be designed with multi-tap windings or multi-voltage configurations to meet complex load requirements, especially for multi-site operations or industrial plants with diverse voltage needs.
Higher Insulation Class: The transformer can be customized with a higher insulation class (such as Class F, Class H, etc.) to improve its tolerance to temperature extremes, increasing its operational lifespan and reliability.
Bushing and Terminal Configurations: Transformers can be customized with specialized bushings or terminal connections for high-voltage and high-current applications, ensuring safe and efficient energy transfer.
Differential Protection: Custom transformers can be equipped with differential protection schemes that monitor the input and output currents and immediately detect internal faults such as short circuits or winding faults.
Arc Flash Protection: Transformers can be customized with enhanced arc flash protection systems to minimize the risk of an arc flash event, which can cause significant damage and safety hazards.
Predictive Maintenance: With remote monitoring, some advanced transformers integrate predictive maintenance capabilities. Using real-time data, these transformers can predict failures based on trends and analytics, helping reduce downtime and avoid unexpected failures. Data such as temperature trends, oil condition, and vibration patterns can be analyzed using AI (Artificial Intelligence) and machine learning algorithms to forecast potential issues before they occur.
Self-Diagnosis and Alerts: Many modern transformers are capable of self-diagnosis. They continuously monitor internal parameters and generate alerts if abnormal conditions are detected. This data can be sent to operators or maintenance teams, minimizing the need for manual inspections.
Cybersecurity: For transformers with remote monitoring, cybersecurity measures are critical to prevent unauthorized access or cyber-attacks. Custom transformers can include secure communication protocols, firewalls, and encryption technologies to ensure that data transmitted from the transformer remains secure.
Access Control: User authentication and role-based access control can be implemented for the remote monitoring platform to ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical transformer data and settings.
Yes, oil-immersed transformers can be customized for various special requirements, including remote monitoring capabilities. Through the integration of advanced sensors, communication systems, and monitoring platforms (SCADA, IoT, Modbus, etc.), transformers can provide real-time data on parameters such as temperature, load, oil quality, and fault detection. Additionally, transformers can be customized for environmental, operational, and safety requirements, including extreme temperature handling, seismic protection, corrosion resistance, and predictive maintenance. These customizations help ensure that the transformer operates optimally and can be efficiently monitored and maintained, even in remote or challenging environments.
Environmental and safety compliance are critical considerations for oil-immersed transformers, as these units contain large amounts of insulating oil, which can pose environmental risks if leaks or spills occur. Transformer manufacturers implement a variety of environmental protection measures and safety features to mitigate these risks and ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations. Here’s an overview of the key environmental and safety compliance features typically found in oil-immersed transformers:
Oil containment is essential to prevent transformer oil from leaking into the environment, particularly in the event of a rupture, seal failure, or other malfunction. Oil is typically a mineral-based or bio-degradable insulating fluid, and its release can lead to soil contamination, groundwater pollution, and fire hazards. Therefore, transformers are designed with various containment features:
Oil Containment Trays (Bunded Areas):
Oil Drainage and Recovery System:
Oil-Resistant Gaskets and Seals:
Double-Walled Tanks:
Automatic Shutoff Valves:
Even with containment measures in place, having an effective spill response plan is crucial for dealing with unforeseen incidents. Many transformers come with features that support fast cleanup and emergency response.
Oil Spill Kits: Transformers located in sensitive or high-risk environments may be equipped with an oil spill kit, which includes absorbent materials, disposal bags, and personal protective equipment for responders. These kits help contain and clean up any spilled oil quickly.
Transformer Emergency Shutdown Features:
Monitoring for Environmental Compliance:
To meet regulatory standards and protect the environment, oil-immersed transformers must comply with various local, national, and international environmental laws and industry standards. Key regulations focus on oil usage, waste disposal, and leak management:
While transformers are generally safe, there is always the potential risk of a fire or explosion, especially if the transformer oil overheats, leaks, or becomes contaminated. Transformer manufacturers implement various fire safety features to reduce this risk.
Fire-Resistant Oil: As an alternative to conventional mineral oils, fire-resistant oils (such as phosphate esters) are used in some transformers, especially in applications where fire risk is a primary concern, such as near residential areas, chemical plants, or high-traffic zones.
Fire-Resistant Enclosures: For locations with a high fire risk, the transformer’s enclosure can be built to resist external fires or to prevent fire from spreading to surrounding areas. This could include using fire-resistant coatings or insulated enclosures.
Overtemperature Protection: Temperature sensors, overload relays, and cooling fans ensure the transformer operates within safe thermal limits, preventing overheating that could lead to fire.
Explosion Venting: To minimize the risk of explosions caused by gas buildup inside the transformer, many designs include explosion vents or pressure relief valves. These safety devices release excess pressure from within the transformer in a controlled manner, preventing dangerous rupture or explosion.
Explosion-Proof Design (for hazardous locations): In environments with an increased risk of explosion (such as mines, oil rigs, or chemical plants), the transformer can be designed to meet ATEX or IECEx standards, ensuring that the transformer is explosion-proof and capable of operating safely in hazardous atmospheres.
Transformers can generate noise and electromagnetic fields, which may need to be minimized to meet environmental and safety regulations.
Oil-immersed transformers are equipped with various environmental and safety compliance features to protect against oil spills, leaks, and other potential hazards. Key features include:
These features help ensure the transformer operates in
a safe, environmentally responsible manner, minimizing the risk of harm to people, wildlife, and the surrounding environment.
The lead time for manufacturing and delivery of an oil-immersed transformer depends on several factors, including the specific model and customization requirements, production capacity, and logistical considerations. Below is a breakdown of key factors that influence lead time and typical timelines for various scenarios:
Standard Models: For transformers that meet standard industry specifications (e.g., off-the-shelf models with typical ratings and configurations), the lead time is typically 12 to 16 weeks from order confirmation to delivery. This timeline includes manufacturing, testing, and basic logistical arrangements.
Customized Transformers: If the transformer requires special features such as:
The manufacturing process for an oil-immersed transformer typically includes the following stages:
Design and Engineering (2 to 4 weeks):
Core and Coil Assembly (4 to 6 weeks):
Tank Construction and Oil Filling (2 to 4 weeks):
Testing (2 to 3 weeks):
Final Inspection and Documentation (1 to 2 weeks):
Shipping and Delivery: Depending on the destination and transformer size, shipping time can vary. For domestic deliveries (e.g., within the same country), delivery might take 1 to 2 weeks. For international deliveries, shipping can take 4 to 8 weeks or longer, depending on:
On-Site Installation (Optional): If installation services are required, this could add another 2 to 4 weeks depending on the location and complexity of the installation, especially if there are challenges like remote locations or site preparation.
Several variables can impact the lead time, including:
If an expedited timeline is required (e.g., urgent project deadlines), some manufacturers may offer an expedited manufacturing service, though this will typically come with additional costs. This can reduce the lead time to 8 to 12 weeks for certain standard transformer models, but customized models will still take more time due to the engineering and testing complexity.
For an accurate lead time estimate, it’s important to provide specific details about the model, location, and any customization needs to the manufacturer.
Welcome to contact us for further information.
In response to fierce market competition and to meet customer demands, our company adheres to a market-oriented approach and a customer-centric philosophy. We have earned widespread recognition from our clients through efficient, comprehensive services and superior product quality.
We offer comprehensive after-sales services, including free guidance for installation and commissioning. After the product is operational, if the customer requires support, our service team will respond promptly:
Additionally, we have established a robust regular follow-up system. We conduct periodic written or on-site visits to monitor the performance of in-service products, ensuring our customers have continuous peace of mind.
The inclusion of installation services in the purchase of an oil-immersed transformer depends on the supplier, the contract terms, and the specific project requirements. Typically, installation is not automatically included in the base price of the transformer, but some manufacturers may offer it as an option or part of a turnkey solution. Here's a breakdown of how installation typically works and what to expect in terms of additional costs:
In most cases, installation is not included in the base price of the transformer. This is especially true for large transformers that require specialized equipment for transportation, handling, and installation. Typically, the following steps are involved in the process:
Installation services typically include a combination of the following:
The cost of installation is usually not included in the transformer’s base price and is considered a separate service. Installation costs can vary widely based on factors such as:
Typical costs for installation may range from 10% to 20% of the total purchase price of the transformer, depending on the factors listed above. For example:
Some manufacturers offer turnkey solutions, where both the transformer and its installation are included in the price. In this case, the manufacturer or a third-party service provider would manage the entire process from design to commissioning, including:
A turnkey solution may be ideal for customers who prefer a single point of contact and want to avoid the complexity of coordinating multiple contractors. However, turnkey solutions generally come with a premium price to cover the installation costs, as well as any project management overhead.
Post-Installation Support: Most manufacturers will offer post-installation support to assist with any operational issues or troubleshooting that may arise after the transformer is up and running. Some also provide a warranty for the transformer, which may cover faulty components for a defined period.
Extended Warranty and Service Contracts: Some suppliers offer extended warranties or service contracts that include maintenance, inspections, and support for a fixed period. These contracts are often offered as an additional service and may cover scheduled oil sampling, cooling system checks, and performance reviews.
In some cases, particularly for international projects or in regions with travel restrictions, remote commissioning may be offered. This could involve:
This option can help reduce costs and ensure the timely completion of the installation, though it may not replace on-site presence for critical tasks (e.g., oil filling or electrical connections).
To get an accurate estimate of installation costs and whether it's included in the purchase price, it’s essential to discuss your requirements with the manufacturer or supplier and ensure that all aspects of installation (transportation, on-site handling, electrical work, commissioning) are covered in the contract.
Routine maintenance of an oil-immersed transformer, such as a Taishan® transformer, is essential to ensure its efficient operation, long lifespan, and safety. The maintenance tasks typically fall into daily, weekly, monthly, and annual checks, which involve both visual inspections and more technical tests. Below is a detailed look at the typical maintenance requirements and the associated costs.
Daily checks are essential for monitoring the transformer’s operational status and identifying potential issues early:
These inspections are slightly more in-depth and can be carried out either by in-house personnel or external specialists:
Annual maintenance requires more thorough inspections and sometimes professional technicians:
The cost of maintenance varies depending on several factors, including transformer size, complexity, and location. Below is a breakdown of possible costs for the maintenance of a typical oil-immersed transformer like the Taishan® model:
If your transformer has customized features or operates in a high-risk environment, specialized maintenance services may be required. For instance:
Many manufacturers, including Taishan®, offer preventive maintenance contracts that provide routine checks, repairs, and emergency services for a fixed annual fee. These contracts typically cost between $5,000 to $20,000 per year for a standard transformer, depending on the size and complexity of the unit. These contracts often cover:
Routine maintenance for an oil-immersed transformer like a Taishan® transformer involves a combination of daily checks, weekly/monthly inspections, and annual tests. These checks ensure the transformer operates efficiently and safely over its lifespan.
While routine maintenance costs depend on the transformer’s size, age, and operational environment, it is important to budget for labor, oil maintenance, and component replacements. For a more predictable cost structure, preventive maintenance contracts can be a viable option. These contracts typically cost $5,000 to $20,000 per year but help extend the transformer’s lifespan and minimize the risk of unplanned downtime.
The inclusion of spare parts with a Taishan® oil-immersed transformer depends on the specific agreement, package, and manufacturer policies. Here's a detailed breakdown of how spare parts are typically handled:
For most standard purchases of Taishan® oil-immersed transformers, the basic set of spare parts required for initial installation and operation (such as gaskets, oil, and fasteners) may be provided at no additional cost or included in the warranty period. These could cover minor components that are essential for the transformer’s setup and initial functioning.
However, spare parts for long-term maintenance (e.g., bushings, cooling fans, oil pumps, pressure relief valves, transformer oil, etc.) are usually not included in the standard package. These parts typically need to be purchased separately. The need for such components would arise as part of regular maintenance or due to particular operational issues during the transformer's lifecycle.
Taishan® typically offers a spare parts catalog for clients. Customers can either:
Some manufacturers, including Taishan®, may offer comprehensive service contracts that include spare parts as part of the agreement. These contracts typically cover:
This option could significantly reduce the overall cost of maintenance and ensure quick availability of spare parts in case of urgent needs.
Under the warranty period, most minor parts (such as gaskets, seals, or other smaller components) should be covered by the manufacturer's warranty, provided the malfunction or damage is not caused by improper usage or external factors. Major parts (like the transformer oil or larger mechanical components) are typically not covered under standard warranties and will need to be purchased separately.
It is advisable to discuss specific spare part needs and service options with your Taishan® distributor or sales representative for a tailored solution based on your project’s requirements.
When purchasing a Taishan® oil-immersed transformer, comprehensive technical support is typically available during both installation and commissioning to ensure the transformer is properly integrated into your system and operates at peak efficiency. The level of support depends on the contract terms and service options you choose. Here is a breakdown of the typical technical support available:
Taishan® usually offers installation assistance either as part of the service package or as an additional service option, which typically includes the following:
Pre-Installation Guidance:
On-Site Supervision:
Mechanical and Electrical Integration: Support during the physical installation and connection to the electrical system (e.g., wiring, busbars, grounding, cooling systems, and transformer protection devices) is typically provided.
Commissioning is the process of testing and verifying that the transformer operates according to design specifications. This is a critical phase for ensuring that the transformer is functioning optimally and safely in the operational environment. Typical commissioning support includes:
System Testing:
Protective Relays and Control Systems:
System Integration:
Safety Checks:
On-Site Technical Support: If any issues arise during installation or commissioning, on-site support is typically available. An engineer or technician from Taishan® can assist with troubleshooting and corrective actions.
Remote Support: For advanced troubleshooting or monitoring, remote technical support is available in some cases, particularly for transformers with monitoring systems (e.g., remote diagnostics via IoT or cloud-based systems). This can include assistance via phone, email, or video calls to guide you through any complex commissioning issues.
As part of the commissioning process, training for local staff is often offered. This ensures that:
Taishan® typically provides a range of technical documentation, including:
These documents are invaluable for future reference and can support in-house technicians with routine maintenance and troubleshooting.
After the transformer is commissioned, Taishan® often offers ongoing technical support, which may include:
The cost for installation and commissioning support can vary depending on the location, complexity, and terms of the agreement. In many cases:
Taishan® transformers typically come with robust technical support during installation and commissioning to ensure proper integration into your system. Support includes on-site guidance, system testing, operator training, and documentation. For more specialized support or extended assistance, you can opt for preventive maintenance contracts and additional services.
To get specific details regarding costs and scope of installation and commissioning support, it's recommended to consult directly with a Taishan® representative or distributor based on your project requirements.
Yes, when you purchase a Taishan® oil-immersed transformer, you can typically expect to receive a comprehensive set of technical documentation to guide the installation, operation, and maintenance of the transformer. These documents are essential for ensuring the safe and efficient functioning of the transformer throughout its lifespan. Here’s an overview of the types of documentation typically provided, along with their contents:
The operation manual is the primary document that provides detailed information on how to operate the transformer under normal conditions. It typically includes:
Wiring diagrams and electrical schematics are provided to guide the installation and maintenance of the transformer’s electrical connections. These documents typically include:
These diagrams are especially important during the installation phase to ensure all electrical connections are properly made and during maintenance or repair to troubleshoot or upgrade the system.
The maintenance guide offers comprehensive instructions for maintaining the transformer to ensure it performs optimally throughout its service life. It usually includes:
If your transformer has been customized (e.g., with remote monitoring capabilities or special cooling systems), you may receive additional documentation related to those features:
Taishan® provides a complete set of technical documentation that includes operation manuals, wiring diagrams, maintenance guides, test reports, and warranty documentation. These documents are essential for safe installation, optimal operation, and proper maintenance throughout the transformer's lifespan. You can typically receive these documents with your transformer purchase, and additional copies can be requested from the Taishan® support team if needed.
When dealing with Taishan® oil-immersed transformers, the primary hazardous material involved is typically transformer oil. While the transformer itself is generally safe to handle, certain procedures are essential for oil handling, maintenance, and spill management. Transformer oil may contain polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in older models, or modern transformers often use mineral oil or vegetable-based oils. Both types of oils require careful handling due to their flammability, potential toxicity, and environmental impact.
Here are the standard procedures for handling hazardous materials, particularly transformer oil, during different stages of the transformer's life cycle:
Depending on the type of oil used (e.g., mineral oil or vegetable-based oil), the procedures may vary, but the core principles of safe handling remain consistent.
In the event of an oil spill:
While oil is the primary hazardous material in an oil-immersed transformer, other materials also require proper handling, particularly during repairs, maintenance, and end-of-life disposal.
Transformer Components (Bushings, Gaskets, etc.):
Flammable Gases and Fumes:
Transformer Scrap Disposal:
To manage the risks associated with hazardous materials, Taishan® oil-immersed transformers are designed to meet international environmental and safety standards, including:
The transformer also includes safety labels and warning notices to remind personnel of the potential hazards during installation, operation, and maintenance.
Handling hazardous materials during the installation, maintenance, and disposal of Taishan® oil-immersed transformers involves a number of safety protocols, including proper PPE, oil storage, spill containment, and disposal methods. Special attention is needed when dealing with transformer oil (especially older oil that may contain PCBs) and flammable gases. Following these procedures ensures the safety of personnel and compliance with environmental regulations.
The recommended maintenance schedule for a Taishan® oil-immersed transformer (or any similar oil-immersed transformer) is crucial to ensure its longevity, efficient operation, and safe performance. Regular maintenance is typically based on factors such as the transformer’s operating environment, load conditions, and manufacturer’s specifications. Below is a general maintenance schedule that includes both routine checks and periodic servicing:
These tasks are typically conducted on a monthly or quarterly basis to ensure the transformer is functioning properly.
These checks should be carried out at least twice a year, focusing on more in-depth analysis.
This should be more thorough and include equipment checks, detailed tests, and cleaning, typically conducted by a professional technician or a service team.
A major overhaul involves significant disassembly and inspection of the transformer’s internal components. This is generally recommended every 4 to 6 years or after a major fault, depending on the usage and condition of the transformer.
The regular maintenance of Taishan® oil-immersed transformers should follow a structured schedule, with monthly or quarterly checks for routine inspections and basic functionality, semi-annual checks for oil testing and load measurements, and annual checks for more in-depth diagnostics. A major overhaul is typically required every 4 to 6 years or sooner if performance issues arise. Adhering to this maintenance schedule ensures that the transformer operates efficiently, extends its operational life, and minimizes the risk of unexpected failures or safety hazards.
Taishan® oil-immersed transformers come with a range of after-sales support services designed to ensure their efficient operation, troubleshoot issues, and perform necessary repairs. Below are the key after-sales support features typically available with Taishan® transformers:
Many customers opt for preventative maintenance contracts that provide ongoing support for the transformer. These contracts typically cover:
Taishan® oil-immersed transformers come with a robust after-sales support package, which includes:
This comprehensive support ensures that any issues can be addressed quickly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and extending the operational life of the transformer.
Yes, Taishan® oil-immersed transformers typically offer service contracts and extended warranty options designed to provide ongoing support and peace of mind throughout the transformer’s operational life. These options are customizable depending on the specific needs of the customer and the critical nature of the transformer’s application. Below are the key service contracts and extended warranty options typically available:
A service contract provides a structured framework for regular maintenance, support, and emergency services, ensuring that the transformer remains in optimal operating condition. The typical components of a service contract for Taishan® transformers include:
An extended warranty provides extended protection beyond the standard manufacturer warranty, ensuring coverage for repairs, parts replacement, and services even after the standard warranty expires. Extended warranties are beneficial for companies seeking additional peace of mind for longer-term operations.
Taishan® transformers often allow customers to tailor service contracts and extended warranty options based on their specific operational needs. Some tailored options might include:
Typically, service contracts and extended warranties are offered as add-ons or can be bundled with the purchase at a discounted rate. Costs may vary, and customized quotations can be provided based on individual needs.
Taishan® oil-immersed transformers come with various options for service contracts and extended warranties, providing peace of mind and ensuring optimal performance over the transformer’s lifespan. The service contracts offer routine maintenance, emergency support, diagnostic services, and spare parts availability, while extended warranties extend coverage for repairs, parts replacement, and labor costs. These options help reduce downtime, lower the total cost of ownership, and ensure the transformer’s reliability in critical operations.
The speed at which spare parts for Taishan® oil-immersed transformers can be obtained and their typical cost depend on several factors, such as the specific part needed, the location of the customer, and the supplier's inventory management system. Here's a detailed breakdown:
Taishan® transformers are designed to be maintained over long periods, and the availability of spare parts is a key factor in ensuring minimal downtime. The typical lead times for spare parts are as follows:
The costs of spare parts for Taishan® oil-immersed transformers vary widely depending on the component’s size, complexity, and function. Below are the approximate costs for common and specialized spare parts:
This approach helps ensure that the Taishan® oil-immersed transformer continues to perform reliably over the long term, with minimal impact from repair needs.
For in-house maintenance teams, Taishan® oil-immersed transformers offer comprehensive training and support programs to ensure that internal staff can effectively manage the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the transformers. These programs are designed to improve the technical proficiency of your team and minimize downtime through efficient maintenance practices. Below are the details on the training and support options available:
Taishan® provides structured training programs that can be tailored to your specific needs, typically including both theoretical and practical components. These training programs cover key aspects of transformer operation, diagnostics, and maintenance procedures.
The training programs typically cover the following key topics, depending on the scope of the training:
Transformer Fundamentals:
Routine Maintenance Procedures:
Troubleshooting and Fault Diagnosis:
Transformer Protection Systems:
Maintenance of Auxiliary Systems:
Safety Procedures:
In addition to formal training programs, Taishan® provides ongoing technical support to ensure that your in-house maintenance teams have the resources and assistance they need throughout the lifespan of the transformer.
Service contracts (which often include maintenance support) typically cover aspects such as:
Taishan® offers comprehensive training and support for in-house maintenance teams, including on-site training, remote support, and documentation. These programs are designed to help your team maintain, troubleshoot, and repair transformers efficiently. By investing in training, your team can improve safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in the long term. Additionally, service contracts can provide ongoing support and scheduled training to keep your team up to date on the latest transformer maintenance practices and technologies.
Testing and maintaining transformer oil is a critical part of ensuring the safe operation and long-term reliability of an oil-immersed transformer. The oil serves multiple functions, such as cooling and insulating the transformer’s internal components, making regular maintenance of the oil essential for transformer health.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to the testing, maintenance, and oil replacement procedures, as well as guidelines for oil management:
Regular testing of transformer oil helps assess its quality, purity, and effectiveness in insulating and cooling the transformer. Common oil tests include:
Purpose: Measures the insulating capability of the oil. If the oil’s dielectric strength is low, it indicates contamination or degradation of the oil.
Method: This is done by applying an electric field to the oil until the oil breaks down. The voltage at which the breakdown occurs indicates its dielectric strength.
Acceptable Range: Typically, the oil should have a dielectric strength of at least 30 kV per 2.5 cm gap, although this varies by transformer design and voltage ratings.
Testing Frequency: At least once a year or when the oil shows signs of contamination (e.g., moisture).
Purpose: Moisture in the oil can degrade its insulating properties and lead to accelerated deterioration of the transformer’s components. The presence of moisture can also reduce the dielectric strength.
Test Methods:
Acceptable Range: Transformer oil should have moisture content less than 20 ppm (parts per million).
Testing Frequency: Typically annually or when DGA or other tests indicate possible issues.
Purpose: These tests assess the oxidation state of the oil. As the oil ages, it oxidizes and forms acids, which can degrade the oil and components inside the transformer.
Acid Number: A measure of how acidic the oil is. An increase in acid number indicates that the oil is breaking down.
Neutralization Number: The number of milligrams of KOH required to neutralize the acidic components in 1 gram of oil.
Testing Frequency: Annually or if other signs of oil degradation are observed.
Maintaining transformer oil is essential for optimizing the insulating and cooling properties of the oil. Key maintenance procedures include:
Purpose: Routine oil monitoring through online sensors or manual sampling helps track oil quality over time.
Methods:
Frequency: Oil monitoring should be done at regular intervals as part of the predictive maintenance plan. This could be as frequent as quarterly or based on the load condition of the transformer.
While oil replacement is not usually needed on a routine basis, there are situations where oil change or oil topping-up may be necessary. Here are the key guidelines for oil replacement:
Draining the Old Oil: Care should be taken to safely drain and dispose of the old oil in an environmentally responsible manner.
Cleaning the Transformer: After draining the oil, the transformer is usually cleaned to remove any contaminants or sludge before new oil is added.
Filling with New Oil: Fresh transformer oil is added, and the transformer is then tested for any issues like leaks, oil level, and performance.
Reconditioning Oil: In some cases, instead of full replacement, it is possible to recondition the oil (through filtration and dehydration) to restore its properties.
Frequency of Oil Replacement: Typically, oil replacement is not required for 20-30 years, depending on the operating conditions of the transformer. However, it’s more common in transformers that are subjected to frequent load variations, overloading, or harsh environmental conditions.
Regular oil testing (DGA, dielectric strength, moisture content, etc.) is essential for the long-term health of the transformer. Routine oil maintenance through filtration, dehydration, and regeneration helps keep the oil in optimal condition, while oil replacement may be needed in cases of significant contamination or degradation. By adhering to these testing and maintenance guidelines, the performance of the Taishan® oil-immersed transformer can be preserved for many years, ensuring optimal operation, safety, and reliability.
The disposal of a transformer at the end of its life cycle is a complex process that involves environmentally responsible methods to handle the various materials within the transformer, including the transformer oil, metal components, insulation materials, and electrical parts. Proper disposal is essential to minimize environmental impact and comply with local regulations regarding hazardous waste, oil disposal, and recycling.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to the expected procedure for transformer disposal:
Before the transformer can be disposed of, it must be properly decommissioned and prepared for disposal. This involves several important steps to ensure that the process is safe and compliant with regulations:
One of the most important steps in transformer disposal is the handling of the transformer oil, which may be contaminated and requires careful disposal or recycling.
Before disposal, the oil may be tested to determine its condition:
If oil is heavily contaminated (e.g., with PCBs, high acidity, or excessive moisture), it must be disposed of as hazardous waste. This involves:
After the oil has been drained and any hazardous materials have been handled, the transformer is dismantled for recycling or disposal.
Once the transformer is dismantled, the individual components are sent to specialized facilities for recycling or disposal.
Once the disposal and recycling process is complete, the following actions should be taken:
The disposal of an oil-immersed transformer at the end of its life cycle involves a series of steps to safely handle hazardous materials (such as oil, PCBs, and other contaminants), dismantle the transformer, and recycle valuable components like metal windings and steel. Proper documentation and adherence to environmental regulations are critical throughout the process to ensure safe disposal and minimize environmental impact. By following the appropriate procedures, the transformer’s end-of-life disposal can be carried out in an environmentally responsible and compliant manner.
Yes, many manufacturers of oil-immersed transformers, including Taishan® Transformers, offer monitoring software or diagnostic tools that enable real-time performance tracking and remote diagnostics. These tools are designed to enhance the operation, safety, and maintenance of transformers by providing insights into critical operational parameters, helping prevent failures, and extending the transformer’s lifespan.
Here’s an overview of what monitoring tools and software are typically available for Taishan® transformers, along with the types of features you can expect:
While Taishan® Transformers may not list proprietary software by name, many manufacturers of oil-immersed transformers, including Taishan, offer integrated monitoring systems in collaboration with third-party vendors or their own in-house solutions. Typical systems include:
The use of monitoring software and tools provides numerous benefits:
By providing detailed insights into transformer performance, predictive maintenance becomes more accurate. This allows for:
Continuous monitoring helps identify issues such as overheating, moisture accumulation, or gas buildup that could shorten the transformer’s lifespan. By addressing these issues proactively, the lifespan of the transformer can be significantly extended.
Real-time performance tracking ensures that potential faults are detected before they lead to serious damage, reducing the risk of fire, explosion, or electrical outages, and increasing overall safety.
By having detailed performance data and reports, users can meet regulatory requirements more easily, such as ensuring that maintenance and diagnostics are carried out as required by standards.
For transformers installed in remote or hard-to-access locations, remote monitoring allows operations and maintenance teams to track and troubleshoot performance from anywhere, minimizing the need for frequent on-site visits.
Some advanced monitoring systems integrate with IoT (Internet of Things) devices and AI-based analytics to:
Taishan® Transformers, like many other manufacturers, likely provides monitoring software or tools to track the performance, safety, and operational efficiency of their oil-immersed transformers. These tools often include features like real-time performance monitoring, predictive diagnostics (e.g., DGA), remote access, and reporting capabilities. The use of such monitoring systems enhances the reliability, efficiency, and lifespan of the transformer, while also improving safety and regulatory compliance.
Emergency repair requests for Taishan® oil-immersed transformers (or similar transformer models) are typically handled through a structured process designed to address critical situations quickly, minimize downtime, and restore normal operation as soon as possible. The response time and procedures may vary depending on factors such as location, the severity of the issue, and the level of support included in the service agreement.
Here is an outline of how emergency repair requests are generally handled, including key details about response time and service procedures:
Once the emergency request is received, the following steps are typically taken:
The response time for emergency repairs depends on several factors:
Once the service team arrives at the location, they will immediately assess the damage. This may include:
Once the repair is completed, post-repair testing is conducted to ensure the transformer is operating as expected. This includes:
After emergency repairs are made, monitoring may continue for a period (e.g., 24–48 hours) to ensure that the transformer is functioning properly and there are no recurring issues.
A detailed report of the emergency repair will typically be provided to the customer, outlining:
Taishan® Transformers (and similar manufacturers) handle emergency repair requests through a systematic process that includes rapid response, diagnostic analysis, and on-site repair. Response times typically range from 4–24 hours, depending on the severity of the issue and location, with service agreements ensuring faster intervention. Emergency dispatch teams conduct repairs, restore functionality, and perform post-repair testing to ensure reliable operation. Emergency repairs may incur higher costs due to the urgency of the situation, but these are often covered under warranty or service contracts.
For Taishan® oil-immersed transformers, the list of authorized service centers or technicians for repairs is typically provided by the manufacturer or its regional distributors. These service centers and technicians are specially trained and equipped to handle the repair, maintenance, and troubleshooting of transformers to ensure compliance with manufacturer standards and safety protocols.
While I can't pull up a direct list for you here, I recommend the following approaches:
You can reach out to Taishan® Transformers through their official website, customer service hotline, or local office to obtain a list of authorized repair centers and technicians in your region. They typically provide the contact details of authorized partners, service agents, and service providers.
If your transformer is located in a specific country or region, Taishan® may work with authorized service providers for that specific area. In regions like North America, Europe, or Asia, there may be official service hubs equipped to provide repairs, maintenance, and emergency services.
If Taishan® transformers are part of a larger transformer brand network or global service group, authorized repair centers may fall under that umbrella. You may inquire about service access points through organizations like:
If you have a maintenance contract with Taishan® Transformers, they would provide authorized service providers as part of your agreement. Contractual support typically includes access to certified repair technicians as well as emergency repair services.
By reaching out through these channels, you’ll receive detailed information on the nearest authorized service centers or technicians who can assist with repairs and ensure the highest level of service and support.
This guidebook serves as an extensive resource for professionals, engineers, and researchers interested in Oil-Immersed Transformers. It covers the fundamental principles, technology advancements, design considerations, operational challenges, and environmental impacts of Oil-Immersed Transformers. Through detailed explanations, case studies, and practical insights, readers will gain a deep understanding of Oil-Immersed Transformers technology and its applications in modern power.
Luneng Taishan Transformer is a key national-level manufacturer specializing in transformers, recognized as a “Contract-Honoring and Promise-Keeping” enterprise, a high-tech enterprise, and a national-level enterprise technology center. It is recommended in the national directory for rural and urban power grid construction and renovation, as well as a recommended supplier of major electromechanical equipment for hydropower projects. Its products have been awarded the title of “National Quality Inspection Qualified Product – Quality Trustworthy Product” and “Nationally Recognized Product for Mechanical Industry Users.
Our products not only dominate the domestic market but are also exported to more than 30 countries and regions, including Russia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and the Americas, serving industries such as power, municipal engineering, metallurgy, and petrochemicals.
We're here for you !
let's Talk about your Project!