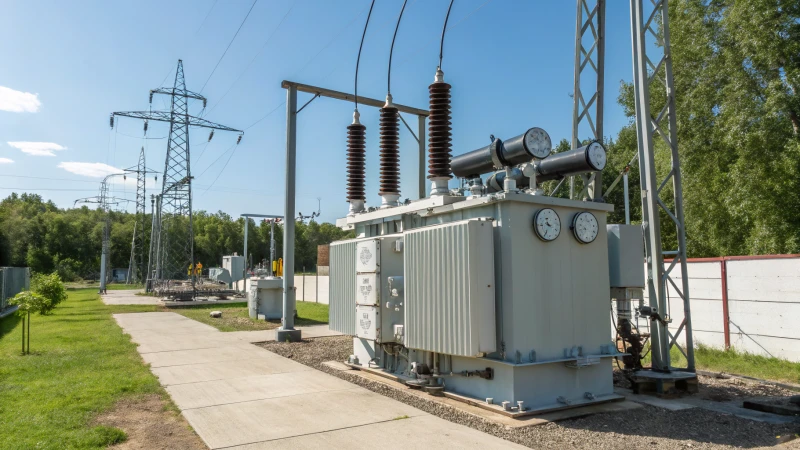
Oil-immersed transformers play a crucial role in high-voltage power transmission systems. These transformers are responsible for stepping down the high-voltage electricity generated at power plants to lower voltages that can be safely used by industries, businesses, and homes. The oil inside the transformer is not only a cooling medium but also an insulating material, ensuring that the transformer operates efficiently and safely. Without oil-immersed transformers, the high-voltage power generated by power plants could not be safely transmitted to end-users, making them essential to modern electrical grids.
In this article, we will explore the role of oil-immersed transformers in high-voltage power transmission, the importance of transformer oil, and the key functions they serve in the electrical grid.
What is an Oil-Immersed Transformer?
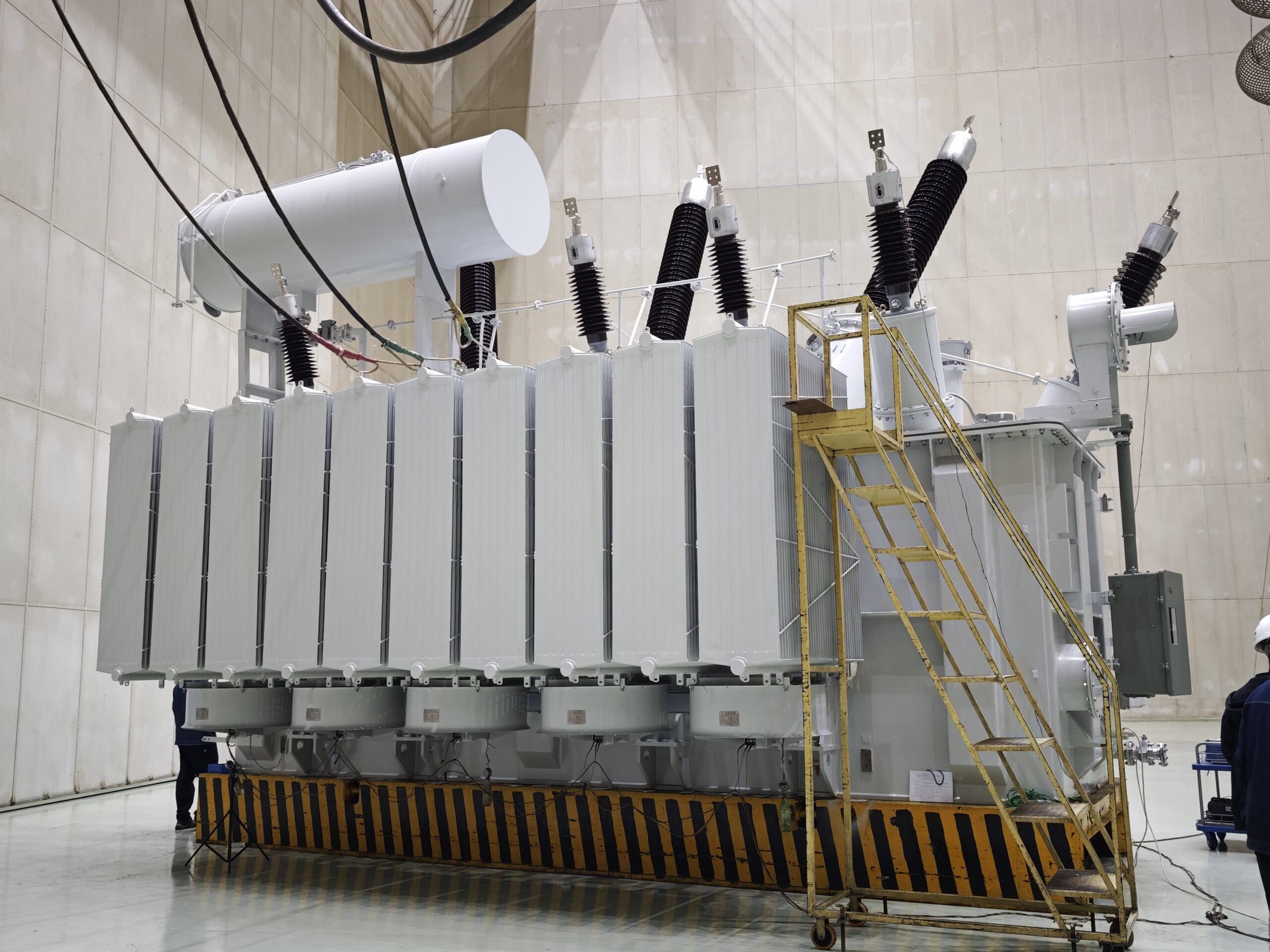

An oil-immersed transformer is one of the most commonly used types of transformers in electrical power systems. It uses transformer oil to cool and insulate the electrical components inside the transformer, including the windings and core. The oil is contained in a sealed tank and circulates within the transformer to manage heat generation from the electrical processes occurring during power conversion.
In this article, we will explore what oil-immersed transformers are, their components, how they work, and why they are integral to the power distribution and transmission systems.
How Do Oil-Immersed Transformers Work?
Oil-immersed transformers primarily function to step up or step down voltage in an alternating current (AC) power supply. The transformer consists of primary and secondary windings wound around a core made of laminated steel to minimize energy loss. The transformer oil plays a crucial role in two primary ways:
Cooling: Transformers generate heat during operation, especially when high currents are flowing through the windings. The oil acts as a coolant, absorbing the heat from the transformer’s core and windings and dissipating it through a cooling system or by convection.
Insulation: In addition to cooling, transformer oil serves as an insulating medium. The oil prevents electrical arcing and short circuits between the windings, allowing the transformer to operate safely and effectively.
The oil is contained within a large tank that surrounds the core and windings. In some cases, the transformer may also include additional cooling components, such as radiators or fans, to increase the heat dissipation capacity.
Key Components of an Oil-Immersed Transformer
An oil-immersed transformer consists of several key components, each working in synergy to ensure the transformer's effective operation:
Transformer Oil: The key element in the design of an oil-immersed transformer, transformer oil is used to insulate the windings and core while also cooling the components. It is typically a mineral-based oil, although there are eco-friendly alternatives, such as vegetable oils and synthetic esters, being increasingly used.
Core: The core of the transformer is made from laminated steel sheets, which are stacked together to form a magnetic path. The core helps in transferring the magnetic field between the primary and secondary windings.
Windings: The windings are usually made of copper or aluminum, and they are responsible for carrying the electrical current. The windings are immersed in oil to ensure proper cooling and insulation.
Tank: The oil-immersed transformer has a sealed tank to contain the oil. This tank is usually made of steel and is designed to handle internal pressure and temperature changes. The tank is equipped with an oil level indicator to monitor the oil level and ensure the system is properly filled.
Radiators: Some oil-immersed transformers are equipped with radiators, which are large metal fins that increase the surface area for cooling. The oil inside the transformer circulates through these radiators, allowing heat to dissipate more efficiently into the surrounding environment.
Bushings: These are insulating devices used to connect the transformer to the external circuits, such as power lines or buses, ensuring that the electrical components are insulated from the external environment.
Tap Changer: An on-load tap changer allows for voltage regulation by adjusting the number of turns in the windings. This can help the transformer adapt to variations in the load or supply voltage.
Benefits of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers offer a number of advantages that make them suitable for various applications in power distribution systems:
Efficient Cooling: Transformer oil absorbs heat from the core and windings, ensuring that the transformer remains at a safe operating temperature. The cooling system can be further enhanced with external radiators, ensuring efficient heat dissipation.
Longer Lifespan: Due to the effective cooling and insulation properties of the oil, oil-immersed transformers tend to have longer operational lifespans compared to air-cooled transformers. Proper maintenance of the oil also contributes to a transformer’s longevity.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: While oil-immersed transformers require regular monitoring of oil quality and levels, they generally have lower operational and maintenance costs compared to dry-type transformers. The oil helps in preventing electrical arcing and short circuits, reducing the need for frequent repairs.
High Voltage Capability: Oil-immersed transformers are typically able to handle higher voltages compared to dry-type transformers, making them ideal for large power systems and high voltage transmission networks.
Flexibility in Installation: Oil-immersed transformers are widely used in various applications, ranging from small distribution transformers to large power transformers for substations, offering significant flexibility in their installation and use.
Applications of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers are used in a variety of electrical systems, such as:
- Power Plants: To step up or step down the voltage for the transmission of electrical power.
- Substations: To regulate voltage levels for the distribution of power to residential, commercial, and industrial areas.
- Industrial Settings: Oil-immersed transformers are used in factories and manufacturing plants where there is a need for high-voltage systems and reliable performance.
- Renewable Energy Systems: They are also used in solar and wind power plants to handle high-voltage output and ensure energy is properly distributed.
Environmental Considerations and Oil Alternatives
Although oil-immersed transformers are effective at cooling and insulating, there are growing concerns about the environmental impact of using mineral oils. Synthetic esters and vegetable oils are being increasingly adopted as environmentally friendly alternatives to mineral oils. These alternatives offer several benefits, including better biodegradability and lower toxicity in the event of spills.
Why it matters:
The use of environmentally friendly oils contributes to sustainability and reduces the ecological risks associated with mineral oil, making the entire transformer system more eco-conscious.
Maintenance of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Some key maintenance practices include:
- Oil Testing: Regular tests for dielectric strength, moisture content, and acidity ensure that the oil maintains its insulating and cooling properties.
- Oil Filtration and Purification: Removing contaminants such as moisture, sludge, and gas from the oil helps maintain its quality and prevent transformer failure.
- Leak Detection: Monitoring oil levels and detecting leaks prevents environmental hazards and ensures that the oil remains at the required level.
- Temperature Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of transformer oil temperature ensures that the transformer does not overheat, reducing the risk of damage.
How Do Oil-Immersed Transformers Facilitate High-Voltage Power Transmission?
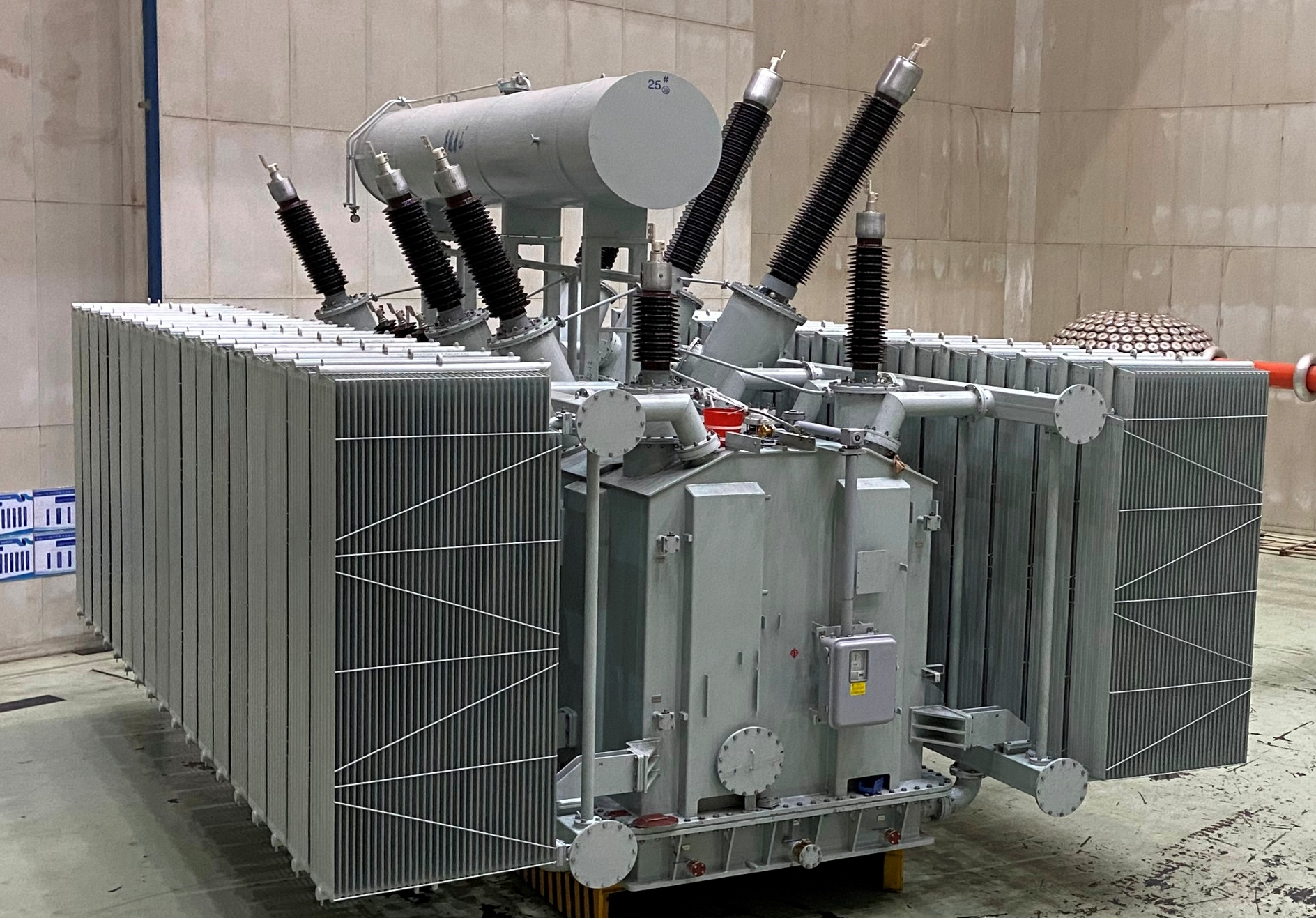
Oil-immersed transformers play a crucial role in high-voltage power transmission, enabling the efficient movement of electricity over long distances. These transformers are integral to the functioning of modern electrical grids, especially for the transfer of power from power stations to substations and ultimately to end users. They handle the critical job of stepping up or stepping down voltage levels while ensuring that electricity is transmitted safely, efficiently, and without significant loss.
In this article, we will explore how oil-immersed transformers are designed and operated to facilitate high-voltage power transmission, highlighting their key features, benefits, and functions within the power network.
How Oil-Immersed Transformers Operate in High-Voltage Systems
Oil-immersed transformers are designed to manage the thermal and electrical stresses that come with high-voltage transmission. The process begins when power is generated at a power plant or other electrical sources and needs to be transmitted to distant locations through high-voltage lines. Transformers are essential for converting the voltage from the generator level to a level suitable for long-distance transmission.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how oil-immersed transformers facilitate high-voltage transmission:
Step-Up and Step-Down Functionality:
High-voltage power transmission systems require both step-up and step-down transformers. A step-up transformer increases the voltage for efficient long-distance transmission, while a step-down transformer reduces the voltage to a usable level for distribution to homes, factories, and commercial areas.Oil-immersed transformers are typically used in both roles, depending on the location in the power grid. In power plants, step-up transformers increase voltage for transmission, and at substations, step-down transformers reduce the voltage to make it suitable for end-user consumption.
Oil Immersion for Cooling and Insulation:
High-voltage transformers generate significant heat during operation due to the large amounts of electrical power being processed. Oil immersion plays a critical role in both cooling and insulating the transformer’s core and windings:- Cooling: The oil circulates through the transformer’s internal components, absorbing heat produced by the electrical current flowing through the windings. This prevents the transformer from overheating and ensures safe, continuous operation, even under high electrical loads.
- Insulation: Oil also serves as an insulating medium, preventing electrical arcing and short circuits between the windings and the transformer tank. At high voltages, insulation is critical to avoid catastrophic failures, and oil provides this essential protection.
The combination of heat dissipation and electrical insulation allows the transformer to handle high-voltage applications reliably.
Voltage Regulation and Load Management:
Oil-immersed transformers are equipped with an on-load tap changer (OLTC), a device that adjusts the number of active turns in the transformer’s windings to regulate the voltage. As the load on the transformer changes throughout the day, the OLTC automatically adjusts the voltage to maintain a steady output despite fluctuations in demand.This is especially important in high-voltage transmission systems, where maintaining consistent voltage levels is critical for the stability of the entire power grid.
Key Benefits of Oil-Immersed Transformers for High-Voltage Transmission
Oil-immersed transformers provide numerous advantages that make them ideal for high-voltage power transmission systems. Let’s look at some of the primary benefits:
Efficient Cooling for High Voltages:
High-voltage transformers generate a lot of heat. Oil immersion is one of the most effective cooling methods, helping to maintain safe operating temperatures and prevent thermal damage to the transformer. Without this cooling mechanism, transformers would overheat and fail in a short period.High Electrical Insulation:
Transformer oil’s excellent dielectric properties ensure that the high-voltage electrical components are well-insulated. This insulation protects against electrical breakdowns or arcing, which could lead to catastrophic failure, especially in high-voltage systems. The oil provides a solid barrier that keeps the electricity contained within the windings.Reliability in Harsh Conditions:
Oil-immersed transformers are designed to operate in challenging environments, handling fluctuations in voltage, temperature, and electrical loads. Whether used in remote locations or in large industrial settings, these transformers remain reliable under varying operating conditions.Extended Transformer Life:
The combination of cooling and insulation reduces stress on transformer components, which in turn extends the life of the transformer. Proper maintenance of the oil, including regular checks for moisture, acidity, and other contaminants, ensures that the transformer remains operational for many years without significant degradation.Safety and Protection:
Oil-immersed transformers are equipped with various safety mechanisms, such as pressure relief valves, oil level indicators, and temperature sensors, to prevent unsafe operating conditions. In case of an electrical fault, these safety features allow the transformer to shut down or be isolated from the grid, preventing further damage.
Applications of Oil-Immersed Transformers in High-Voltage Transmission
Oil-immersed transformers are widely used in high-voltage transmission networks due to their ability to handle large electrical loads safely and efficiently. Here are some common applications:
Power Generation Stations: Oil-immersed transformers are used to step-up the voltage generated by power plants, allowing the electricity to be transmitted over long distances with minimal loss.
Substations: In substations, oil-immersed transformers are used to step-down high-voltage electricity for distribution. These transformers ensure that the voltage is reduced to safe levels for use by homes, businesses, and industrial facilities.
High-Voltage Transmission Lines: Oil-immersed transformers are used to maintain voltage levels along transmission lines, ensuring that the electricity reaches its destination without significant loss in power quality or quantity.
Renewable Energy Plants: With the growth of renewable energy sources, oil-immersed transformers are increasingly being used in solar and wind power plants to convert and manage the electrical output for integration into the grid.
Maintenance and Oil Management
For an oil-immersed transformer to perform optimally in high-voltage systems, regular maintenance of both the transformer and the oil is essential. Here are some key maintenance practices:
Oil Testing: Regular tests should be conducted to assess the dielectric strength, moisture content, and acidity of the oil. These tests ensure that the oil maintains its cooling and insulating properties, which is crucial for safe operation.
Oil Filtration: Over time, transformer oil can accumulate contaminants, such as water, gases, and sludge. Periodic oil purification or filtration can remove these contaminants, ensuring that the oil remains effective.
Monitoring Temperature and Oil Levels: Consistent monitoring of the oil temperature and oil levels ensures that the transformer remains within its safe operational range. High oil temperatures or low oil levels can cause damage to the windings and other internal components.
Why is Transformer Oil Essential in High-Voltage Power Transmission?
In high-voltage power transmission systems, transformer oil plays an essential role in ensuring safe, reliable, and efficient electrical operations. Transformers are crucial components in electrical grids, responsible for stepping up or stepping down voltages to facilitate the transmission of electrical energy over long distances. For transformers to perform this job effectively and efficiently, the oil inside the transformer must meet specific functional and performance criteria.
In this article, we will explore why transformer oil is indispensable to high-voltage power transmission, focusing on its core functions such as cooling, insulation, and reliability. We will also discuss the properties that make transformer oil so effective and the critical role it plays in maintaining the transformer’s operational lifespan.
Key Functions of Transformer Oil in High-Voltage Power Transmission
Transformer oil performs several essential tasks, which are particularly important when managing high-voltage electrical systems. These functions primarily revolve around cooling and insulating the transformer’s internal components, both of which are crucial for safe and efficient power transmission.
Cooling:
High-voltage transformers generate significant amounts of heat due to the electrical currents passing through the windings and other internal components. Transformer oil serves as the primary medium for heat dissipation. As the oil circulates through the transformer, it absorbs the heat produced by the current and helps maintain a stable operating temperature. Without oil, the transformer could overheat, leading to inefficiency, failure, or even catastrophic damage.The heat transfer properties of the oil are vital for regulating the internal temperature of the transformer. The oil is typically circulated through cooling fins, radiators, or external heat exchangers that help expel the absorbed heat into the surrounding environment.
Electrical Insulation:
One of the most critical roles transformer oil plays in high-voltage systems is that of insulation. At high voltages, electrical breakdowns or arcing can occur if the internal components of the transformer are not properly insulated. Transformer oil helps to prevent this by creating a stable dielectric barrier between the windings and the transformer tank.Transformer oil has excellent dielectric properties, meaning it is highly resistant to electrical conductivity and can withstand high-voltage stress without breaking down. This insulation protects the internal parts of the transformer from electrical shorts, preventing faults that could lead to power outages, damage, or safety hazards.
Dissolving Gases and Contaminants:
Over time, moisture and gases can accumulate inside transformers, which can deteriorate the oil and affect its insulating properties. Transformer oil acts as a dissolving agent for gases that are produced due to electrical arcing, overheating, or oil oxidation. By absorbing these gases, the oil prevents them from accumulating in pockets within the transformer, which could lead to internal faults.Preventing Oxidation and Corrosion:
Transformer oil not only cools and insulates but also acts as a protective coating for metallic parts within the transformer. The oil prevents the formation of rust or corrosion on critical components like windings and bushings, especially in high-voltage conditions. This protective action helps extend the transformer’s lifespan and ensures its reliable operation over the years.
Properties of Transformer Oil for High-Voltage Applications
The success of transformer oil in high-voltage power transmission systems can be attributed to its unique properties. Let’s take a closer look at the key characteristics that make transformer oil highly effective:
Dielectric Strength:
Transformer oil must have a high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltage without breaking down. This property prevents arcing and electrical faults within the transformer. Transformer oils are tested regularly for dielectric strength to ensure they maintain their insulating properties.Thermal Stability:
In high-voltage applications, transformers can experience extreme temperature fluctuations. Transformer oil must be able to withstand these temperature changes without degrading, maintaining its cooling and insulating properties. Oils used in transformers are specially formulated to be thermally stable over a wide range of temperatures.Oxidation Resistance:
Over time, exposure to heat and oxygen can cause the oil to oxidize, which reduces its effectiveness as an insulating and cooling agent. High-quality transformer oils are engineered to resist oxidation and maintain their properties for long periods, minimizing the need for frequent oil changes and reducing maintenance costs.Moisture Control:
Moisture in transformer oil can drastically reduce its insulating properties and lead to internal faults. Good transformer oil should be able to resist absorbing moisture and should allow for easy removal of any water that might find its way into the system.Low Viscosity:
The oil should have low viscosity to ensure it circulates freely throughout the transformer. This ensures that heat is transferred efficiently from the internal components to the cooling system. Low viscosity allows the oil to flow easily through tight spaces and radiators, which is critical in maintaining the cooling efficiency of the transformer.
Why Transformer Oil is Essential for High-Voltage Power Transmission
Given the complex demands of high-voltage power transmission, transformer oil is indispensable for the following reasons:
Ensures Safety:
In high-voltage power transmission systems, safety is paramount. Transformer oil’s ability to prevent electrical breakdowns and act as a heat sink ensures the safety of the transformer and surrounding infrastructure. The oil provides the necessary protection to avoid short circuits, arcing, and overheating, all of which could result in dangerous conditions.Optimizes Transformer Efficiency:
Without transformer oil, the heat generated by electrical currents would cause the transformer to malfunction or fail. The oil ensures that the transformer operates within the optimal temperature range, which increases its efficiency and performance. In turn, this reduces the risk of energy loss, which is especially important in high-voltage transmission systems where efficiency is critical.Increases Operational Lifespan:
Transformers that are properly maintained with high-quality oil are less likely to experience wear and tear over time. The oil’s role in reducing oxidation, preventing moisture buildup, and dissipating heat helps extend the lifespan of the transformer. By preventing overheating and damage to the internal components, transformer oil ensures reliable performance over the long term.Reduces Maintenance Costs:
Properly managed transformer oil reduces the need for frequent maintenance, as it protects the transformer from many common problems like overheating, arcing, and corrosion. Oil testing, filtration, and treatment ensure that the transformer remains in top condition, helping to avoid costly repairs and downtime.
How Do Oil-Immersed Transformers Ensure Efficiency and Reliability in Power Transmission?
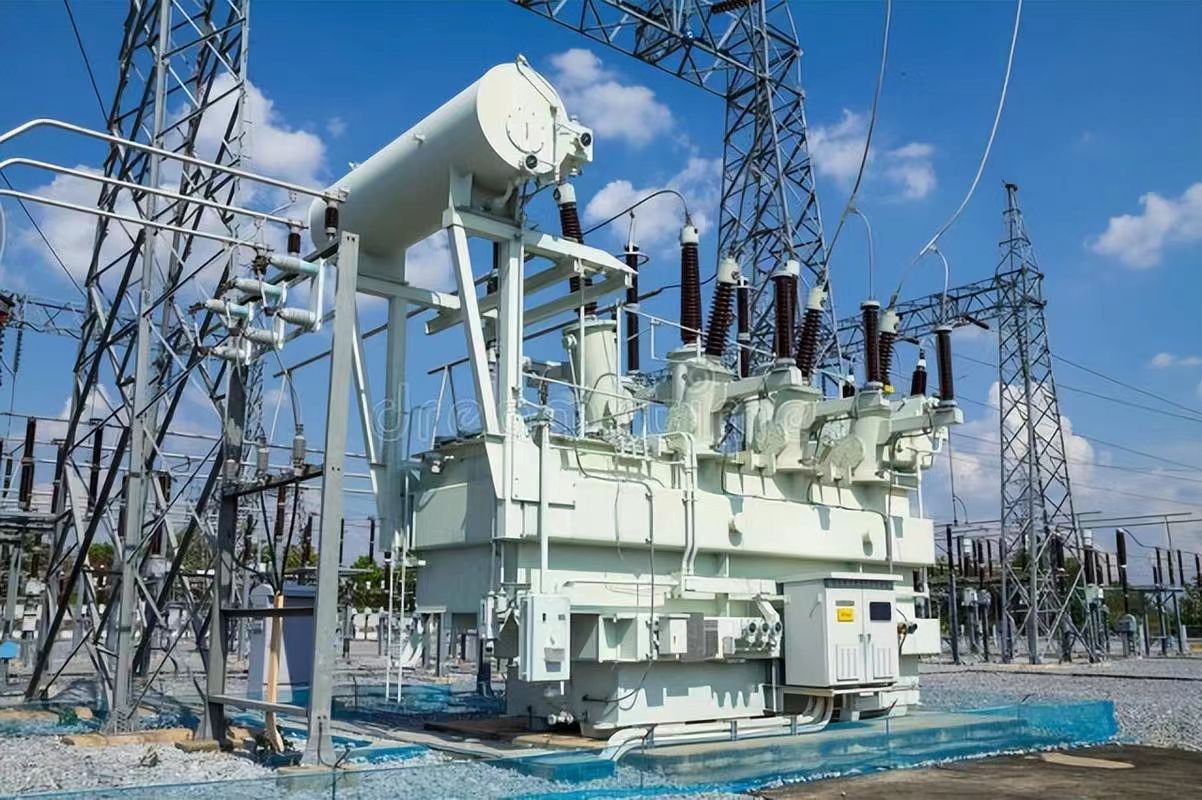

Oil-immersed transformers are a cornerstone of power transmission systems, enabling the efficient and reliable transmission of electricity across vast distances. These transformers are crucial for stepping up or stepping down voltage to ensure power is safely and effectively transmitted through the grid, particularly in high-voltage applications.
The role of transformer oil in these systems is critical as it facilitates not only the functioning of the transformer but also contributes to maintaining its efficiency, reliability, and safety. In this article, we will dive into how oil-immersed transformers work and why they are integral to power transmission systems worldwide.
Key Functions of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Oil-immersed transformers are engineered to meet the challenges of high-voltage power transmission, and they achieve this through two core functions: cooling and insulation. These transformers are immersed in transformer oil, which performs a critical role in maintaining the optimal conditions for transformer operation.
Cooling Efficiency
One of the primary challenges in power transformers is heat generation. When high-voltage electrical current flows through the transformer’s windings, it generates heat that needs to be dissipated to avoid overheating. Oil-immersed transformers effectively use the heat transfer properties of transformer oil to draw heat away from the windings and internal components.As the oil circulates through the transformer, it absorbs the heat and carries it away to external cooling systems, such as radiators or cooling fins. The oil is constantly in motion, either through natural circulation (based on temperature differences) or through forced circulation via pumps, ensuring efficient heat dissipation. This cooling process not only maintains the transformer’s temperature within safe operational limits but also improves the overall efficiency of power transmission.
Electrical Insulation
Oil-immersed transformers use transformer oil as a dielectric medium, preventing electrical arcing and breakdowns. The oil provides excellent electrical insulation, ensuring that the transformer’s internal components remain isolated from each other electrically. This is especially important in high-voltage applications, where insulation must withstand tremendous electrical stress.The oil’s ability to insulate is determined by its dielectric strength, which is a key property of transformer oil. A higher dielectric strength allows the oil to prevent short circuits and electrical faults that could otherwise lead to transformer failure. This insulating property also protects sensitive components like bushings, windings, and tap changers from electrical overloads.
Efficiency Benefits of Oil-Immersed Transformers
The operational efficiency of oil-immersed transformers is critical to ensuring that energy is transmitted across vast distances with minimal loss and at a steady pace. These transformers play an essential role in maintaining the overall stability of the grid while ensuring minimal disruptions.
Minimizing Energy Loss
Transformer oil helps reduce energy losses in the transformer system by maintaining a stable internal temperature. If a transformer overheats, it may result in higher energy losses due to the resistance of the windings increasing with temperature. Transformer oil ensures that the transformer stays within an optimal operating temperature range, thereby minimizing energy losses.Continuous and Stable Performance
Oil-immersed transformers are designed to operate continuously without requiring frequent maintenance, thanks to the oil’s ability to protect the transformer from internal damage. The oil prevents the formation of rust or corrosion on metallic components, maintaining their functionality over time. Regular oil maintenance, including monitoring for the oil’s dielectric strength, moisture levels, and temperature, ensures that the transformer maintains peak performance over its lifespan.Improved Load Handling
Oil-immersed transformers are capable of handling varying load conditions without compromising performance. The oil acts as a buffer to protect the transformer from thermal overload during periods of heavy demand. By providing efficient cooling, the oil ensures that the transformer remains stable and operational during peak periods.
Reliability of Oil-Immersed Transformers
Reliability is another key feature of oil-immersed transformers, especially when used in high-demand environments such as substations, power plants, and remote power stations.
Long Operational Lifespan
One of the standout features of oil-immersed transformers is their long lifespan. Proper maintenance of the transformer oil—through regular testing and filtration—ensures that the transformer remains in optimal condition for decades. The oil helps preserve the integrity of the internal components, reducing the risk of component degradation due to heat, oxidation, or electrical stress.The transformer’s ability to operate reliably over long periods with minimal breakdowns makes it a vital asset in power transmission systems that need to be operational 24/7. Oil-immersed transformers are especially valued in high-demand areas where downtime can cause significant disruptions in the power supply.
Protection Against Faults
The insulation properties of transformer oil help prevent faults such as electrical breakdowns, arcing, and short circuits. When there is a failure within the transformer, the oil absorbs and dissipates the electrical energy, preventing it from causing widespread damage. This makes oil-immersed transformers more resilient to faults compared to dry-type or air-cooled transformers.Oil Quality Monitoring
Regular oil testing for properties such as dielectric strength, acidity, and moisture content plays a crucial role in the reliability of oil-immersed transformers. Advanced sensors and diagnostic tools can continuously monitor the oil’s condition, detecting any degradation or contaminants that might compromise the transformer’s functionality. This proactive approach to oil monitoring and maintenance ensures the transformer remains reliable over time.
The Role of Transformer Oil in Enhancing Safety
Apart from its roles in cooling and insulation, transformer oil also contributes to the safety of the transformer by minimizing the risk of fires and explosions. Transformer oil is highly refined to reduce the risk of ignition, and it typically has a high flash point, making it safe to use in high-voltage environments. Furthermore, the oil’s insulating properties prevent electrical shorts that could otherwise cause hazardous conditions.
Properties of Transformer Oil in Oil-Immersed Transformers
The effectiveness of oil-immersed transformers in power transmission is directly tied to the unique properties of transformer oil. Let’s examine the key properties of oil used in these transformers:
Dielectric Strength:
The oil’s ability to withstand high voltages without breaking down is essential for preventing electrical breakdowns in the transformer.Thermal Conductivity:
Transformer oil must have excellent heat transfer properties to effectively dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating conditions.Oxidation Resistance:
Oil must be resistant to oxidation to maintain its insulating properties over time, reducing the need for frequent oil changes.Moisture Control:
The oil must be able to prevent moisture ingress, as water contamination reduces the oil’s dielectric strength and can lead to faults.Viscosity:
Low viscosity allows the oil to circulate efficiently through the transformer’s internal components, ensuring effective cooling.
What Are the Benefits of Using Oil-Immersed Transformers in High-Voltage Systems?
Oil-immersed transformers are essential components in the power transmission and distribution system, particularly in high-voltage systems. These transformers not only play a critical role in stepping up or stepping down voltage levels but also ensure the efficiency, reliability, and safety of electrical grids worldwide. By using oil as both a coolant and an insulating medium, oil-immersed transformers have proven to be indispensable in systems that require high-voltage power transmission over long distances.
The advantages of oil-immersed transformers in high-voltage systems are far-reaching. This article explores these benefits, including enhanced cooling, insulation, reliability, and long-term operational efficiency, among other critical factors.
Key Benefits of Oil-Immersed Transformers in High-Voltage Systems
1. Efficient Heat Dissipation
One of the main challenges in high-voltage power transmission is managing the heat generated by the electrical components, especially within transformers. When electrical current flows through the windings of a transformer, it generates a significant amount of heat. Without an effective cooling mechanism, excessive heat can cause transformer components to fail, leading to outages and operational disruptions.
Oil-immersed transformers address this issue through the cooling properties of transformer oil. Transformer oil is a highly effective heat transfer medium. As the oil circulates within the transformer, it absorbs heat from the windings and other internal components. The oil then carries this heat away to cooling surfaces like radiators, fins, or external cooling systems.
This cooling action allows oil-immersed transformers to operate at optimal temperatures even under high-load conditions, minimizing the risk of overheating. Proper heat dissipation is essential for maintaining the efficiency and performance of high-voltage systems, ensuring that the transformer can handle substantial electrical currents without the risk of failure.
2. Superior Electrical Insulation
Transformer oil also functions as an insulating medium within the transformer. Electrical insulation is vital in high-voltage transformers to prevent electrical arcing, short circuits, and other potentially catastrophic faults that could disrupt power transmission.
The oil in oil-immersed transformers acts as a dielectric, preventing direct electrical contact between components that are under different electrical potentials. Transformer oil’s dielectric strength allows it to resist electrical breakdowns, maintaining the integrity of the electrical insulation in high-voltage environments. This capability is particularly crucial when stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission, where the voltage levels can be several hundred kilovolts (kV).
By preventing electrical faults and reducing the risk of arcing and other electrical disturbances, oil-immersed transformers help maintain the safety and reliability of the entire electrical grid. Additionally, the oil also plays a role in moisture control, as it seals the transformer’s internal components, further enhancing insulation and protecting sensitive parts from external contaminants.
3. Longer Operational Lifespan
Oil-immersed transformers are known for their long operational lifespan, especially when compared to other types of transformers, such as dry-type transformers. The presence of transformer oil not only helps with heat dissipation but also reduces the wear and tear on the internal components of the transformer.
The oil acts as a protective barrier, preventing rust and corrosion from forming on metallic components like the transformer’s windings and bushings. It also ensures that these parts remain in top condition by minimizing the risks associated with high electrical and thermal stress.
With regular oil maintenance (such as testing for moisture, dielectric strength, and acidity levels), oil-immersed transformers can last for several decades, reducing the need for frequent replacements. This durability translates into lower long-term operational costs and better return on investment (ROI) for utility companies.
4. Reliability Under Heavy Load
Oil-immersed transformers are highly reliable, even under heavy loads, making them ideal for high-voltage systems that need to transmit large amounts of power over long distances. These transformers can handle varying load conditions without compromising on performance. As electrical demand increases during peak hours or special events, oil-immersed transformers are capable of adapting to these fluctuations without overheating or experiencing failures.
The cooling mechanism ensures that the transformer remains stable under heavy electrical loads, preventing thermal overloads that could lead to equipment failure. Additionally, transformer oil absorbs thermal energy even during transient load conditions, improving the transformer’s ability to handle sudden spikes in electrical demand.
This flexibility and load resilience make oil-immersed transformers a dependable choice for high-voltage transmission systems in urban areas, industrial zones, and power plants.
5. Fault Protection and Safety
The safety of high-voltage systems is paramount, and oil-immersed transformers contribute significantly to this by providing an added layer of fault protection. In the event of an internal electrical fault, such as a short circuit, the transformer oil acts as a fire suppressant, reducing the chances of ignition or explosion.
Transformer oil’s high flash point (the temperature at which it could potentially catch fire) ensures that the oil remains stable even in high-temperature environments. Furthermore, the arc quenching properties of transformer oil help suppress the arc formation that might occur during fault conditions, preventing damage to the transformer and surrounding equipment.
Additionally, transformer oil’s low flammability is particularly advantageous in protecting against fires, making oil-immersed transformers suitable for use in areas where safety is a concern, such as industrial zones, power plants, and urban environments.
6. Minimal Maintenance and Monitoring
While oil-immersed transformers require periodic maintenance, their maintenance needs are relatively low compared to other types of transformers. Regular oil testing to monitor parameters such as dielectric strength, acidity, and moisture content is essential to maintaining optimal performance.
Advanced diagnostic technologies allow utilities to monitor the condition of transformer oil in real-time. These tools can detect changes in oil properties and identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By monitoring the transformer oil’s condition, utilities can prevent costly breakdowns, reduce downtime, and extend the transformer’s operational life.
Routine inspections and monitoring systems (such as oil-level indicators, temperature sensors, and pressure gauges) make it easy to maintain transformer efficiency and safety without requiring constant intervention. The self-sustaining nature of oil-immersed transformers makes them a practical and low-maintenance solution for high-voltage transmission applications.
7. Versatility for Different Applications
Oil-immersed transformers are highly versatile, making them suitable for a wide range of high-voltage applications. They can be used in everything from large power substations to industrial sites and renewable energy generation plants. Their ability to handle various voltage levels, from stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission to stepping down voltage for distribution networks, gives them broad adaptability in complex power systems.
Additionally, the ability to customize the transformer’s design based on application-specific needs, such as size, voltage, and cooling systems, makes oil-immersed transformers a flexible solution for high-voltage electrical networks worldwide.
How Are Oil-Immersed Transformers Maintained for Optimal Performance?
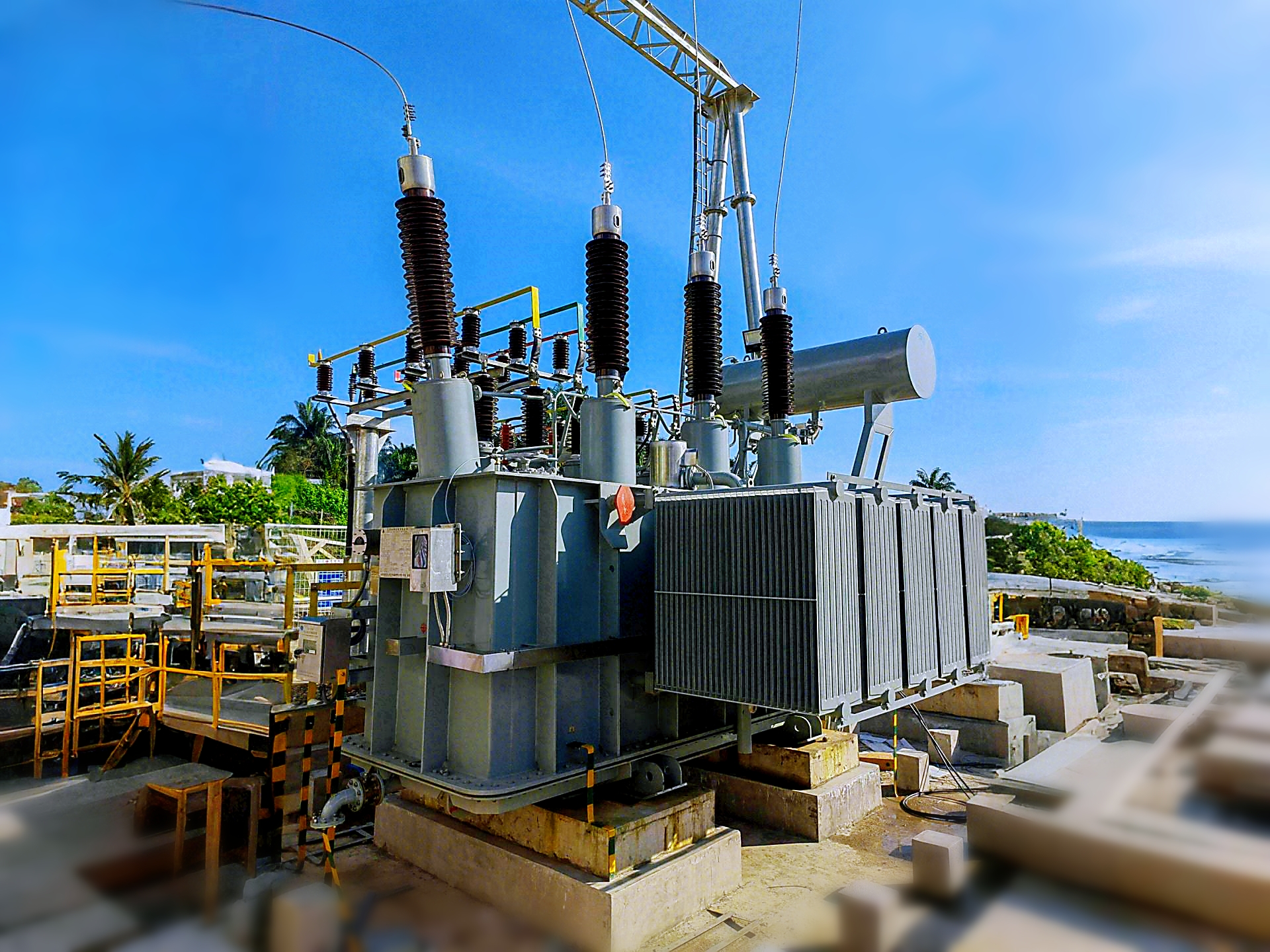

Maintaining oil-immersed transformers is essential for ensuring their long-term reliability, efficiency, and safety in high-voltage power systems. Transformer oil plays a vital role in both cooling and insulating the transformer’s components, which means that its condition is directly linked to the overall performance of the transformer. Regular maintenance ensures that the transformer continues to operate at its best, preventing costly failures, downtime, and safety hazards.
This article outlines the most important aspects of oil-immersed transformer maintenance—from monitoring oil quality to performing physical inspections and implementing proactive diagnostic measures. By understanding the key maintenance practices, operators can ensure the optimal performance and extended lifespan of their oil-immersed transformers.
Key Maintenance Practices for Oil-Immersed Transformers
1. Regular Oil Quality Monitoring and Testing
The condition of transformer oil directly impacts the performance and safety of the transformer. Regular oil testing is crucial for monitoring various characteristics that influence the effectiveness of both cooling and insulation functions.
Key parameters to monitor include:
- Dielectric Strength: This test measures the oil’s ability to resist electrical breakdown. Over time, transformer oil can degrade, lowering its dielectric strength and making it less effective at insulating electrical components.
- Moisture Content: Water is one of the most harmful contaminants for transformer oil, as it reduces dielectric strength and accelerates the aging process of both oil and transformer components. Moisture can enter through leaks, condensation, or poor seals, so it’s essential to keep track of water content.
- Acidity and Oxidation: Transformer oil becomes acidic over time due to oxidation, particularly if the transformer is exposed to high temperatures. Acidic oil can damage transformer parts and reduce efficiency. Regular testing for acidity levels ensures that the oil remains within acceptable limits.
- Contamination Levels: Physical impurities, such as dirt, dust, and metal particles, can contaminate the oil and affect its performance. Regular sampling helps identify the level of contamination and indicates when the oil needs to be replaced or filtered.
Recommended Maintenance Action: If oil testing reveals any of the following, immediate action is required:
- Low dielectric strength: Oil filtration or replacement may be necessary.
- Excessive moisture content: Use oil dehydration or vacuum methods to remove water.
- High acidity or oxidation: Perform oil regeneration or replace the oil if necessary.
2. Oil Filtering and Regeneration
Over time, the oil in the transformer becomes less effective due to the accumulation of contaminants, oxidation, and moisture. Oil filtration and regeneration are processes that help restore the oil’s insulating and cooling properties without the need for a full oil change.
- Oil filtration: This process removes physical contaminants, including dirt, dust, and metal particles, using specialized filters. Filtration is often done on-site and is useful for maintaining oil cleanliness without completely replacing the oil.
- Oil regeneration: This more extensive process involves treating the oil to remove dissolved gases and acids, essentially restoring its insulating properties. Regeneration is typically performed when oil contamination levels are high or when oxidation and acidity levels become problematic.
Regeneration techniques include the use of clay filtration, silica gel filtration, or vacuum dehydration.
Recommended Maintenance Action: If oil quality tests indicate that the oil is significantly degraded but still usable, regeneration can extend the life of the transformer. However, if the oil is severely contaminated, a full oil replacement may be required.
3. Oil Replacement
While oil filtering and regeneration are effective for minor issues, complete oil replacement may be necessary if the oil has become too contaminated, acidic, or if its dielectric strength has significantly decreased. Replacing transformer oil ensures that the transformer continues to operate efficiently and safely.
Steps for oil replacement:
- Drain the Old Oil: Carefully drain the used oil from the transformer. The oil should be stored in proper containers for disposal or recycling according to environmental regulations.
- Inspect the Transformer: Before filling the transformer with new oil, inspect the internal components to ensure there are no signs of corrosion or damage caused by degraded oil.
- Fill with New Oil: Once the transformer is inspected and cleaned, refill it with fresh, high-quality transformer oil that meets the required specifications.
- Air Removal: Use vacuum pumps or degassing equipment to remove any trapped air from the transformer’s windings and oil chamber, which can prevent optimal functioning and lead to partial discharge during operation.
Recommended Maintenance Action: Transformer oil should be replaced every 5-10 years or based on the condition of the oil as indicated by regular testing. In highly contaminated or operationally stressed environments, oil replacement might occur more frequently.
4. Regular Visual and Physical Inspections
Beyond oil maintenance, physical inspections of the transformer and its components are crucial for detecting signs of damage or wear that could impact performance. Regular visual inspections help identify:
- Oil leaks: Check for any oil leakage around seals, valves, and gaskets. Leaks can lead to oil loss, reduced cooling capacity, and potential fire hazards.
- Corrosion or rust: Inspect external parts of the transformer for signs of rust or corrosion, especially in humid or exposed environments. Corrosion can weaken the transformer’s structure and affect its efficiency.
- Overheating: Look for signs of overheating, such as discoloration, burnt areas, or melted insulation. Overheating could indicate a cooling issue or excessive load on the transformer.
- Excessive vibration or noise: Abnormal sounds or vibrations during operation can indicate internal mechanical issues, such as winding movement or loose components.
Recommended Maintenance Action: If any abnormalities are detected, take immediate action to investigate and repair the issue. Leaks should be sealed, rust removed, and damaged components replaced to prevent further damage.
5. Monitoring and Testing of Cooling and Ventilation Systems
The cooling system of oil-immersed transformers is vital for maintaining operational temperatures. Transformers often have oil pumps, radiators, and fans to ensure effective cooling. Monitoring these systems is critical for preventing overheating and ensuring the transformer’s efficiency.
- Oil pump efficiency: Ensure that the oil pumps are functioning properly to circulate the oil. Reduced circulation could lead to inadequate cooling.
- Radiator condition: Inspect the radiators for blockages, dirt, or damage. Clogged or damaged radiators can impede the cooling process, leading to higher temperatures inside the transformer.
- Airflow system: If the transformer is equipped with fans or ventilation systems, check that these components are operating as intended. Blockages or malfunctioning fans can lead to overheating.
Recommended Maintenance Action: Regularly clean radiators and ensure that oil pumps and fans are functioning at full capacity. If any cooling system components fail, they should be repaired or replaced promptly.
6. Protection and Control System Checks
Oil-immersed transformers are equipped with protective devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, and relays to prevent faults from damaging the transformer. Regularly testing and maintaining these systems ensures the transformer can handle abnormal conditions, such as short circuits or overloads, without suffering irreparable damage.
- Protective relay testing: Verify that protective relays are functioning correctly by testing their trip settings and ensuring they will activate during fault conditions.
- Circuit breaker testing: Check that circuit breakers trip appropriately in case of faults to prevent further damage to the transformer and the system.
- Temperature and pressure monitoring: Ensure that temperature sensors, pressure relief valves, and oil-level indicators are working correctly to monitor the internal conditions of the transformer.
Recommended Maintenance Action: Conduct periodic testing of all protection and control systems to ensure they are calibrated correctly and can act effectively in case of faults.
Conclusion
Oil-immersed transformers are essential components in the high-voltage power transmission system, responsible for stepping down voltage to safer levels suitable for distribution to homes, businesses, and industries. The transformer oil inside these devices plays a critical role in insulating electrical components and cooling the transformer, allowing it to operate under high loads without overheating.
By ensuring efficient voltage transformation, preventing overheating, and providing safe insulation, oil-immersed transformers contribute significantly to the reliability and safety of the power grid. The durability and long lifespan of oil-immersed transformers make them a preferred choice in high-voltage transmission applications, ensuring that electricity is reliably and safely transmitted over long distances.
Proper maintenance, including oil testing and monitoring, is vital to maintaining transformer efficiency and performance. With their ability to manage high-voltage electricity, prevent breakdowns, and optimize energy use, oil-immersed transformers are indispensable in today’s electrical power infrastructure.
FAQ
Q1: What role do oil-immersed transformers play in high-voltage power transmission?
A1: Oil-immersed transformers are essential in high-voltage power transmission as they efficiently step down high voltage to lower levels for distribution. The oil provides insulation and cooling, preventing overheating, and ensuring safe and reliable operation of transformers in high-voltage systems.
Q2: How does the oil in oil-immersed transformers help with high-voltage transmission?
A2: The oil in oil-immersed transformers serves two key functions: insulation and cooling. It prevents electrical arcing by providing high dielectric strength, and it absorbs and dissipates heat generated during operation, allowing transformers to handle high-voltage loads without overheating.
Q3: Why is oil used in transformers for high-voltage power transmission?
A3: Oil is used in high-voltage transformers because of its excellent insulating properties, which help prevent electrical short circuits and maintain the stability of the electrical system. It also aids in the cooling process, which is crucial in preventing thermal damage to transformer components during high-voltage operations.
Q4: What are the advantages of using oil-immersed transformers in high-voltage systems?
A4: Oil-immersed transformers are durable, efficient, and capable of handling the high electrical loads typically found in high-voltage power transmission systems. The oil enhances the transformer's ability to operate in extreme conditions by providing both cooling and insulation, thereby increasing the transformer's lifespan and reliability.
Q5: How do oil-immersed transformers contribute to the safety of high-voltage transmission networks?
A5: Oil-immersed transformers enhance safety by preventing electrical faults such as short circuits and by efficiently cooling the transformer components. The oil acts as a barrier to external elements that could cause sparks or overheating, while also maintaining optimal temperature levels to avoid fire hazards or transformer failure.
References
"The Role of Oil-Immersed Transformers in High-Voltage Power Systems" - https://www.powermag.com/oil-immersed-transformers-high-voltage - Power Magazine
"Oil-Immersed Transformers in Electrical Power Transmission" - https://www.transformertech.com/oil-immersed-transformers-high-voltage - Transformer Tech
"Understanding High-Voltage Power Transmission and Oil-Immersed Transformers" - https://www.electrical4u.com/oil-immersed-transformers-high-voltage - Electrical4U
"Oil-Immersed Transformers and Their Role in Power Distribution" - https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/oil-immersed-transformers - ScienceDirect
"Cooling and Insulation in High-Voltage Transformers" - https://www.researchgate.net/transformers-insulation-cooling - ResearchGate
"Why Oil is Used in High-Voltage Transformers" - https://www.smartgridnews.com/oil-transformers - Smart Grid News
"Oil-Immersed Transformers: Enhancing Safety in High-Voltage Networks" - https://www.energycentral.com/c/ee/oil-immersed-transformers - Energy Central
"Power Transmission and the Importance of Oil-Immersed Transformers" - https://www.powergrid.com/oil-immersed-transformers - PowerGrid


