Transformers are a foundational technology in the electrical power industry. While they may not be visible in our daily lives, they are critical for making sure electricity is delivered safely, efficiently, and in the right form. From stepping up voltages for transmission to stepping them down for home use, transformers serve many vital purposes that keep modern life powered and connected.
How Do Transformers Enable Efficient Long-Distance Power Transmission?
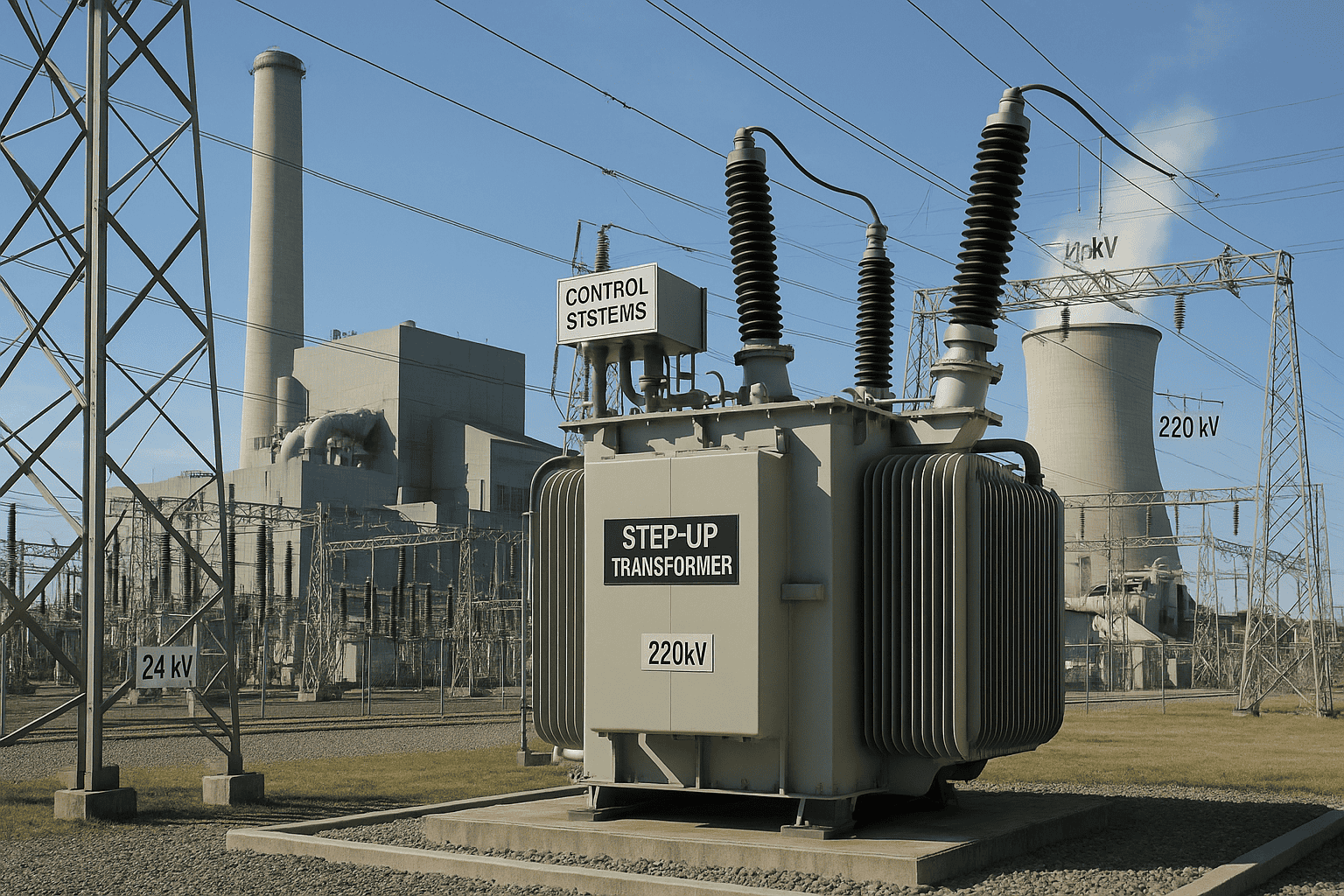
Electricity is often generated hundreds or even thousands of kilometers away from where it’s consumed. To move this power over vast distances without significant losses or infrastructure overload, the electrical grid relies on a crucial piece of technology: the transformer. Without transformers, long-distance transmission would require unfeasibly thick and expensive cables to handle high currents. Instead, transformers make high-voltage transmission possible and efficient, forming the backbone of modern power delivery systems.
Transformers enable efficient long-distance power transmission by stepping up voltage at the generation source to reduce current, minimizing I²R losses during transmission. At the receiving end, they step the voltage back down to safe, usable levels. This voltage transformation reduces energy loss, improves system efficiency, and enables electricity to travel over hundreds of kilometers with minimal infrastructure strain.
This fundamental role makes transformers the most important component in power grids beyond the generating station.
Transformers reduce power losses in long-distance transmission by stepping up voltage and reducing current.True
Higher voltage means lower current for the same power, which significantly reduces resistive (I²R) losses in transmission lines.
Long-distance power transmission is more efficient at low voltages because it reduces insulation needs.False
Low-voltage transmission would require extremely high current, resulting in massive losses and impractically large conductors.
How Transformers Enable Long-Distance Transmission Efficiency
| Process Stage | Transformer Role | Voltage Levels |
|---|---|---|
| Power Plant Output | Step-up transformer increases voltage | 11–25kV → 132–765kV |
| High-Voltage Transmission | Reduced current means lower line losses | Maintains high voltage |
| Regional Substation Entry | Step-down transformer reduces voltage | 765–132kV → 66–11kV |
| Local Distribution Feeder | Final step-down for end-user compatibility | 11kV → 400V / 230V |
This voltage transformation chain ensures energy is delivered efficiently, safely, and economically over long distances.
Why High Voltage = Lower Losses
Power Equation:
P = V × I (Power = Voltage × Current)
To transmit the same power over a line:
- If voltage is increased, current can be reduced
- Lower current → Lower resistive losses (I²R) in the line
- Smaller conductors and fewer support structures needed
| Voltage Level | Current for 100 MW Load | Relative Line Loss (I²R) |
|---|---|---|
| 11kV | 5,250 A | Very High |
| 132kV | 757 A | Much Lower |
| 400kV | 250 A | Extremely Low |
Stepping up to 400kV reduces losses by over 90% compared to transmitting at 11kV.
Types of Transformers Used in Transmission Networks
| Transformer Type | Installed At | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Step-Up Transformer | Power plant switchyards | Raise voltage for efficient transmission |
| Autotransformer | Transmission substations | Link different HV levels and support efficiency |
| Phase-Shifting Transformer | Interconnection points | Control power flow direction and magnitude |
| Step-Down Transformer | Regional grid entry points | Lower voltage for distribution or local networks |
Each of these transformer types is rated for very high voltage (up to 765kV) and power (100–500 MVA or more).
Example: Transmission System with Transformers
| System Component | Voltage Level | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Generator Output | 13.8kV | Step-up to 400kV |
| Transmission Line | 400kV over 200 km | Reduced current = low losses |
| Regional Substation | Step-down to 132kV | Interfaces with sub-transmission grid |
| Distribution Substation | Step-down to 11kV | Feeds local distribution networks |
| End-User Transformer | 11kV → 400V/230V | Final conversion for homes and small businesses |
Design Features of Long-Distance Transformers
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High Insulation Strength | Withstands extreme voltage levels (up to 765kV) |
| On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC) | Maintains output voltage during fluctuating input/load |
| Low-Loss Core Steel | Minimizes magnetization losses in continuous operation |
| Advanced Cooling Systems | Ensures thermal stability under high current loads |
| Remote Monitoring | Enables live data on voltage, temperature, oil, and load |
These transformers are designed to operate 24/7 for decades, often with digital integration into SCADA and smart grid systems.
Global Transmission Projects Using Ultra-High Voltage Transformers
| Country | Voltage Level | Project | Distance Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | ±1100kV DC | Changji-Guquan UHVDC Line | Over 3,200 km |
| India | 765kV AC | Western-Northern UHV Line | 1,000+ km |
| Brazil | ±800kV DC | Belo Monte UHVDC Link | 2,500 km |
| USA | 500kV AC | Pacific AC Intertie | 1,400 km |
These projects rely on gigantic transformers to move gigawatts of power over long distances with high reliability.
What Is the Role of Transformers in Voltage Conversion for Safe Usage?
Electricity is generated at power plants at relatively low voltages but must travel vast distances through high-voltage transmission lines. However, neither the original voltage from generation nor the transmission-level voltage is suitable for direct use in homes, offices, or sensitive equipment. This is where transformers play their most fundamental role—converting voltage levels to make power both efficient to transmit and safe to use. Without them, power would be dangerous or incompatible at the point of use, posing risks of electrocution, equipment failure, or fire.
Transformers convert electricity from high-voltage levels (used for transmission) to lower, safe voltage levels suitable for end users. They step down electricity from 132kV, 66kV, or 11kV to 400V or 230V for use in homes, commercial buildings, and industries, ensuring that voltage is appropriate for appliances and systems without posing safety risks.
Transformers allow the same power source to be safely shared across sectors with very different voltage needs.
Transformers convert high-voltage electricity to safe, usable voltage levels for homes and businesses.True
By stepping down transmission voltages to levels like 230V, transformers protect people and equipment from overvoltage dangers.
End users can safely receive electricity directly from transmission lines without transformers.False
Transmission voltage is too high for direct use and would damage appliances or pose electrocution hazards. Transformers reduce voltage to safe levels.
How Transformers Perform Safe Voltage Conversion
| Stage | Voltage Input | Voltage Output | Transformer Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation Site Output | 11–25kV | 132–400kV | Generator Step-Up Transformer | Enables efficient long-distance transmission |
| Transmission Substation | 400kV | 132kV / 220kV | Interconnection Transformer | Connects regions and balances loads |
| Regional Distribution Substation | 132kV / 66kV | 33kV / 11kV | Step-Down Transformer | Prepares for localized distribution |
| Local Distribution Transformer | 11kV | 400V / 230V | Pole/Pad-Mounted Transformer | Final conversion for safe residential/commercial use |
At each level, transformers are configured to match the voltage requirements of the next grid segment or end-use environment.
Why Voltage Conversion Is Necessary
1. Safety
- High voltage poses shock, burn, and fire hazards
- Transformers reduce voltage to 230V or 400V, which is safe for humans and compatible with standard wiring insulation
2. Equipment Compatibility
- Home and office appliances are designed for specific voltage ranges
- Sudden overvoltage can instantly damage sensitive devices
3. Efficiency
- High voltages minimize current (I), reducing I²R losses in long cables
- At the point of use, lower voltage ensures system optimization and avoids overload
4. Grid Flexibility
- Different voltage levels are needed for lighting, motors, servers, HVAC, etc.
- Transformers create modular, scalable systems where each load is matched to its ideal voltage
Real-World Voltage Conversion Examples
| Environment | Input Voltage | Output Voltage | Transformer Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential Home | 11kV | 230V | Pole-mounted transformer |
| Commercial Office | 33kV or 11kV | 400V / 230V | Indoor dry-type transformer |
| Industrial Workshop | 11kV | 690V / 400V | Oil-immersed transformer with OLTC |
| Hospital Operating Room | 400V | 230V (isolated) | Isolation transformer |
| Solar Farm Output | 400V AC | 11kV | Step-up pad transformer at inverter |
The final step-down is the most critical from a human safety and equipment performance standpoint.
Transformer Features for Voltage Control and Safety
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC) | Maintains output voltage under load variation |
| Grounding and Shielding | Prevents electrical shocks and EMI interference |
| Thermal Protection Relays | Prevents overheating during voltage imbalances |
| Surge Arresters | Absorbs lightning and switching surges |
| Voltage Ratio Testing | Ensures accurate voltage conversion performance |
These features ensure that voltage conversion is not just functional—but safe, stable, and fault-tolerant.
Common Voltage Levels in Use
| Application | Voltage Level | Typical Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Network | 220kV – 400kV | Step-up/Step-down at substations |
| Urban Grid Feeders | 33kV or 11kV | Distributed via ring main units |
| Household Power | 230V (single-phase) | Final conversion by distribution transformer |
| Industrial Motors | 400V – 690V | Transformer-fed MCC or VFD system |
Why Are Transformers Important for Industrial and Commercial Power Needs?

Powering commercial buildings and industrial facilities requires far more than simply connecting to the grid. These environments host complex equipment, varying voltage requirements, sensitive electronics, and round-the-clock operations. Electricity must be delivered at the correct voltage, with stable frequency, and uncompromised quality to keep businesses running efficiently and safely. Transformers are the indispensable link that makes this possible. They adapt voltage levels, isolate critical systems, and support high power demands in a flexible and scalable way. This article explains why transformers are essential for industrial and commercial power needs and how they support modern infrastructure.
Transformers are essential in industrial and commercial power systems because they step down high-voltage electricity from the grid to usable levels (typically 400V or 230V), distribute power to various systems, isolate sensitive equipment, and ensure voltage stability and safety. They allow facilities to operate machinery, lighting, HVAC, IT equipment, and control systems efficiently and reliably.
Without transformers, the high-voltage utility supply would be unsafe and incompatible with commercial and industrial equipment.
Transformers step down and distribute electricity in commercial and industrial environments to meet diverse load requirements safely.True
They enable power adaptation for machinery, lighting, HVAC, data centers, and other critical systems, while isolating and protecting sensitive equipment.
Industrial and commercial facilities can use electricity directly from medium-voltage grid lines without any transformers.False
Grid voltage levels (typically 11kV or higher) are far too high for direct use in commercial equipment and require conversion via transformers.
Where Transformers Are Used in Industrial and Commercial Settings
| Location | Transformer Role | Voltage Conversion |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Main Power Room | Step-down from 33kV or 11kV to 400V | 33/11kV → 400V / 230V |
| Shopping Mall or Hotel | Distributes power to HVAC, lighting, and stores | 11kV → 400V |
| Data Center Power Block | Provides clean, isolated power for servers and UPS | 11kV → 400V, with K-rated isolation |
| High-Rise Office Building | Floor-by-floor power distribution | 11kV → 400V per zone |
| Control Systems and Panels | Supplies 230V, 110V, or 24V for electronics | 400V → lower voltages via control transformers |
Transformers are strategically deployed to optimize power delivery based on load type, voltage requirement, and safety class.
Key Roles of Transformers in Commercial and Industrial Power
1. Voltage Conversion
- Step down utility supply from 11kV/33kV to 400V or 230V
- Adapt power for motors, compressors, lighting, computers, and automation
2. System Isolation and Safety
- Separate sensitive loads (e.g., IT systems, medical devices) from electrical noise
- Prevent faults from propagating across systems
3. Load Distribution
- Enable zonal or department-level power management
- Support multi-tenant buildings with load metering and segmentation
4. Power Quality Stabilization
- Minimize voltage drops, harmonic distortion, and transient surges
- Improve power factor and reduce equipment wear
Types of Transformers in Use
| Transformer Type | Typical Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Oil-Immersed Transformer | Outdoor or high-power industrial plants | High capacity, thermal stability, long lifespan |
| Dry-Type Transformer | Indoor installations (offices, hospitals, malls) | Safe, compact, low maintenance |
| K-Rated Transformer | Data centers, UPS loads | Handles non-linear loads with harmonics |
| Isolation Transformer | Laboratories, telecom, medical systems | Protects against noise and ground loops |
| Auto Transformer | Motor startup, HVAC compressors | Efficient and cost-effective for voltage shifts |
Transformers are selected based on load type, environment (indoor/outdoor), harmonic levels, and fire safety regulations.
Example: Power Distribution in an Industrial Facility
| Power Stage | Component | Voltage | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid Entry | Step-down transformer | 11kV → 400V | Supplies main plant load |
| MCC (Motor Control Center) | Auto transformer or OLTC unit | 400V | Feeds variable-speed drives and pumps |
| Automation and Controls | Isolation transformer | 230V or 110V | Protects PLCs, sensors, and control systems |
| Office Block | Dry-type transformer | 400V → 230V | Serves lights, PCs, HVAC |
| Backup Generator Integration | Matching transformer | 400V ↔ 400V | Synchronizes with existing transformer output |
The entire system is orchestrated around transformer-based voltage layers, each serving a unique role in load compatibility and protection.
Transformer Design Features for Commercial/Industrial Use
| Feature | Function |
|---|---|
| On-Load Tap Changer (OLTC) | Maintains voltage under changing load conditions |
| Temperature & Oil Monitoring | Prevents overheating and supports predictive maintenance |
| Harmonic Tolerance | Avoids overheating in non-linear loads (e.g., drives, UPS) |
| Fire-Retardant Insulation | Meets safety codes for indoor installations |
| Low Impedance Configuration | Reduces voltage drop during peak load switching |
These features ensure transformers support uninterrupted and safe operations, even in power-intensive environments.
Commercial and Industrial Load Examples
| Load Type | Voltage Requirement | Transformer Role |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC Systems | 400V | Feeds motors, chillers, AHUs |
| CNC Machines and Drives | 400V / 690V | Power distribution and surge filtering |
| LED Lighting and Signage | 230V | Stable, flicker-free power supply |
| Data Servers and Networks | 230V (via UPS) | Isolation and voltage stability |
| Lifts and Escalators | 400V | Supplies high starting current loads |
How Do Transformers Contribute to Power Reliability and Stability?
In every part of the electrical grid—from generation to consumption—transformers are not just voltage conversion devices, they are critical for system reliability, safety, and voltage stability. In fact, without transformers, the power grid would not be able to deliver continuous, balanced, and disturbance-free electricity. They support voltage regulation, isolate faults, manage load flows, and prevent cascading failures, playing a central role in making sure your power stays on, safe, and stable. This article explores how transformers contribute to power reliability and stability, and why they’re indispensable in any modern energy system.
Transformers contribute to power reliability and stability by regulating voltage levels, balancing loads, isolating faults, minimizing losses, supporting grid interconnectivity, and enabling dynamic response to fluctuations in demand or supply. Their presence ensures consistent voltage quality, system protection, and uninterrupted operation under both normal and emergency conditions.
From generation step-up to final distribution, transformers are the foundation of the grid’s resilience.
Transformers help stabilize and protect the power system by regulating voltage and isolating faults.True
Transformers maintain voltage levels across grid tiers, prevent fault propagation, and ensure load balance, contributing to grid reliability.
Transformers only convert voltage and do not impact power system stability.False
In addition to voltage conversion, transformers regulate voltage, isolate disturbances, and enable reliable, continuous power flow.
Key Ways Transformers Enhance Power Reliability and Stability
| Function | Contribution to Grid Reliability and Stability |
|---|---|
| Voltage Regulation | Ensures all grid nodes receive appropriate and stable voltage |
| Load Balancing | Distributes demand evenly to avoid overloading and ensure power quality |
| Fault Isolation | Prevents faults from affecting upstream or downstream systems |
| Reactive Power Management | Maintains voltage levels and supports inductive or capacitive load needs |
| Redundancy and Backup Power | Allows critical loads to remain powered via dual-fed transformer setups |
| Grid Synchronization | Supports interconnection between regional or national grids |
Each of these roles contributes to reducing outages, limiting system stress, and improving overall grid performance.
Transformer Features That Support Reliability
| Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| OLTC (On-Load Tap Changer) | Adjusts voltage output under live load conditions for stable voltage delivery |
| Dual Winding / Auto Transformers | Enables inter-voltage transfer between grids |
| Fault Detection Relays | Detects insulation breakdown or thermal overloads |
| Surge Arresters | Absorbs voltage spikes from lightning or switching transients |
| Grounding & Neutral Systems | Prevents shock risk and enables safe fault currents |
| SCADA/IoT Integration | Enables real-time voltage, temperature, and fault monitoring |
These features make transformers intelligent power quality guardians, not just passive components.
Power System Stability Functions Supported by Transformers
1. Voltage Stability
- Maintains voltage under varying load conditions
- Compensates for distance-related voltage drops
- Prevents undervoltage or overvoltage that may cause blackouts
2. Frequency Stability (Indirect)
- Supports synchronized power exchange between different frequency zones (via interties)
- Balances load and generation, reducing stress on frequency-sensitive equipment
3. Fault Management and Protection
- Limits the spread of short circuits or ground faults
- Works with circuit breakers and relays for sectionalizing the faulted area
- Enables fast reclosure and recovery
4. Redundancy for Critical Systems
- Dual transformer configurations provide continuous supply during maintenance or failure
- Ensures hospitals, data centers, and factories remain operational during disturbances
Example: Grid Transformer Configurations for Stability
| Transformer Placement | Function | Reliability Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| GSU at Generation Plant | Steps up 11–25kV to 132–400kV | Enables efficient high-voltage transmission |
| Transmission Intertie | 400kV ↔ 220kV Interconnecting Transformer | Balances regional power flows and stabilizes voltage |
| Urban Distribution Substation | 33kV ↔ 11kV Step-Down Transformer | Ensures stable delivery to city infrastructure |
| Industrial Dual Feed Setup | 11kV → 400V Redundant Transformer with A/B Switching | Maintains uptime for production lines or data centers |
Grid Failure Case Without Transformer Protection
| Scenario | With Transformer | Without Transformer |
|---|---|---|
| Lightning Strike on Feeder | Surge absorbed by transformer arrester | Voltage spike travels to multiple users |
| Substation Equipment Failure | Fault isolated to affected area | Entire feeder or region could lose power |
| Load Spike in City Block | Tap changer adjusts to maintain voltage | Local undervoltage causes flickering or shutdowns |
| Fault in Manufacturing Plant | Isolation prevents backfeeding into grid | Risk of grid instability and prolonged outage |
Transformers act as firewalls and regulators throughout the power system.
Compliance and Design Standards for Stability
| Standard | Purpose in Power Stability |
|---|---|
| IEC 60076 | Design and performance of power transformers |
| IEEE C57 | Operation and testing of distribution and power transformers |
| IEEE 1159 | Power quality and monitoring for disturbances |
| ISO 9001 | Quality assurance in transformer manufacturing |
| ANSI/IEEE 519 | Harmonic control, ensuring transformers handle distorted loads |
What Role Do Transformers Play in Renewable Energy Integration?

Renewable energy sources like solar and wind are revolutionizing how we generate electricity, but they also pose unique challenges to power system integration. These sources produce energy at low voltages and fluctuate based on weather and time. For their power to be effectively transmitted, stabilized, and used across the grid, transformers are indispensable. They are the critical link that allows variable, decentralized renewable energy to become a reliable, grid-compatible power supply. This article explains the essential role transformers play in renewable energy integration, enabling clean energy to power modern society.
Transformers play a crucial role in renewable energy integration by stepping up the low-voltage output of solar and wind systems to medium or high voltages, enabling efficient transmission to the grid. They also provide electrical isolation, manage voltage fluctuations, support reactive power control, and ensure safe, stable connection between renewable sources and utility networks.
Without transformers, renewable power would remain isolated and unusable at large scale.
Transformers allow solar and wind energy to be stepped up and connected safely to the power grid.True
Solar panels and wind turbines produce low-voltage electricity that must be increased using transformers to match grid transmission levels.
Renewable energy systems can be connected directly to the transmission grid without voltage conversion.False
Voltage must be stepped up using transformers to match the grid’s operational voltage levels and ensure safe, efficient integration.
Key Functions of Transformers in Renewable Energy Systems
| Function | Purpose in Integration |
|---|---|
| Voltage Step-Up | Converts 400–690V from inverters/turbines to 11–33kV or higher |
| Grid Matching | Aligns voltage and phase with utility standards |
| Aggregation at Substations | Combines multiple feeders for efficient grid feed-in |
| Reactive Power Support | Manages voltage regulation across variable generation |
| Electrical Isolation | Prevents fault backfeed and isolates renewables from the grid |
| Bidirectional Flow Capability | Enables both injection and withdrawal of energy in smart grids |
These functions make transformers indispensable in both centralized and distributed renewable architectures.
Transformer Use in Solar Energy Systems
| Stage | Voltage Conversion | Transformer Type | Typical Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| PV Inverter Output | 400–690V AC | Inverter step-up transformer | 250kVA–2.5MVA |
| Collector Feeder | 11–33kV | Ring main-connected transformer | 2.5–10MVA |
| Solar Farm Substation | 33kV → 132/220kV | Power transformer | 10–100MVA |
Step-up transformers are usually pad-mounted or skid-based for fast deployment and compact footprint in solar PV sites.
Transformer Use in Wind Energy Systems
| Stage | Voltage Conversion | Transformer Type | Typical Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Turbine Generator | 690V → 11kV or 33kV | Tower base or nacelle transformer | Inside or near turbine base |
| Wind Collector Line | 33kV | Pad-mounted or GIS transformer | Along collection path |
| Wind Farm Substation | 33kV → 132/220/400kV | Large oil-immersed transformer | Centralized substation |
Wind systems often use autotransformers and compact dry-types in remote or offshore environments to reduce weight and space.
Integration into the Utility Grid
| Interface Location | Transformer Function | Voltage Level |
|---|---|---|
| Grid-Tie Substation | Final step-up to match transmission grid voltage | 132kV, 220kV, 400kV |
| Battery Storage System (BESS) | Bidirectional isolation and voltage adjustment | 11kV ↔ 400V or 33kV |
| Hybrid Microgrid Interface | Match between renewable AC and diesel or grid systems | 400V ↔ 400V |
Transformers enable flexibility in mixed generation environments, allowing renewables to coexist with traditional sources.
Design Considerations for Renewable Transformers
| Requirement | Design Response |
|---|---|
| High Ambient Temperatures | Natural/forced air cooling, robust thermal insulation |
| Harmonic Load from Inverters | K-rated or low-loss core materials for harmonic handling |
| Outdoor/Offshore Conditions | Corrosion-resistant enclosures, sealed oil tanks |
| Fast Voltage Changes | On-load tap changers or dynamic voltage regulation |
| Smart Grid Readiness | SCADA/IoT-enabled sensors and monitoring |
These ensure transformers remain stable, durable, and efficient even in harsh and dynamic renewable environments.
Real-World Example: 100MW Wind Project Integration
| Component | Voltage | Transformer Used |
|---|---|---|
| Turbine Output | 690V | Compact dry-type transformer |
| Collector Feeder | 33kV | Oil-immersed pad transformer |
| Project Substation | 33kV → 220kV | Power transformer (OLTC-equipped) |
| Utility Transmission Grid | 220kV | Synchronization with national grid |
This configuration enables the plant to deliver stable, grid-compliant renewable energy over long distances.
How Do Transformers Improve Safety in Sensitive Environments Like Hospitals and Data Centers?

Hospitals and data centers are mission-critical facilities where power failure or electrical faults can result in life-threatening consequences or catastrophic data loss. Sensitive medical equipment, patient monitoring systems, surgical tools, servers, and IT infrastructure all demand clean, continuous, and safe electricity. In these environments, transformers are not optional—they are essential. Their role goes far beyond voltage conversion; they ensure electrical isolation, surge protection, fault containment, and safe grounding, making them the cornerstone of power safety in critical environments.
Transformers improve safety in sensitive environments like hospitals and data centers by providing electrical isolation, stabilizing voltage, protecting against electrical faults, filtering harmonics, and ensuring compatibility with backup systems. They shield vital equipment from disturbances, prevent electrical shocks, and reduce fire hazards, all while enabling uninterrupted and secure operation.
These specially designed transformers meet the highest standards in power protection, medical safety, and IT infrastructure reliability.
Transformers provide isolation and surge protection in sensitive environments to ensure operational and patient safety.True
In hospitals and data centers, transformers isolate power sources, filter disturbances, and protect equipment from electrical faults and voltage spikes.
Power in hospitals and data centers can be supplied directly from the grid without transformers.False
Direct grid power is unregulated and may carry voltage disturbances, harmonics, or faults that can compromise safety-critical systems without transformer isolation.
Primary Safety Functions of Transformers in Hospitals and Data Centers
| Safety Function | Transformer Contribution |
|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Separates critical equipment from the main power source to prevent shock, EMI, or feedback |
| Voltage Stabilization | Maintains safe operating voltage for medical devices and servers |
| Ground Fault Protection | Limits fault current and prevents unsafe grounding conditions |
| Surge and Transient Filtering | Absorbs spikes from lightning, switching, or grid instability |
| Load Segmentation | Allows selective shutdown or maintenance without disrupting full system |
These transformers are engineered with patient and data safety as the primary objective, meeting IEC and IEEE medical/IT standards.
Use of Isolation Transformers in Hospitals
| Hospital Zone | Transformer Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Theaters | Medical-grade isolation transformer | Prevents ground faults and limits leakage currents |
| Intensive Care Units (ICUs) | Low-leakage, isolated transformers | Continuous clean power for life-support equipment |
| Diagnostic Imaging (MRI/CT) | Shielded transformer | Prevents EMI from affecting imaging resolution |
| General Ward/Lighting Panels | Standard dry-type transformer | Voltage conversion and general safety |
Isolation transformers must comply with IEC 60364-7-710 for medical systems and include insulation monitoring devices.
Use of K-Rated and Shielded Transformers in Data Centers
| Data Center Function | Transformer Feature | Safety Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Server Rack Power | K-rated transformer (K-13 or K-20) | Handles harmonics without overheating |
| UPS System Interface | Isolation transformer with bypass option | Allows safe transition during UPS switchovers |
| Network Operation Center | Shielded transformer | Blocks electromagnetic interference from affecting data flows |
| Generator Backup Transfer | Matching transformer | Smooth integration of emergency power |
Tier III and Tier IV data centers often use redundant transformer systems (2N architecture) for zero-failure tolerance.
Key Safety Features in Transformers for Sensitive Sites
| Feature | Function in Safety Context |
|---|---|
| Electrostatic Shielding | Prevents noise and EMI from entering sensitive circuits |
| Fire-Retardant Dry-Type Insulation | Reduces fire risks in enclosed indoor spaces |
| Low Impedance Windings | Maintains voltage stability and protects connected loads |
| Monitoring & Alarm Systems | Tracks transformer temperature, fault currents, and insulation status |
| Double Insulation and Isolation | Prevents accidental contact voltage and leakage |
In hospitals, transformers often support medical IT power systems that detect insulation faults in real-time.
Compliance and Safety Standards
| Standard / Regulation | Applies To | Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| IEC 60364-7-710 | Medical Facilities | Requires isolated power supply in group 2 medical locations |
| NFPA 99 / NEC 517 | Hospital Electrical Systems | Calls for isolated grounding and transformer redundancy |
| TIA-942 | Data Centers | Specifies transformer design for reliability and EMI immunity |
| ISO 13485 / IEC 60601 | Medical Devices | Demands clean, stable, non-fluctuating power input |
| IEEE C57.110 | K-Rated Transformers | Classifies performance under non-linear harmonic loads |
Practical Example: Redundant Power System in a Hospital
| Power Stage | Voltage Level | Transformer Type | Safety Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Utility Feed | 11kV | Step-down oil-immersed | Converts grid power to usable levels (400V) |
| OR & ICU Supply | 400V → 230V | Isolation transformer | Provides shock-free, fault-isolated power |
| UPS for Life-Support Systems | 400V ↔ 400V | K-rated dry-type transformer | Filters harmonics and integrates UPS safely |
| Emergency Generator Interface | 400V | Matching dry-type transformer | Maintains continuity during power outage |
Conclusion
Transformers are good for far more than just adjusting voltage—they make efficient, stable, and safe electricity possible at every scale. Whether powering a city, running a factory, or supporting the grid integration of wind and solar energy, transformers are essential for maintaining the integrity and flexibility of the electrical system. Their quiet, dependable function is what keeps our modern world energized.
FAQ
Q1: What are transformers good for?
A1: Transformers are good for:
Changing voltage levels (stepping up or down)
Efficient power transmission over long distances
Safe power distribution to homes and businesses
Isolating circuits to enhance safety
Powering devices that require specific voltage levels
They are essential for a stable and reliable electrical system.
Q2: How do transformers improve energy efficiency?
A2: By increasing voltage and reducing current during transmission, transformers help minimize energy losses in the form of heat, making long-distance electricity delivery more efficient and cost-effective.
Q3: Are transformers important for electrical safety?
A3: Yes. Transformers provide:
Electrical isolation to prevent shock and equipment damage
Surge protection through dedicated isolation units
Stable voltage supply that protects sensitive devices
Q4: What are transformers used for in everyday life?
A4: Everyday applications include:
Powering home electronics and appliances
Providing electricity to residential areas via utility distribution transformers
Operating machinery in factories
Supporting medical devices, telecom systems, and charging stations
Q5: Why are transformers essential to the power grid?
A5: Transformers are critical to the power grid because they:
Allow voltage adjustment for safe and efficient delivery
Connect different parts of the grid (generation, transmission, distribution)
Enable the integration of renewables and smart grid technologies
References
"Benefits and Uses of Transformers" – https://www.transformertech.com/transformer-benefits
"Why Transformers Are Good for Power Systems" – https://www.powermag.com/transformer-role-electricity
"Understanding the Advantages of Transformers" – https://www.electrical4u.com/transformer-benefits-uses
"Transformers in Modern Energy Infrastructure" – https://www.energycentral.com/c/ee/transformer-importance
"Smart Grid Applications of Transformers" – https://www.smartgridnews.com/transformer-uses
"ScienceDirect: Why Transformers Matter" – https://www.sciencedirect.com/transformer-utility-analysis
"ResearchGate: Transformer Advantages in Industry" – https://www.researchgate.net/transformer-application-study
"PowerGrid: What Makes Transformers Indispensable" – https://www.powergrid.com/transformer-essential-functions


