Dry-type transformers are increasingly gaining traction as the power sector evolves toward safer, greener, and more flexible infrastructure. With rising demand from commercial buildings, data centers, renewable energy installations, and microgrids, manufacturers are innovating in materials, design, and digital integration. Meanwhile, regulatory pressures and sustainability goals are driving development of high-efficiency, compact, and transformer systems with longer lifespans. This article explores the latest technological advancements and market trends shaping dry-type transformer adoption worldwide.
How Are High-Efficiency Core Materials Changing Dry-Type Transformer Design?

In commercial complexes, energy-intensive facilities, data centers, renewable energy projects, and other continuous-operation environments, users face a growing challenge: traditional dry-type transformers often struggle with high no-load losses, elevated temperature rise, hot-spot concentration, increased noise, and shortened insulation life—especially under harmonic-rich, high-frequency, or heavy-load conditions. With global energy-efficiency requirements becoming increasingly strict, transformers must evolve to deliver higher performance and lower operating costs. This shift has made high-efficiency magnetic core materials, including amorphous alloys, nanocrystalline materials, and advanced oriented silicon steel, a pivotal force reshaping dry-type transformer design.
These advanced core materials significantly reduce magnetic losses, lower temperature rise, improve noise performance, and enhance stability under harmonic stress—ultimately driving dry-type transformers toward higher efficiency, longer service life, and better long-term economy.
Amorphous metal cores significantly reduce no-load losses compared to traditional silicon steel cores.True
The disordered atomic structure of amorphous alloys enables easier magnetic reversal, reducing hysteresis losses by 60–70% compared to CRGO.
High-efficiency core materials do not influence thermal performance.False
Reduced losses directly translate to lower heat generation, which lowers temperature rise and extends insulation life.
Evolution of Core Materials: From Traditional Silicon Steel to Advanced Magnetic Alloys
For decades, cold-rolled grain-oriented silicon steel (CRGO) dominated transformer manufacturing. However, as energy-efficiency regulations tighten and continuous-operation loads increase, CRGO is reaching its performance limits. Higher losses, elevated temperatures, and increased noise make it less suitable for today’s demanding applications.
In response, new materials are transforming the industry:
Main Types of High-Efficiency Core Materials
Amorphous Metal
• Ultra-low hysteresis loss
• Thin ribbon structure minimizes eddy currents
• Very low magnetostriction, providing quieter operationNanocrystalline Alloy
• Very high permeability
• Higher saturation flux density
• Ideal for harmonic-rich or inverter-based systemsAdvanced Oriented Silicon Steel (Hi-B, Super-Oriented)
• Laser-scribed domain refinement
• Lower losses compared to standard CRGO
• Excellent cost-to-performance ratio
Material Performance Comparison
| Core Material | No-Load Loss Level | Cost Level | Typical Applications | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard CRGO | Medium | Low | General distribution | Lowest cost |
| Hi-B Silicon Steel | Low | Medium | Commercial buildings, industrial loads | Higher efficiency |
| Amorphous Alloy | Very low | Medium-High | Renewable energy, 24/7 loads | 60–70% lower losses |
| Nanocrystalline | Ultra-low | High | UPS, data centers, VFD systems | High permeability + low loss |
Reducing Losses and Enhancing Performance: The Core Role of High-Efficiency Materials
Significant Reduction in No-Load Loss
No-load loss represents the largest component of lifetime transformer operating cost.
High-efficiency materials reduce hysteresis and eddy-current losses, enabling major energy savings for continuously operating sites.
Lower Temperature Rise and Extended Service Life
Lower losses generate less heat, producing multiple benefits:
- 10–20°C temperature reduction
- 2–3× extension in insulation life
- Reduced thermal stress on windings and resin
- Less need for auxiliary cooling systems
Temperature Rise Comparison
| Core Material | Temperature Improvement | Insulation Life Impact |
|---|---|---|
| CRGO | Baseline | Standard lifespan |
| Amorphous Alloy | ↓10–15°C | Up to 2× lifespan |
| Nanocrystalline | ↓15–20°C | Up to 3× lifespan |
Design Innovations: More Compact, Quieter, and More Stable Transformers
Smaller Core Cross-Section
Higher permeability allows for maintaining magnetic flux with a smaller core.
Benefits include:
- Reduced size
- Lower weight
- More optimized frame design
Improved Partial Discharge Performance
Lower temperature and more uniform magnetic fields help prevent local electric-field concentration, enhancing insulation stability.
Lower Noise Levels
Amorphous metal exhibits very low magnetostriction, significantly reducing noise in environments such as:
- Hospitals
- Office buildings
- Retail spaces
Superior Harmonic Handling
Nanocrystalline materials excel in power-electronics environments:
- UPS systems
- Data centers
- Variable-frequency drives
- Solar inverter applications
Regulatory Pressure: High-Efficiency Cores Becoming the Industry Standard
Global policies favor high-efficiency transformer designs:
- IEC 60076-20
- EU EcoDesign Tier 2
- U.S. DOE 2016 & 2023 standards
- National MEPS requirements
High-efficiency core materials are now the easiest and most economical way to meet compliance.
They also support:
- LEED certification
- BREEAM compliance
- ESG energy-saving goals
Real-World Case Studies: Proven Performance Gains
1. Commercial Complex (1500 kVA)
- Old CRGO transformer: 3.8 kW no-load loss
- New amorphous-core transformer: 1.4 kW
- Annual energy savings: ~21,000 kWh
2. Data Center (2500 kVA)
- Nanocrystalline core reduced harmonic-induced heat by 18%
- Lower thermal burden on cooling systems
3. Wind Farm Dry-Type Step-Up Transformer
- 60% lower no-load losses
- Smaller enclosure possible due to reduced heat
What Role Does Smart Monitoring and IoT Play in Dry-Type Transformer Technology?
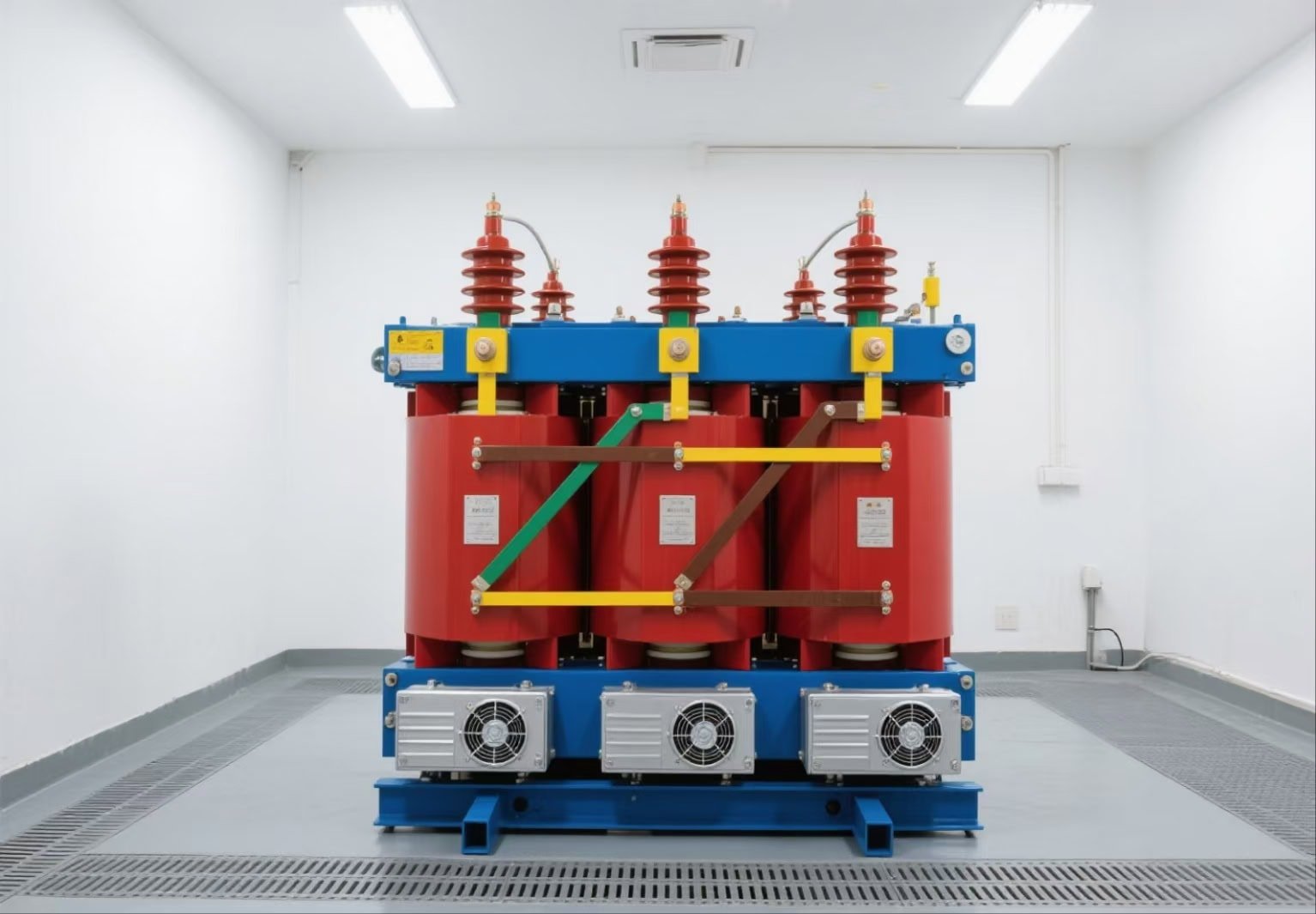
In the modern industrial era, power systems are expected to support higher load density, operate with improved efficiency, and maintain resilient performance in environments where reliability cannot be compromised. However, many facility owners, EPC contractors, and engineers still struggle with a critical pain point: traditional dry-type transformers operate as “blind machines,” providing no visibility into internal temperature, insulation condition, hotspot development, partial discharge activity, or harmonic stress—until a failure occurs. This blind operation model often leads to unexpected shutdowns, accelerated insulation aging, cumulative thermal degradation, and costly unplanned maintenance. These issues escalate rapidly in mission-critical environments such as data centers, hospitals, semiconductor production lines, wind farms, and high-rise commercial buildings. As energy demands intensify and electrical systems become more complex, the inability to detect early warning signs becomes a severe operational risk. Fortunately, smart monitoring systems and IoT-enabled technologies offer a transformative solution, allowing dry-type transformers to evolve from passive devices into predictive, self-reporting, and self-optimizing assets. The result is higher uptime, extended service life, reduced maintenance costs, and unprecedented operational intelligence—making smart monitoring no longer optional but essential for modern power infrastructure.
Smart monitoring and IoT technologies enable dry-type transformers to continuously measure critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, partial discharge, harmonic distortion, insulation condition, and load behavior. These real-time data streams are transmitted to cloud platforms or SCADA systems for predictive analytics, allowing engineers to detect faults early, optimize loading, prevent overheating, reduce energy loss, and extend transformer lifespan. By shifting maintenance from reactive to predictive, IoT transforms the transformer from a passive component to an intelligent asset that enhances reliability, safety, and lifecycle management.
Modern dry-type transformers are no longer simple static devices; they are evolving into smart, connected components of a digital power ecosystem. To fully understand the scope of this transformation and the value it delivers, it is important to explore how IoT, digital monitoring, data analytics, and automation integrate directly into transformer design, operation, and long-term technical performance. The following sections will examine how these technologies increase safety, reduce costs, improve energy efficiency, extend equipment longevity, and enable real-time, data-driven decision-making for critical electrical infrastructure.
Smart monitoring significantly improves the reliability of dry-type transformers.True
Real-time monitoring of temperature, partial discharge, and harmonic stress enables predictive maintenance, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
IoT-enabled transformers eliminate the need for regular maintenance.False
Although IoT reduces maintenance frequency and enhances predictability, periodic inspections and physical component assessments are still essential.
Digital Transformation of Dry-Type Transformers Through Smart Monitoring and IoT
The electrification of industries, the rise of automation, and the rapid expansion of renewable energy have created an unprecedented demand for transformers that can operate reliably under fluctuating conditions. Traditional dry-type transformers rely on periodic inspections and manual readings, creating blind spots in performance evaluation. Smart monitoring systems, however, integrate sensors, communication modules, cloud platforms, and analytics tools directly into transformer infrastructure, enabling continuous visibility. These systems measure core temperature, winding hotspots, environmental humidity, partial discharge intensity, overload duration, and harmonic content. With IoT connectivity, this data is processed through machine learning algorithms to predict failures, optimize load distribution, and ensure compliance with efficiency standards. As dry-type transformers become part of an interconnected grid, they support automated load response, remote health diagnostics, and grid-wide fault coordination—capabilities that would have been unimaginable just a decade ago.
Key Parameters Monitored by IoT-Enabled Dry-Type Transformers
Real-Time Data Categories and Their Importance
Smart monitoring systems typically track a wide range of operational variables, each of which reveals specific aspects of transformer health. These include:
- Winding temperature
- Core temperature and hotspot behavior
- Ambient humidity and moisture trends
- Partial discharge activity
- Load cycles and load imbalance
- Harmonic distortion levels
- Cooling efficiency (airflow, thermal response)
- Insulation condition indicators
- Energy efficiency and loss patterns
- Mechanical vibrations and structural stability
Together, these interdependent parameters provide a holistic view of real-time transformer health.
Table 1: Common IoT Monitoring Sensors and Their Functions
| Sensor Type | Measured Parameter | Purpose | Benefit to Transformer Operation |
|---|---|---|---|
| RTD / Fiber-Optic Sensors | Winding & hotspot temperature | Detect overheating | Prevent thermal aging and insulation failure |
| Humidity Sensors | Ambient & enclosure moisture | Identify condensation risk | Prevent insulation breakdown and PD |
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Partial discharge | Detect electrical degradation | Predict insulation end-of-life |
| Vibration Sensors | Mechanical oscillation | Identify structural stress | Prevent core and winding deformation |
| Current & Voltage Sensors | Load behavior | Optimize loading | Prevent overload and hot spots |
| Harmonic Analyzers | THD, waveform distortion | Detect power-quality issues | Reduce heat and dielectric stress |
How Smart Monitoring Enhances Thermal Management and Extends Insulation Life
Thermal stress is one of the most significant causes of insulation degradation in dry-type transformers. When winding temperatures exceed threshold values, resin polymer chains begin to decompose, leading to microcracks, reduced dielectric strength, and potential partial discharge activity. Smart temperature monitoring reduces these risks by tracking hotspots with high accuracy. Fiber-optic sensors embedded directly in windings enable real-time hotspot detection, ensuring that operators are alerted long before thermal runaway occurs. When combined with IoT analytics, the system can identify abnormal heating patterns, such as asymmetrical phase loading, reduced cooling airflow, or harmonic-induced heating. This allows the transformer to operate closer to optimal temperature ranges, extending its usable lifespan and improving operational safety.
Load Optimization Through IoT-Enabled Monitoring
Dry-type transformers often experience irregular load patterns, including sudden spikes, prolonged overloading, or cyclic loading common in factories, commercial complexes, and renewable energy systems. Traditional transformers cannot respond to these changes in real time, increasing the risk of overload-induced damage. Smart monitoring systems, however, detect load patterns instantly and analyze them using cloud-based algorithms. Operators can view load trends, identify overload conditions, adjust distribution strategies, and schedule maintenance based on real data. This ensures that transformers operate within safe boundaries, lowering the likelihood of premature failure.
Table 2: Operational Benefits Enabled by Load Monitoring
| Operational Benefit | Description | Impact on Asset Life |
|---|---|---|
| Overload Detection | Real-time load alerts | Prevents overheating and resin degradation |
| Load Balancing | Identifies phase imbalances | Reduces hotspot formation |
| Trend Analysis | Provides historical load data | Enables predictive planning |
| Energy Optimization | Adjusts load for efficiency | Lowers operational costs |
Partial Discharge Monitoring and Its Critical Role in Predictive Maintenance
Partial discharge (PD) is one of the earliest indicators of insulation failure in dry-type transformers. Because PD activity often begins at extremely low levels and gradually worsens over time, manual inspections typically detect it too late. IoT-enabled PD monitoring systems use ultrasonic sensors, high-frequency current transformers (HFCTs), and UHF antennas to detect PD signatures in real time. When combined with digital analytics, PD patterns are correlated with environmental factors, load cycles, vibration, and temperature rise to predict breakdown pathways. This capability dramatically reduces the risk of catastrophic failure, especially in critical facilities like data centers, underground substations, and offshore wind turbines.
Harmonic Monitoring and Power Quality Optimization in IoT Transformers
Harmonics, introduced by variable-speed drives, solar inverters, UPS systems, and EV chargers, can cause severe overheating in dry-type transformers. IoT-connected harmonic analyzers provide continual feedback on total harmonic distortion (THD), waveform shape, and resonance behavior. Advanced analytics identify sources of harmonic pollution and estimate the thermal burden imposed on windings. By correlating harmonic levels with temperature data, operators can implement mitigation strategies, such as installing filters or redistributing nonlinear loads. This not only reduces heating but also slows insulation aging.
Integration of Dry-Type Transformers Into Smart Grid Infrastructure
As smart grids evolve, dry-type transformers are becoming key nodes in a distributed intelligence network. IoT connectivity allows them to communicate with SCADA, EMS, DMS, and DERMS systems. This integration enables:
- Remote diagnostics
- Automated load shifting
- Fault isolation
- Self-healing grid functions
- Optimization of renewable energy flows
- Dynamic voltage regulation
Digital transformers contribute to grid stability by providing continuously updated operational data, allowing operators to make informed decisions based on real-world conditions.
Digital Twins: Virtual Models Enhancing Transformer Lifecycle Management
A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical transformer that simulates its thermal, electrical, and mechanical behavior. IoT sensors feed real-time data into the digital model, allowing engineers to evaluate stress, simulate fault conditions, and optimize performance. Digital twins enable:
- Predictive maintenance modeling
- Failure scenario simulations
- Long-term aging prediction
- Real-time performance visualization
- Optimization of cooling and loading strategies
This approach bridges the gap between engineering design and operational reality, dramatically improving asset management.
Cybersecurity Challenges in IoT-Enabled Dry-Type Transformers
As transformers become more connected, cybersecurity becomes a critical concern. Threats include unauthorized access, data manipulation, malware, and disruption of communication systems. To address these challenges, modern IoT-enabled transformers use:
- Encrypted communication protocols
- Zero-trust access architecture
- Secure firmware upgrades
- Network segmentation
- Authentication-based device pairing
This ensures that operational integrity is preserved and grid systems remain secure.
How Is Thermal Management Being Improved in New Dry-Type Models?
Modern electrical networks demand higher performance, greater energy efficiency, and increased operational reliability from every component—especially transformers. Yet one of the most persistent and costly challenges remains thermal stress. Traditional dry-type transformers often struggle with uneven temperature distribution, hotspot formation, limited cooling capacity, and accelerated insulation aging under high-load or harmonic-rich environments. These issues lead to reduced lifespan, unexpected failures, and higher maintenance expenditures. In mission-critical applications such as data centers, wind farms, hospitals, rail systems, and industrial automation facilities, thermal mismanagement can cause catastrophic downtime and even threaten safety.
Thermal management in new dry-type transformer models has been significantly improved through advanced insulation materials, optimized airflow designs, high-efficiency cooling geometries, thermally conductive resin systems, heat-pipe technologies, digital thermal monitoring, and predictive AI-driven thermal analytics. These innovations reduce hotspot formation, enhance heat dissipation, support higher load capacities, and extend operational lifespan while maintaining excellent safety and environmental performance.
To fully understand how next-generation dry-type transformers achieve superior thermal control, it is necessary to examine the technological advancements in materials engineering, mechanical design, fluid dynamics, digital sensing, computational simulation, and automation. The following sections explore these innovations in depth, illustrating how thermal performance has become the central pillar of modern transformer design and manufacturing.
Modern dry-type transformers use significantly improved cooling geometries to reduce hotspot temperatures.True
Optimized coil ventilation, enlarged cooling ducts, and advanced airflow paths lower peak thermal stress and extend insulation life.
Thermal management improvements eliminate the need for temperature monitoring.False
Even with advanced cooling systems, continuous thermal monitoring remains essential for predictive maintenance and safe operation.
Advanced Insulation Materials for Better Heat Resistance
The heart of improved thermal management lies in next-generation insulation materials, which now support higher thermal classes (F, H, and even emerging Class 220). Manufacturers are shifting from traditional epoxy to specialized resin systems enhanced with:
- Nano-fillers for improved thermal conductivity
- Silicone-based polymers for flexibility under thermal expansion
- High-thermal-index varnishes
- Insulation papers with superior temperature ratings
- Aramid and meta-aramid materials with enhanced dielectric behavior
These materials resist thermal decomposition, making them suitable for heavy cycling environments, renewable energy inverters, and compact installations where heat concentration is significant.
Optimized Coil and Core Geometry for Superior Heat Dissipation
Modern dry-type transformers use sophisticated geometric designs to enhance natural convection and radiative heat transfer. These improvements include:
- Wider vertical cooling ducts
- Helical and disc-wound coils optimized for airflow
- Increased conductor spacing to reduce hotspot density
- Strategic vent patterning on enclosures
- Fin-optimized core surfaces to increase heat dissipation
These design changes allow transformers to maintain significantly lower temperatures under identical loads compared to older models.
Table 1: Design Improvements and Their Thermal Impact
| Design Improvement | Thermal Benefit | Operational Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Wider Ventilation Channels | Enhanced airflow | Lower winding temperature |
| Disc-Wound Coil Geometry | Even heat distribution | Reduced hotspot formation |
| Thermally Conductive Resin | Faster heat dissipation | Longer insulation life |
| Optimized Core Shape | Increased radiative cooling | Improved efficiency |
| Heat-Pipe Integration | Rapid thermal transfer | Better high-load performance |
High-Thermal-Conductivity Resin Systems
Resin systems have evolved dramatically. Traditional epoxy had limited heat conduction and risked microcracking under thermal cycling. In contrast, modern systems feature:
- Nano-silica or aluminum oxide fillers
- Enhanced molecular bonding for crack resistance
- Lower thermal resistance pathways through the winding
- Improved dielectric stability at elevated temperatures
These enhancements not only move heat more effectively but also maintain structural integrity during repeated thermal expansion cycles.
Heat-Pipe and Phase-Change Technologies
Some advanced dry-type designs integrate heat pipes, similar to those used in aerospace and semiconductor cooling. These systems transport heat through vapor-phase movement within sealed channels. Benefits include:
- Rapid redistribution of heat away from hotspots
- Stable thermal gradients across coils
- Improved overload handling
- Enhanced performance in compact installations
Phase-change materials (PCMs) are also being explored to absorb peak loads without raising winding temperatures.
Enhanced Airflow Management Through CFD-Based Engineering
Manufacturers now use Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations to design optimized internal airflow paths. CFD modeling reveals:
- Regions of stagnant airflow
- Hotspot tendencies under varying load conditions
- The ideal shapes and placements of ducts
- The impact of enclosure geometry on cooling performance
This simulation-driven engineering results in transformers that self-cool more efficiently, even under harsh load conditions.
Table 2: CFD Insights and Their Practical Impact
| CFD Discovery | Engineering Response | Thermal Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Poor Ventilation Zones | Added duct channels | Eliminated hotspots |
| Excessive Air Stagnation | Reangled airflow deflectors | Stronger convection currents |
| Uneven Coil Heating | Coil spacing adjustments | Balanced winding temperature |
| Enclosure Heat Retention | Vent reconfiguration | Cooler ambient chamber |
Digital Temperature Monitoring and Predictive Thermal Analytics
Smart sensors embedded directly into transformer windings and cores feed real-time thermal data into IoT platforms. With advanced analytics, these systems:
- Predict hotspots before they develop
- Identify cooling inefficiencies
- Optimize loading based on thermal limits
- Trigger alarms for overheating events
- Provide temperature trends for maintenance planning
- Enable digital twins for thermal modeling
This combination of hardware and software elevates thermal management from passive engineering to intelligent, adaptive control.
Low-Loss Magnetic Cores Reducing Internal Heat Generation
Heat is not only removed—it is prevented. New magnetic materials such as:
- Amorphous metal cores
- High-permeability grain-oriented silicon steel
- Laser-scribed domain-refined cores
dramatically reduce core losses, meaning less heat is generated in the first place. This allows transformers to run cooler, improving efficiency and extending life.
Noise Reduction Directly Supporting Better Thermal Performance
Mechanical vibration contributes to unwanted heat buildup. Advanced designs use:
- Resin-damped windings
- Improved structural bracing
- Vibration-isolated mounting systems
These approaches minimize friction heat and support overall thermal stability.
Importance of Thermal Symmetry in High-Density Installations
In confined spaces such as underground substations, tunnels, and datacenters, airflow is restricted. New transformer models employ thermal symmetry principles to ensure:
- Faster heat escape from internal regions
- Equalized temperatures between phases
- Reduced localized overheating in constrained environments
Symmetrical thermal profiles significantly extend insulation longevity.
Why Are Biodegradable and Eco-Friendly Insulation Systems Gaining Popularity?

Environmental sustainability has rapidly become a core priority across the global power and electrical industries, and transformer manufacturers are no exception. For decades, mineral oil and conventional solid insulation systems dominated the market due to their low cost and acceptable performance. However, rising environmental regulations, stricter fire-safety demands, and the global transition toward low-carbon and renewable energy infrastructures have drastically changed the expectations placed on insulating materials. Today, biodegradable and eco-friendly insulation systems—including natural ester oils, synthetic ester formulations, non-toxic varnishes, cellulose alternatives, and halogen-free solid insulations—are increasingly becoming the preferred option for utilities, OEMs, and developers. Their advantages extend well beyond environmental friendliness; they offer better fire performance, greater thermal stability, lower maintenance costs, and higher resilience in demanding applications such as wind farms, solar plants, and urban substations. As a result, what began as a sustainability trend is now recognized as a technologically superior solution with long-term operational and economic advantages.
Biodegradable and eco-friendly insulation systems are gaining popularity because they offer superior fire safety, higher thermal stability, lower environmental impact, compliance with global sustainability regulations, compatibility with renewable energy networks, and longer equipment life. These materials help utilities reduce ecological risk, simplify site permitting, improve transformer loading capability, and support corporate decarbonization goals—making them an optimal choice for modern power systems.
Transformer owners and EPC developers increasingly recognize that insulation performance directly influences asset life and failure risk. Eco-friendly insulation systems reduce the likelihood of catastrophic leaks, ground contamination, and high-cost environmental cleanup—crucial considerations for densely populated and environmentally sensitive locations. As the world shifts toward more sustainable grid solutions, biodegradable insulation has evolved from a niche option into a mainstream engineering requirement.
Biodegradable insulation oils reduce environmental risks associated with leaks and spills.True
Natural and synthetic ester fluids rapidly biodegrade in soil and water, minimizing contamination hazards and cleanup costs compared to mineral oil.
Eco-friendly insulation materials have lower thermal performance than mineral oil.False
Many ester-based systems exceed mineral oil in thermal stability, moisture tolerance, and overload capability, enabling extended transformer lifespan.
Environmental Protection and Regulatory Pressure Are Driving Adoption
One of the strongest contributors to the growing popularity of eco-friendly insulation is the increasingly strict regulatory environment. Many countries now enforce tighter rules around soil protection, spill containment, hazardous material handling, and end-of-life transformer disposal. Mineral oil spills can cause long-lasting contamination, requiring expensive remediation and government reporting. By contrast, natural ester fluids are classified as readily biodegradable—meaning that up to 90% of the material decomposes within 21 days. This dramatically reduces environmental liability and makes compliance far easier.
Environmental agencies in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia now recommend ester-based oils for installations near water sources, agricultural land, underground facilities, and urban centers. Utilities are responding by adopting biodegradable insulation not only for regulatory compliance but also to demonstrate environmental stewardship and align with corporate ESG commitments. As sustainable procurement becomes a global priority, eco-friendly transformer materials are becoming strategically important rather than optional.
Superior Fire Safety Performance Makes Eco-Friendly Insulation a Safer Choice
Fire safety is another major driver of adoption. Natural and synthetic ester fluids possess extremely high fire points—typically above 300°C—compared to mineral oil’s flash point of around 155°C. This makes biodegradable fluids inherently less flammable, significantly reducing transformer fire risk. In environments such as hospitals, tunnels, offshore platforms, underground substations, chemical plants, and high-density urban districts, this improved fire resistance is a critical advantage.
Dry-type transformers already have strong intrinsic fire safety characteristics, but when liquid-filled transformers require high safety performance, biodegradable ester fluids make it possible to meet strict requirements without costly fire suppression systems. Insurance premiums can also be lowered because the risk profile is dramatically improved. The result is a safer, more resilient, and more cost-effective installation—one that aligns with both engineering and environmental priorities.
Higher Thermal Stability and Moisture Tolerance Improve Long-Term Reliability
Beyond environmental and safety benefits, biodegradable insulation systems offer significant technical performance advantages. Natural and synthetic ester fluids have far greater moisture saturation limits than mineral oil—meaning they can absorb and retain more moisture without reducing dielectric strength. This is crucial because moisture is one of the primary causes of accelerated insulation aging.
Ester fluids also exhibit superior thermal endurance. Their higher thermal class supports:
- Higher permissible hotspot temperatures
- Greater overload capability
- Longer insulation life
- More stable performance under dynamic load cycles
These characteristics make eco-friendly insulation systems ideal for renewables, where load patterns fluctuate due to wind and solar variability. Their enhanced thermal stability also extends transformer operating life, reducing long-term replacement and maintenance costs.
Compatibility with Renewable Energy and Grid Modernization Projects
Renewable energy systems often operate in remote, outdoor, or environmentally sensitive areas—ideal conditions for biodegradable insulation. In wind farms, transformers are located at the base of towers or in nacelles, where leakage risks pose significant environmental and safety challenges. Similarly, solar plants install numerous pad-mounted or skid-mounted transformers across large land areas, making spill protection important.
Biodegradable insulation systems provide clear advantages such as:
- Safe environmental integration
- Reduced ecological risk
- Extended equipment life under cycling loads
- Compliance with clean energy incentives
- Better thermal performance under harmonic-rich inverter loads
As renewable deployments accelerate globally, eco-friendly insulation is steadily becoming the standard expectation for project developers, utilities, and financial institutions.
Lower Environmental Liability and Cleanup Costs
One of the hidden but substantial advantages of biodegradable insulation is its ability to reduce environmental liability. Mineral oil spills can lead to:
- Soil contamination
- Water pollution
- Large-scale cleanup operations
- Regulatory fines
- Mandatory reporting
- Long-term ecological harm
- Insurance claims and penalties
In contrast, natural esters rapidly break down into non-toxic components. Sites using eco-friendly insulation fluids often do not require specialized containment pits or oil-water separation systems. This reduces installation cost and logistical complexity while improving safety.
For industrial plants, data centers, tunnels, and sensitive landscapes, the financial and operational benefits of reduced liability are significant.
Sustainability and Corporate ESG Targets Encourage Use of Green Materials
With global industries accelerating toward carbon neutrality and sustainable infrastructure development, corporations and utilities are increasingly required to document and improve their environmental performance. Eco-friendly insulation systems contribute to multiple ESG categories:
- Reduced environmental risk
- Lower carbon footprint
- Sustainable material sourcing
- Improved lifecycle management
- Safer end-of-life disposal
Manufacturers promoting eco-friendly transformer designs are now more competitive in markets where environmental scoring affects procurement decisions, financing, and government approvals.
Transformer Efficiency and Lifecycle Improvements
Biodegradable insulation systems support longer transformer life by slowing insulation aging and improving thermal behavior. Their superior moisture handling reduces the need for drying cycles, while enhanced thermal endurance increases permissible loading. As a result, utilities and industries achieve:
- Fewer failures
- Longer operating life
- Better asset utilization
- Reduced maintenance cycles
- Lower total cost of ownership
These operational benefits are driving wide-scale adoption even in regions without strict environmental regulations.
How Are Market Drivers, Such as Renewables and EV Infrastructure, Fueling Demand?
Global shifts toward clean energy and transportation electrification are reshaping power system priorities, with dry-type transformers emerging as a critical component in supporting these changes. As renewable energy installations accelerate and electric vehicle (EV) charging networks expand at unprecedented speed, the demand for safe, durable, compact, and environmentally friendly transformer technologies has increased dramatically. Dry-type transformers—well known for their low fire risk, minimal environmental impact, and strong performance under fluctuating loads—align perfectly with the requirements of wind farms, solar plants, EV fast-charging stations, and grid-modernization projects worldwide. These market forces are not only increasing demand but also influencing the design, performance, and engineering specifications of the newest dry-type transformer models.
Market drivers such as renewable energy expansion, rapid EV charging infrastructure deployment, stricter safety regulations, and the global shift toward cleaner grids are significantly increasing demand for dry-type transformers because they offer higher fire safety, environmentally friendly construction, superior performance under variable loads, and lower maintenance needs compared with traditional oil-immersed units. These drivers are accelerating adoption in solar farms, wind turbines, industrial electrification, and urban EV charging stations.
With governments committing to decarbonization and utilities modernizing outdated infrastructure, dry-type transformers have become essential. Their compactness, high reliability, and immunity to oil-leak risks make them ideal for renewable installations, smart-grid nodes, and EV power cabinets—markets expected to grow strongly over the next decade.
Renewable energy expansion is increasing demand for dry-type transformers.True
Wind and solar installations require safe, low-maintenance transformers capable of handling variable loads and harsh environments, making dry-type units a preferred choice.
EV charging stations typically rely on oil-immersed transformers.False
Most EV charging hubs prefer dry-type transformers due to their fire safety, compact footprint, and compatibility with high-power electronics.
Renewable Energy Growth Directly Boosts Demand for Dry-Type Transformers
Wind and solar power expansion is one of the strongest market drivers worldwide. These facilities often operate in remote or environmentally sensitive areas where oil containment, fire protection, and maintenance access are challenging. Dry-type transformers eliminate oil-spill risks, require minimal servicing, and withstand the variable load profiles typical of renewable operations.
Solar plants benefit from cast-resin transformers capable of handling harmonic-rich inverter outputs. Wind turbines rely on dry-type designs to safely operate in nacelles and tower bases where space is restricted and fire risk must be minimized. As renewable penetration increases globally, dry-type transformer demand continues to rise in parallel.
EV Charging Infrastructure Is Becoming a Major Demand Source
Electric vehicle adoption is accelerating fast, and DC fast-charging stations require highly reliable, safe, compact transformers capable of managing high-energy pulses and demanding thermal cycles. Dry-type transformers are ideal because they:
- Eliminate fire and oil leakage risk in public areas
- Operate safely indoors or outdoors
- Handle rapid load fluctuations during charging peaks
- Fit into compact power cabinets or charging hubs
- Require limited maintenance, reducing operating cost
As cities deploy thousands of EV fast chargers and ultra-fast highway charging corridors expand, dry-type transformer demand is rapidly growing in both public and private installations. Future EV megawatt charging systems (MCS) will push this demand even further.
Utility Grid Modernization and Decentralized Power Architectures Increase Adoption
Power grids are evolving from centralized, predictable networks to decentralized, dynamic systems with distributed generation, energy storage, microgrids, and smart-grid nodes. Dry-type transformers integrate well into these modern architectures because of their safety, modularity, resilience, and ease of installation. Urban substations—especially those located in basements, tunnels, residential districts, or critical public facilities—prefer dry-type units due to reduced fire and environmental hazards.
Utilities upgrading old oil-filled units often transition to dry-type alternatives where space, safety, or environmental regulations restrict oil-based equipment. The shift toward smart distribution, underground substations, and urban electrification continues to drive this trend.
Industrial Electrification and ESG Policies Reinforce Growth
Industries are increasingly adopting electrified heating, advanced automation, energy storage, and high-efficiency power systems. Dry-type transformers fit these needs because they offer:
- High performance under variable industrial loads
- No contamination risk in factories, medical facilities, data centers, or chemical plants
- Better fire resistance and reduced insurance liabilities
- Lower life-cycle environmental impact
Corporate sustainability (ESG) policies further encourage choosing dry-type transformers due to their eco-friendly materials, reduced maintenance needs, and safer operation near employees and sensitive equipment.
Government Incentives and Regulations Accelerate the Shift
Many governments offer incentives or apply regulations affecting transformer selection:
- Renewable integration subsidies favor eco-friendly equipment
- Urban safety regulations discourage oil-filled transformers
- Fire codes often prefer dry-type units in public spaces
- Carbon reduction policies promote environmentally safe materials
- Grid reliability standards reward resilient transformer designs
These regulatory pressures and economic incentives combine to accelerate dry-type transformer adoption across multiple sectors.
What Are the Emerging Applications and Deployment Trends for Dry-Type Transformers?

The global energy sector is undergoing rapid transformation, and dry-type transformers have become increasingly important across both traditional and emerging applications. As industries pursue safer, greener, and more compact electrical solutions, dry-type technology is evolving from a niche alternative to a mainstream choice in modern power networks. This shift is driven by stricter safety regulations, renewable energy expansion, electrification programs, and the rising demand for energy-efficient infrastructure. As a result, dry-type transformers are now appearing in applications that once relied almost exclusively on oil-immersed units, including urban substations, offshore platforms, sustainable manufacturing sites, and digitally integrated power systems.
Emerging applications and deployment trends for dry-type transformers include renewable energy stations, EV fast-charging hubs, data centers, offshore wind platforms, smart-grid nodes, industrial electrification projects, tunnel and subway power systems, and environmentally sensitive installations. These trends highlight the industry’s demand for safer, more compact, low-maintenance, and environmentally friendly transformer solutions. Dry-type designs are increasingly chosen for their fire safety, resilience under variable loads, and compatibility with digital monitoring and smart-grid technologies.
The shift toward dry-type units is not only rooted in regulatory pressure or environmental goals—technical requirements such as compact installation, noise reduction, rapid deployment, and risk-free indoor operation are driving new engineering designs that make dry-type transformers suitable for diverse and challenging environments.
Dry-type transformers are increasingly installed in renewable energy systems due to safety and reliability advantages.True
They handle fluctuating loads, harmonics, and harsh environments common in wind and solar applications, without oil-related fire or leakage risks.
Dry-type transformers are unsuitable for large-scale industrial or urban power installations.False
Modern cast-resin and VPI dry-type transformers are now widely used in metro systems, hospitals, commercial buildings, and industrial electrification projects.
Growing Adoption in Renewable Energy Systems
One of the most significant emerging applications is in renewable energy—specifically wind, solar, and hybrid microgrids. In solar farms, dry-type transformers tolerate harmonic-rich inverter outputs and irregular load cycles. In wind turbines, they are installed inside nacelles or towers, where fire safety and maintenance-free operation are essential. Their environmental robustness makes dry-type units well suited for remote, humid, or coastal environments where oil containment is difficult or undesirable. As global renewable capacity scales exponentially, dry-type deployment is accelerating in both utility-scale and distributed applications.
Deployment in EV Charging Hubs and Transportation Electrification
The rapid expansion of electric vehicle charging is creating one of the fastest-growing markets for dry-type transformers. High-power DC fast chargers and megawatt charging stations require compact, safe, and thermally stable transformers capable of handling fluctuating power pulses. Dry-type transformers fit seamlessly into roadside cabinets, parking garages, fleet depots, and highway rest areas where fire safety and minimal maintenance are crucial. This trend will intensify as cities and logistics operators roll out mass electrification programs for buses, trucks, and autonomous electric fleets.
Rising Use in Data Centers and Mission-Critical Facilities
Modern data centers require high reliability, low fire risk, and minimal downtime. Dry-type transformers—especially cast-resin models—offer excellent performance under continuous load, reduced noise levels, and reduced risk of oil fires. With global data center construction booming to support AI, cloud computing, and digital economies, dry-type transformers are now standard in hyperscale and edge data center designs. Their compatibility with smart monitoring also supports predictive maintenance strategies required for 24/7 uptime.
Integration into Smart Grids and Digitally Monitored Networks
Smart-grid modernization is increasing demand for transformers that support IoT-based monitoring, cyber-secure communication, and dynamic load management. Dry-type transformers integrate easily with sensors for temperature, partial discharge, humidity, and load profiling. Utilities are installing these units in compact substations, feeder stations, and distributed energy nodes where digital visibility and safer operation are necessary. As cities upgrade infrastructure, dry-type models are becoming common in indoor substations embedded within commercial districts, metro tunnels, universities, and government buildings.
Growth in Urban Infrastructure, Tunnels, Subways, and Public Facilities
Urban growth and underground infrastructure expansion require power systems that meet strict fire and environmental standards. Dry-type transformers are increasingly deployed in:
- Subway stations
- Underground tunnels
- Airports
- Stadiums
- Hospitals
- Commercial towers
Their non-flammable insulation and safety characteristics make them ideal for densely populated environments where oil-immersed units pose unacceptable risk. Urbanization and public electrification programs are therefore major drivers of this demand.
Adoption in Oil-Free and Eco-Sensitive Industrial Facilities
Industries operating in clean rooms, pharmaceutical factories, food processing plants, and marine environments increasingly prefer dry-type units due to their minimal contamination risk. Offshore oil and gas platforms, desalination plants, and coastal industrial facilities also benefit from corrosion-resistant dry-type designs. As environmental regulations tighten and industries aim to reduce ecological impact, oil-free transformer deployment is expanding steadily.
Conclusion
Dry-type transformer technology is advancing rapidly, driven by demand for higher efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance. Innovations in core materials, insulation systems, and digital monitoring are making transformers more reliable, compact, and adaptable to modern power systems. Simultaneously, market demand is expanding across sectors—especially in renewable energy, EV charging, and embedded grid applications. As grid architectures continue to evolve, dry-type transformers are emerging as a cornerstone technology for sustainable, intelligent, and resilient power networks.
FAQ
Q1: What are the latest technology trends in dry type transformers?
Dry type transformer technology is evolving rapidly as industries demand better safety, efficiency, and environmental performance. One major trend is the adoption of smart sensors and digital monitoring, allowing operators to track temperature, humidity, partial discharge, and load conditions in real time. This shift reduces downtime through predictive maintenance and extends transformer life. Another key development is the use of high-performance insulation materials such as epoxy resin with nanotechnology additives, improving thermal conductivity and mechanical strength. Manufacturers are also introducing higher efficiency core designs, such as amorphous metal cores and low-loss silicon steel, to meet increasingly strict energy regulations.
Additionally, the industry is embracing compact and modular designs, enabling easier installation in space-constrained environments like data centers and metro stations. Improved cooling systems—such as advanced natural-air (AN) and forced-air (AF) designs—allow for higher load capacity without compromising reliability. Fire-resistant materials, low-smoke resins, and eco-safe insulation are gaining adoption, particularly in commercial and public infrastructure projects. Overall, the technological direction focuses on enhanced safety, digitization, energy efficiency, and sustainable materials.
Q2: Why is market demand for dry type transformers increasing globally?
Global demand is rising due to the expansion of industries that require safe, eco-friendly, and indoor-suitable transformers. Sectors such as data centers, renewable energy, commercial buildings, metro systems, and offshore platforms increasingly depend on dry type transformers for their fire safety and low maintenance advantages. Government regulations pushing for reduced environmental impact and safer equipment in public areas further accelerate adoption.
The renewable energy boom—especially solar and wind—also contributes to demand. Dry type transformers are preferred in wind turbine towers, solar farms, and battery energy storage systems due to their moisture resistance and minimal maintenance requirements. Additionally, electrification of infrastructure in developing countries, rising urbanization, and strict environmental standards in developed markets are all major growth drivers. As industries move toward greener solutions, dry type transformers are becoming a top choice worldwide.
Q3: How are digital features shaping the dry type transformer market?
Digitization is transforming how dry type transformers are managed and maintained. Embedded IoT sensors, real-time temperature monitoring, partial discharge detection, and smart load management help operators make data-driven decisions. Predictive analytics can detect potential failures before they occur, reducing costly outages and improving operational reliability. Digital twins—virtual models of physical transformers—allow engineers to simulate performance under different load conditions, aiding in design optimization and maintenance planning.
Remote monitoring is particularly valuable in renewable energy installations and large industrial facilities where equipment is dispersed or hard to reach. As smart grids expand, utilities increasingly demand digitally enabled transformers that support automation and grid integration. The integration of cloud-based monitoring platforms further strengthens this trend, contributing to sustained market growth.
Q4: What industries are driving technological innovation in dry type transformers?
Key industries influencing innovation include:
Data centers, which require high-efficiency, low-noise, high-reliability transformer designs
Renewable energy, which pushes demand for compact, moisture-resistant, and vibration-resistant units
Railway and metro systems, which need fire-safe, durable transformers for underground and enclosed spaces
Commercial buildings, where safety, noise reduction, and efficiency standards continue to tighten
Manufacturing plants, which seek higher load capacities and better heat management
These sectors demand performance improvements such as better thermal design, lower losses, wider voltage ranges, and enhanced safety—all of which influence technological advancements.
Q5: What future trends are expected for dry type transformers?
The future points toward greater efficiency, smarter monitoring, and more environmentally sustainable materials. Nanocomposite insulation, low-loss amorphous cores, and advanced cooling systems are expected to become standard. Growing interest in smart energy management will push manufacturers to integrate more IoT and AI-based monitoring solutions. Additionally, stricter regulations and carbon reduction policies will continue to favor dry type transformers over oil-filled alternatives in many applications.
Market forecasts indicate strong growth, especially in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and North America. Rapid urbanization, renewable energy expansion, and rising concerns over fire safety will continue to drive demand. Over the next decade, dry type transformers are expected to play a crucial role in smart grids, microgrids, electric transportation infrastructure, and high-reliability industrial environments.
References
IEC 60076-11 – Dry Type Transformers — https://www.iec.ch
IEEE Transformer Technology Innovations — https://ieeexplore.ieee.org
Schneider Electric MV Transformer Developments — https://www.se.com
MarketsandMarkets – Dry Type Transformer Market Report — https://www.marketsandmarkets.com
Global Market Insights – Dry Type Transformer Trends — https://www.gminsights.com
International Energy Agency – Grid & Renewable Expansion Reports — https://www.iea.org
Statista – Transformer Market Growth Data — https://www.statista.com


